Abstract
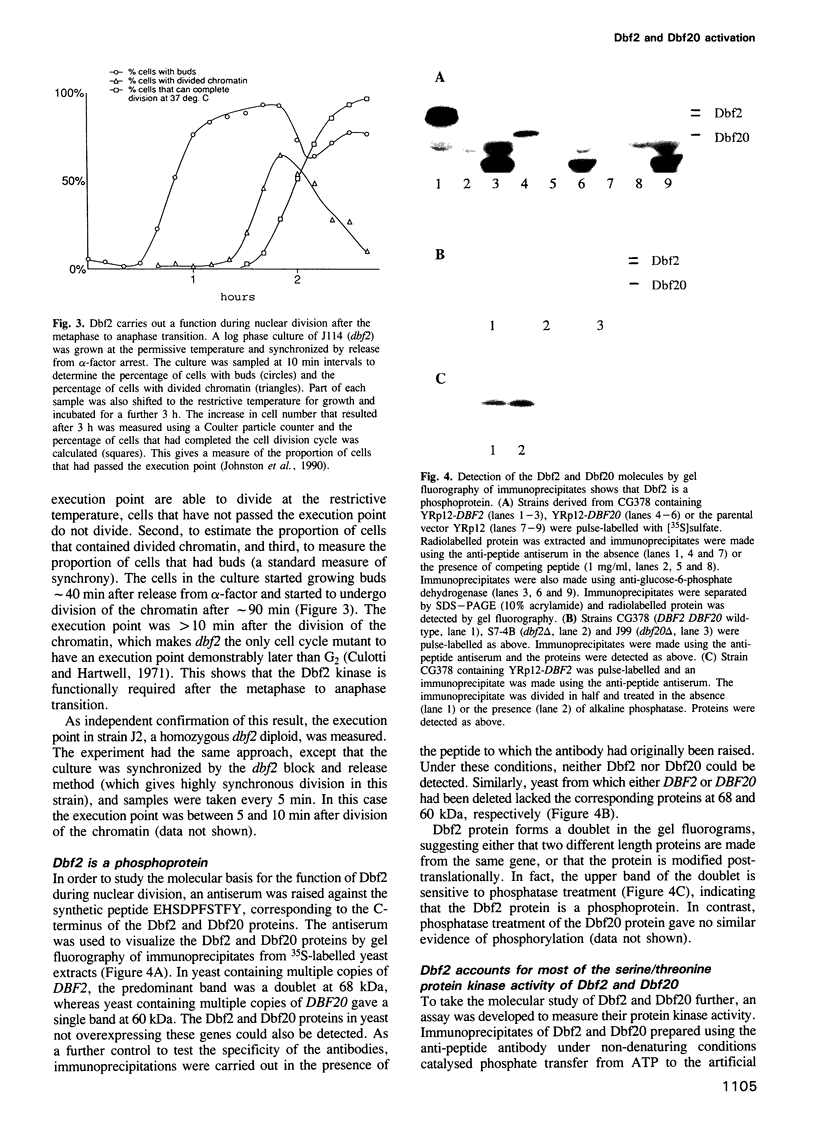
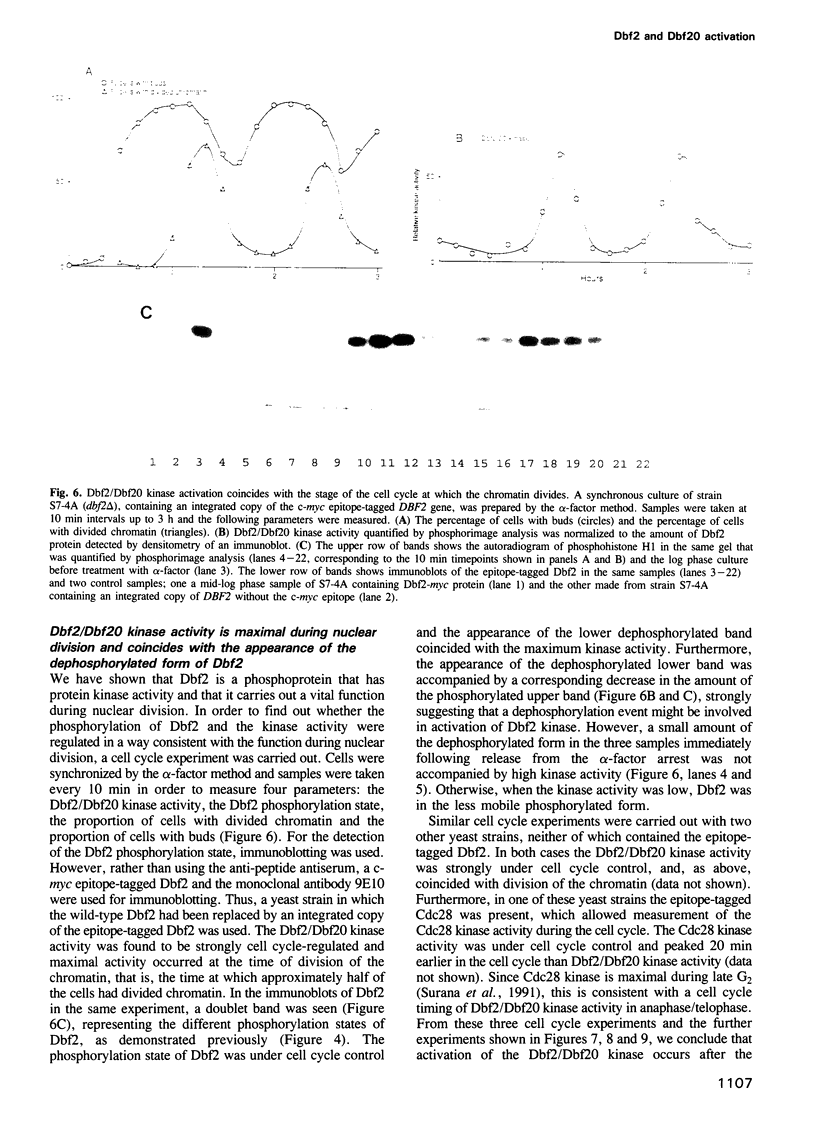
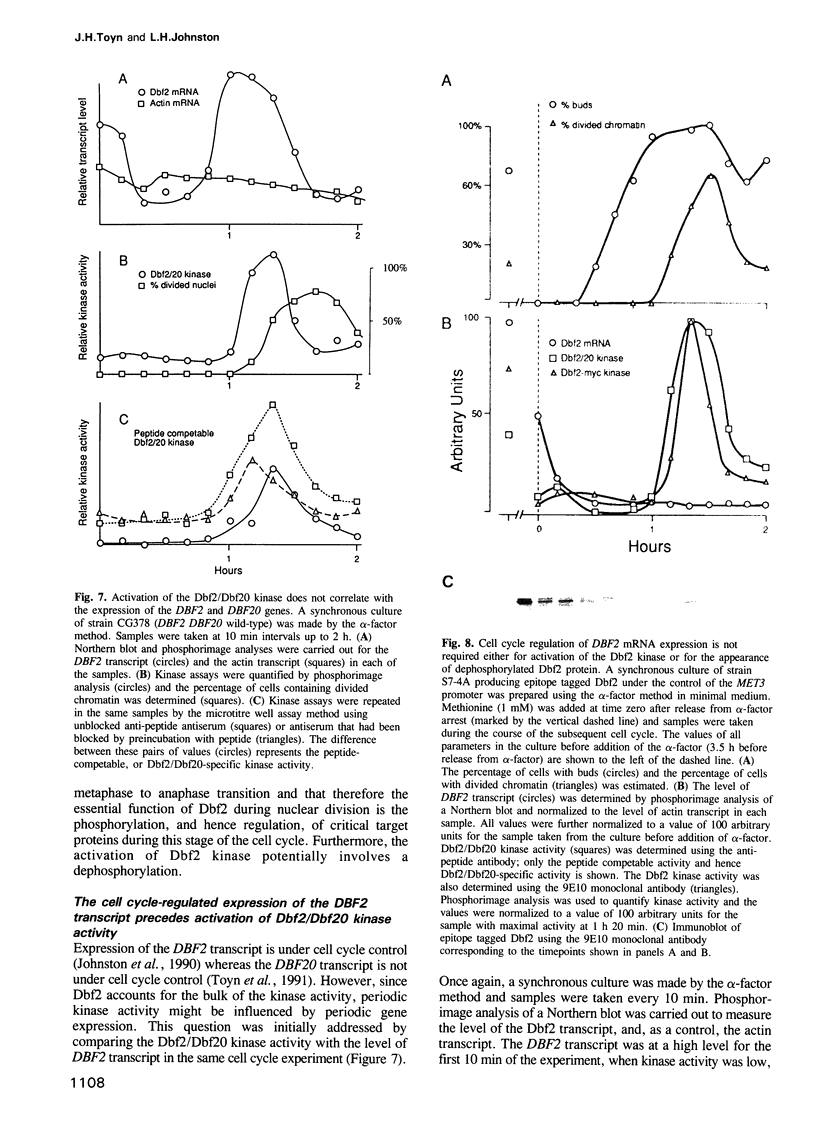
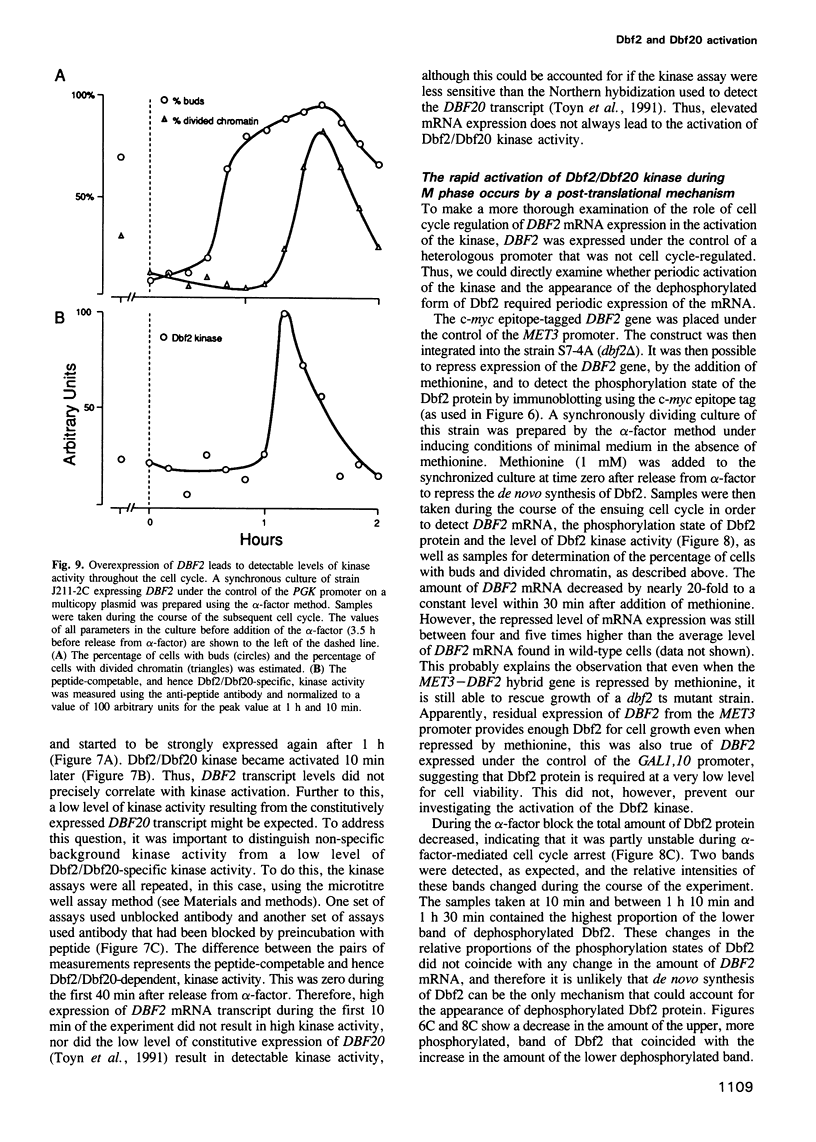
Thermosensitive mutations in the DBF2 gene arrest the cell cycle during nuclear division. Although the chromatin has divided in arrested cells, an elongated mitotic spindle is present and Cdc28 protein kinase activity remains high, indicating that nuclear division is incomplete. By execution point analysis we show that Dbf2 carries out an essential cell cycle function after the metaphase to anaphase transition and is therefore required during anaphase and/or telophase. This cell cycle stage-specific requirement for the function of Dbf2 coincides with the cell cycle regulation of Dbf2/Dbf20 protein kinase activity, which can be detected in immunoprecipitates containing Dbf2 or Dbf20. The kinase activity is specific for serine/threonine residues and Dbf2 accounts for the bulk of the activity, with Dbf20 playing a minor role. Furthermore, Dbf2 is a phosphoprotein and, significantly, the dephosphorylated form appears with the same cell cycle timing as the kinase activity, suggesting a role for dephosphorylation in the activation mechanism. In addition, we show that the DBF2 transcript, which is under cell cycle control, is expressed in advance of the activation of the kinase, but that cell cycle-regulated expression of the mRNA is not required for activation of the Dbf2 kinase during M phase. Thus, Dbf2/Dbf20 kinase activity is precisely regulated in the cell cycle by a post-translational mechanism and phosphorylates its target substrates for an event that occurs during anaphase and/or telophase.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotti J., Hartwell L. H. Genetic control of the cell division cycle in yeast. 3. Seven genes controlling nuclear division. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Aug;67(2):389–401. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90424-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton B., Glover D. M. A conserved mitotic kinase active at late anaphase-telophase in syncytial Drosophila embryos. