Abstract
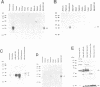
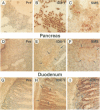
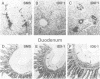
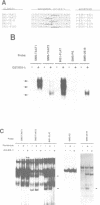
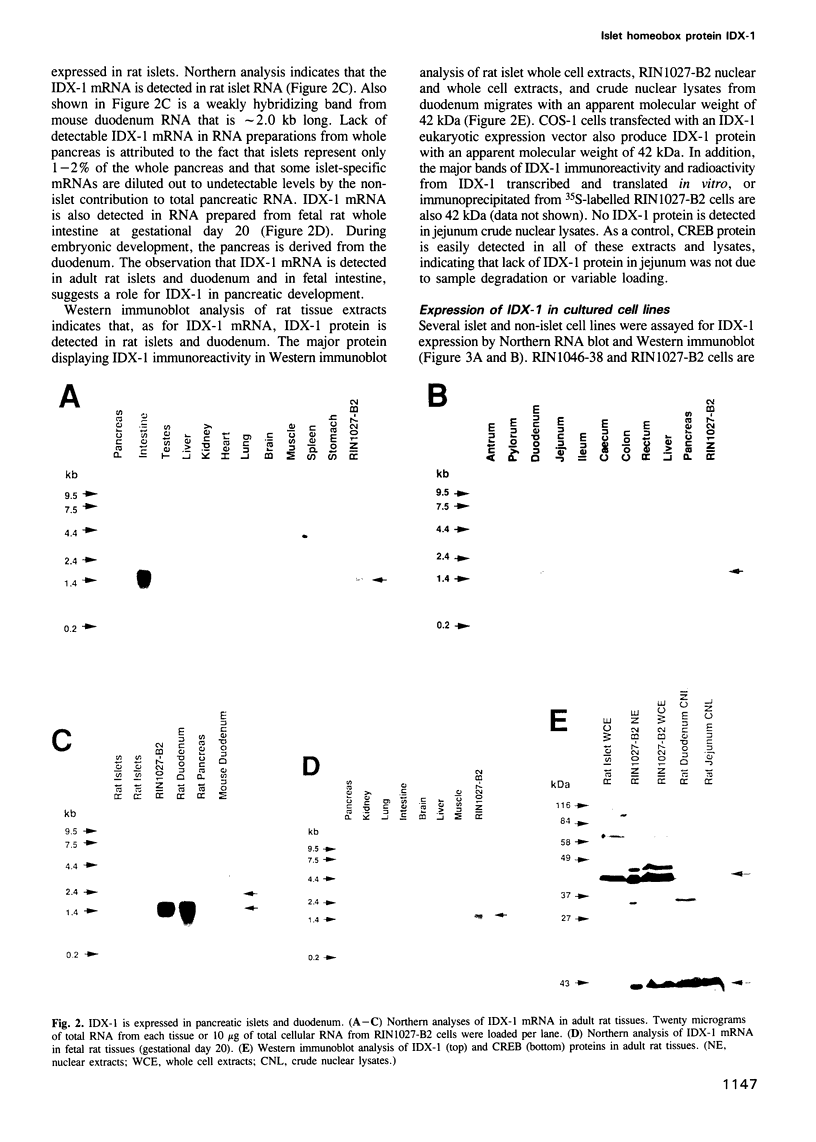
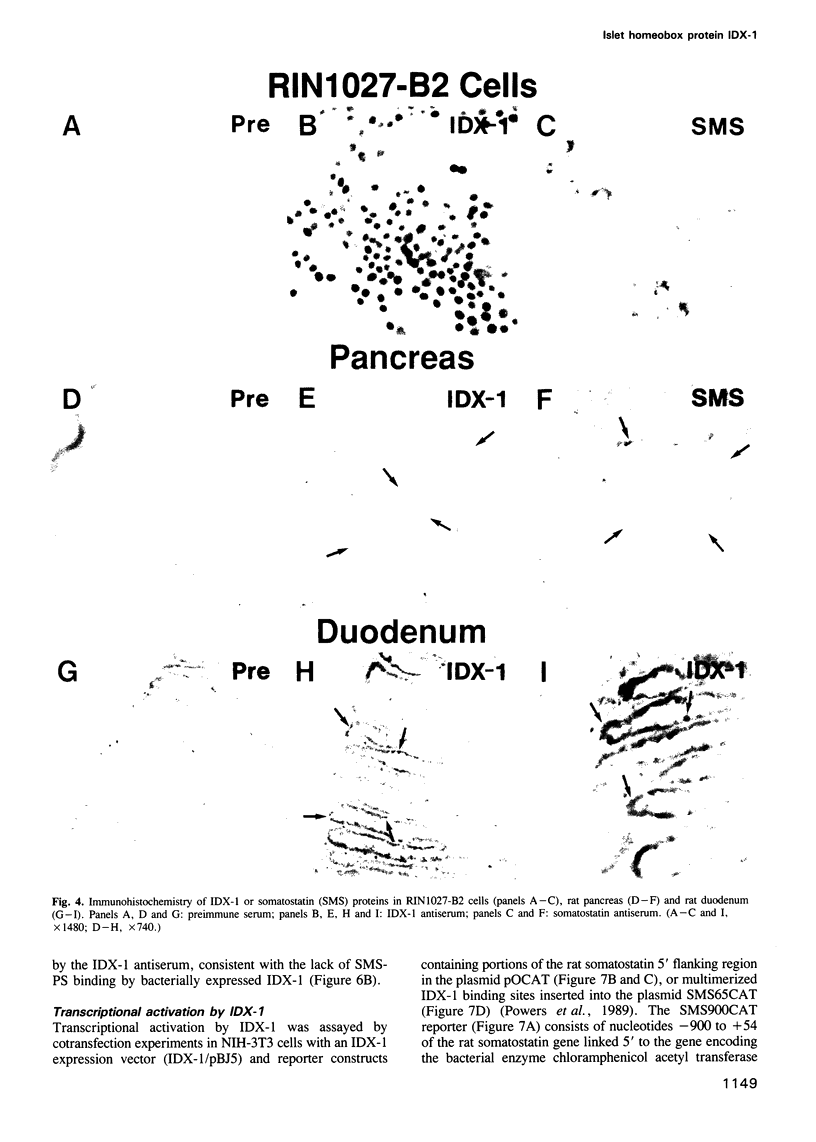
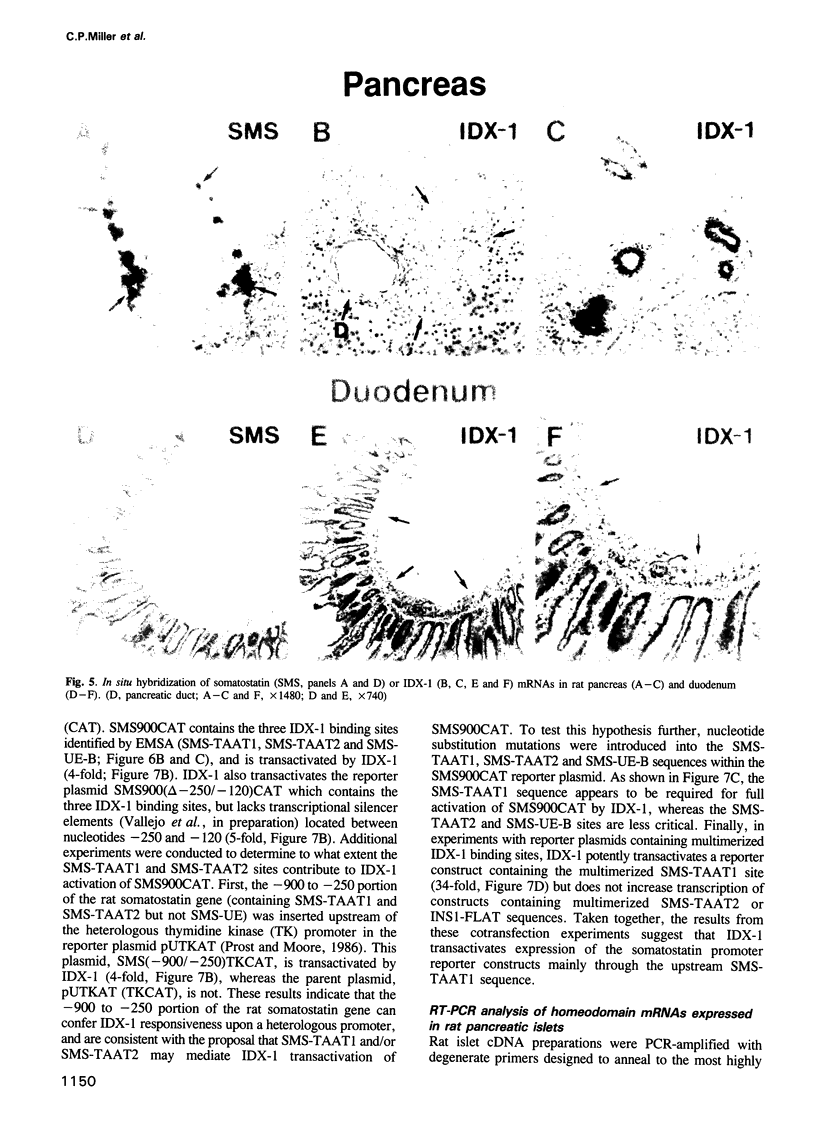
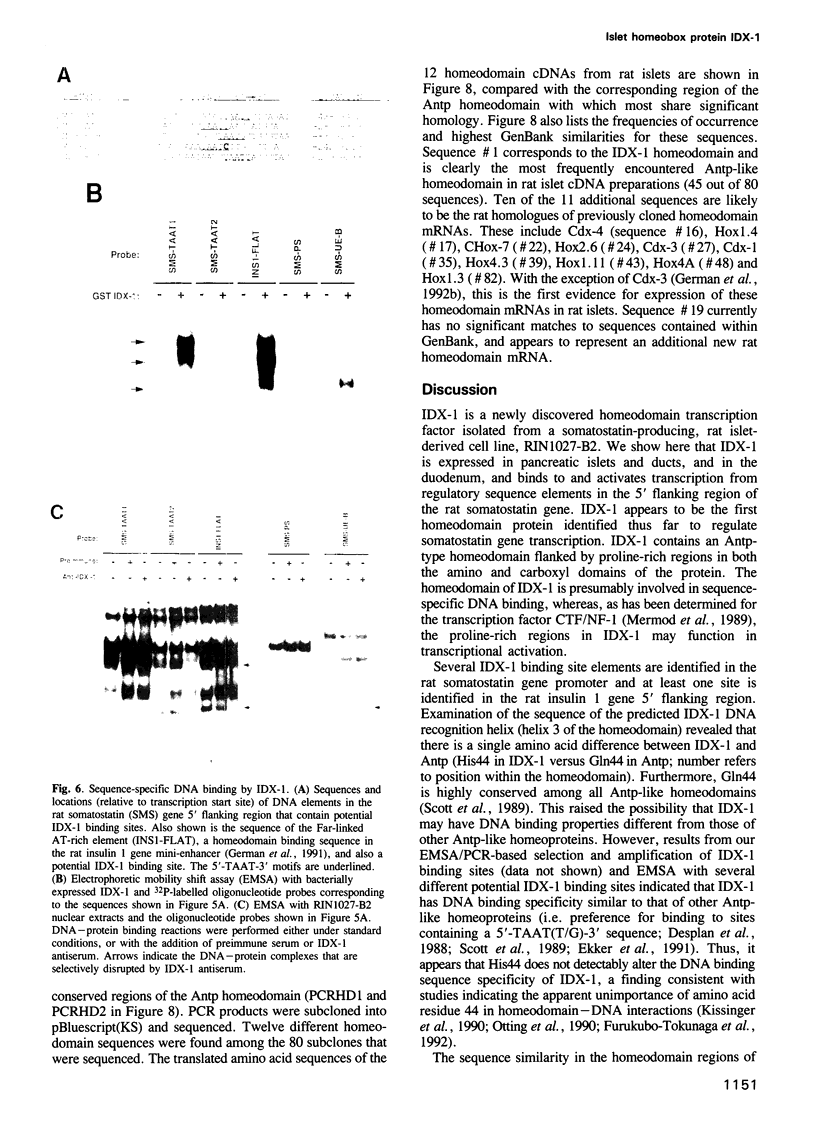
We describe the cloning from a rat islet somatostatin-producing cell line of a 1.4 kb cDNA encoding a new homeoprotein, IDX-1 (islet/duodenum homeobox-1), with close sequence similarity to the Drosophila melanogaster homeobox protein Antennapedia (Antp) and the Xenopus laevis endoderm-specific homeoprotein XlHbox8. Analyses of IDX-1 mRNA and protein in rat tissues show that IDX-1 is expressed in pancreatic islets and ducts and in the duodenum. In electrophoretic mobility shift assays IDX-1 binds to three sites in the 5' flanking region of the rat somatostatin gene. In co-transfection experiments IDX-1 transactivates reporter constructs containing somatostatin promoter sequences, and mutation of the IDX-1 binding sites attenuates transactivation. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction of islet RNA using degenerate amplimers for mRNAs encoding homeoproteins indicates that IDX-1 is the most abundant of 12 different Antp-like homeodomain mRNAs expressed in adult rat islets. The pattern of expression, relative abundance and transcriptional regulatory activity suggests that IDX-1 may be involved in the regulation of islet hormone genes and in cellular differentiation in the endocrine pancreas and the duodenum.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert S., Hanahan D., Teitelman G. Hybrid insulin genes reveal a developmental lineage for pancreatic endocrine cells and imply a relationship with neurons. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron A., Featherstone M. S., Hill R. E., Hall A., Galliot B., Duboule D. Hox-1.6: a mouse homeo-box-containing gene member of the Hox-1 complex. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2977–2986. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02603.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellmann R., Werr W. Zmhox1a, the product of a novel maize homeobox gene, interacts with the Shrunken 26 bp feedback control element. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3367–3374. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05415.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B., Wright C. V., De Robertis E. M., Cho K. W. Organizer-specific homeobox genes in Xenopus laevis embryos. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):194–196. doi: 10.1126/science.1677215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boam D. S., Docherty K. A tissue-specific nuclear factor binds to multiple sites in the human insulin-gene enhancer. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 15;264(1):233–239. doi: 10.1042/bj2640233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R., Finney M., Coulson A., Ruvkun G. Caenorhabditis elegans has scores of homoeobox-containing genes. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):239–243. doi: 10.1038/341239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chick W. L., Warren S., Chute R. N., Like A. A., Lauris V., Kitchen K. C. A transplantable insulinoma in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):628–632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The sequence specificity of homeodomain-DNA interaction. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1081–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudek R. W., Lawrence I. E., Jr, Hill R. S., Johnson R. C. Induction of islet cytodifferentiation by fetal mesenchyme in adult pancreatic ductal epithelium. Diabetes. 1991 Aug;40(8):1041–1048. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.8.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Linde S., Kofod H., Spector D., Delannoy M., Grant S., Hanahan D., Baekkeskov S. Beta-cell lines derived from transgenic mice expressing a hybrid insulin gene-oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9037–9041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., Young K. E., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Optimal DNA sequence recognition by the Ultrabithorax homeodomain of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1179–1186. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emens L. A., Landers D. W., Moss L. G. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha is expressed in a hamster insulinoma line and transactivates the rat insulin I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7300–7304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukubo-Tokunaga K., Müller M., Affolter M., Pick L., Kloter U., Gehring W. J. In vivo analysis of the helix-turn-helix motif of the fushi tarazu homeo domain of Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):1082–1096. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamer L. W., Wright C. V. Murine Cdx-4 bears striking similarities to the Drosophila caudal gene in its homeodomain sequence and early expression pattern. Mech Dev. 1993 Sep;43(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90024-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. Homeo boxes in the study of development. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1245–1252. doi: 10.1126/science.2884726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German M. S., Moss L. G., Wang J., Rutter W. J. The insulin and islet amyloid polypeptide genes contain similar cell-specific promoter elements that bind identical beta-cell nuclear complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1777–1788. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German M. S., Wang J., Chadwick R. B., Rutter W. J. Synergistic activation of the insulin gene by a LIM-homeo domain protein and a basic helix-loop-helix protein: building a functional insulin minienhancer complex. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2165–2176. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. W., Gomez G., Greeley G. H., Jr Gastrointestinal peptides. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1989 Dec;18(4):695–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J. H., Rall L., Rutter W. J. Selective expression of rat pancreatic genes during embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):110–114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. W., Hogan B. L. Expression of homeo box genes during mouse development: a review. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):773–782. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James R., Kazenwadel J. Homeobox gene expression in the intestinal epithelium of adult mice. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3246–3251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Q., Yun Y. D., Hoeffler J. P., Habener J. F. Cyclic-AMP-responsive transcriptional activation of CREB-327 involves interdependent phosphorylated subdomains. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4455–4465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Levine E. M., Schechter N. Homeobox genes are expressed in the retina and brain of adult goldfish. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2729–2733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. Y., Devaux B., Green A., Sagerström C., Elliott J. F., Davis M. M. Expression of T cell antigen receptor heterodimers in a lipid-linked form. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):677–679. doi: 10.1126/science.1696397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtha M. T., Leckman J. F., Ruddle F. H. Detection of homeobox genes in development and evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10711–10715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazarali A., Kim Y., Nirenberg M. Hox-1.11 and Hox-4.9 homeobox genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2883–2887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohno T., Noji S., Koyama E., Ohyama K., Myokai F., Kuroiwa A., Saito T., Taniguchi S. Involvement of the Chox-4 chicken homeobox genes in determination of anteroposterior axial polarity during limb development. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1197–1205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90274-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Thor S., Edlund T. Novel insulin promoter- and enhancer-binding proteins that discriminate between pancreatic alpha- and beta-cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jul;5(7):897–904. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-7-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L. Macro- and micro-domains in the endocrine pancreas. Diabetes. 1982 Jun;31(6 Pt 1):538–565. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.6.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Protein--DNA contacts in the structure of a homeodomain--DNA complex determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in solution. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3085–3092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel C. V., Gorski D. H., LePage D. F., Lincecum J., Walsh K. Molecular cloning of a homeobox transcription factor from adult aortic smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):26085–26090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe J., Chick W. L., Habener J. F. Multipotential phenotypic expression of genes encoding peptide hormones in rat insulinoma cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):351–358. doi: 10.1172/JCI112819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers A. C., Tedeschi F., Wright K. E., Chan J. S., Habener J. F. Somatostatin gene expression in pancreatic islet cells is directed by cell-specific DNA control elements and DNA-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10048–10056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prost E., Moore D. D. CAT vectors for analysis of eukaryotic promoters and enhancers. Gene. 1986;45(1):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renucci A., Zappavigna V., Zàkàny J., Izpisúa-Belmonte J. C., Bürki K., Duboule D. Comparison of mouse and human HOX-4 complexes defines conserved sequences involved in the regulation of Hox-4.4. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1459–1468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05190.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Brasier A. R., Wright K. A., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. An inducible 50-kilodalton NF kappa B-like protein and a constitutive protein both bind the acute-phase response element of the angiotensinogen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1023–1032. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schummer M., Scheurlen I., Schaller C., Galliot B. HOM/HOX homeobox genes are present in hydra (Chlorohydra viridissima) and are differentially expressed during regeneration. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1815–1823. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh G., Kaur S., Stock J. L., Jenkins N. A., Gilbert D. J., Copeland N. G., Potter S. S. Identification of 10 murine homeobox genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10706–10710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Baltimore D. An inhibitory domain of E12 transcription factor prevents DNA binding in E12 homodimers but not in E12 heterodimers. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):459–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90653-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaki R., Ono J., Nakamura M., Yokogawa Y., Kumae S., Hiraoka T., Yamaguchi K., Hamaguchi K., Uchida S. Isolation of glucagon-secreting cell lines by cloning insulinoma cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1986 Mar;22(3 Pt 1):120–126. doi: 10.1007/BF02623498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelman G., Lee J. K. Cell lineage analysis of pancreatic islet development: glucagon and insulin cells arise from catecholaminergic precursors present in the pancreatic duct. Dev Biol. 1987 Jun;121(2):454–466. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo M., Miller C. P., Habener J. F. Somatostatin gene transcription regulated by a bipartite pancreatic islet D-cell-specific enhancer coupled synergetically to a cAMP response element. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12868–12875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo M., Penchuk L., Habener J. F. Somatostatin gene upstream enhancer element activated by a protein complex consisting of CREB, Isl-1-like, and alpha-CBF-like transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12876–12884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedeen C. J., Kostriken R. G., Matsumura I., Weisblat D. A. Evidence for a new family of evolutionarily conserved homeobox genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1908–1908. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessells N. K., Evans J. Ultrastructural studies of early morphogenesis and cytodifferentiation in the embryonic mammalian pancreas. Dev Biol. 1968 Apr;17(4):413–446. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(68)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinari M., Daikoku S. Ontogenetic appearance of immunoreactive endocrine cells in rat pancreatic islets. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