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):637–640. doi: 10.1038/363637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Sarabia M. J., Sutton A., Zhong T., Arndt K. T. SIT4 protein phosphatase is required for the normal accumulation of SWI4, CLN1, CLN2, and HCS26 RNAs during late G1. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2417–2428. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Weinert T. A. Checkpoints: controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):629–634. doi: 10.1126/science.2683079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. L., Pahl P. M., Harrison K., Rosamond J., Sclafani R. A. Cell cycle regulation of the yeast Cdc7 protein kinase by association with the Dbf4 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2899–2908. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
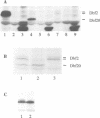
- Johnston L. H., Eberly S. L., Chapman J. W., Araki H., Sugino A. The product of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle gene DBF2 has homology with protein kinases and is periodically expressed in the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1358–1366. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston L. H., Thomas A. P. The isolation of new DNA synthesis mutants in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):439–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00729466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitada K., Johnson A. L., Johnston L. H., Sugino A. A multicopy suppressor gene of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae G1 cell cycle mutant gene dbf4 encodes a protein kinase and is identified as CDC5. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4445–4457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitada K., Johnston L. H., Sugino T., Sugino A. Temperature-sensitive cdc7 mutations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are suppressed by the DBF4 gene, which is required for the G1/S cell cycle transition. Genetics. 1992 May;131(1):21–29. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Dobson M. J., Roberts N. A., Tuite M. F., Emtage J. S., White S., Lowe P. A., Patel T., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Efficient synthesis of enzymatically active calf chymosin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1983 Sep;24(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountain H. A., Korch C. TDH2 is linked to MET3 on chromosome X of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1991 Nov;7(8):873–880. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. Control of the yeast cell cycle by the Cdc28 protein kinase. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):166–179. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90099-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkes V., Johnston L. H. SPO12 and SIT4 suppress mutations in DBF2, which encodes a cell cycle protein kinase that is periodically expressed. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5617–5623. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R., Adams A. E., Drubin D. G., Haarer B. K. Immunofluorescence methods for yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:565–602. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94043-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer B., Philippsen P. CDC15, an essential cell cycle gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, encodes a protein kinase domain. Yeast. 1991 Apr;7(3):265–273. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F. Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:3–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surana U., Amon A., Dowzer C., McGrew J., Byers B., Nasmyth K. Destruction of the CDC28/CLB mitotic kinase is not required for the metaphase to anaphase transition in budding yeast. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1969–1978. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05846.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surana U., Robitsch H., Price C., Schuster T., Fitch I., Futcher A. B., Nasmyth K. The role of CDC28 and cyclins during mitosis in the budding yeast S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):145–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90416-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A., Immanuel D., Arndt K. T. The SIT4 protein phosphatase functions in late G1 for progression into S phase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2133–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyn J. H., Araki H., Sugino A., Johnston L. H. The cell-cycle-regulated budding yeast gene DBF2, encoding a putative protein kinase, has a homologue that is not under cell-cycle control. Gene. 1991 Jul 31;104(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90465-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyn J. H., Johnston L. H. Spo12 is a limiting factor that interacts with the cell cycle protein kinases Dbf2 and Dbf20, which are involved in mitotic chromatid disjunction. Genetics. 1993 Dec;135(4):963–971. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.4.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyn J., Hibbs A. R., Sanz P., Crowe J., Meyer D. I. In vivo and in vitro analysis of ptl1, a yeast ts mutant with a membrane-associated defect in protein translocation. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4347–4353. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03333.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan J., Xu H., Grunstein M. CDC14 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cloning, sequence analysis, and transcription during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11274–11280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Niman H. L., Houghten R. A., Cherenson A. R., Connolly M. L., Lerner R. A. The structure of an antigenic determinant in a protein. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon H. J., Loo S., Campbell J. L. Regulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CDC7 function during the cell cycle. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Feb;4(2):195–208. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]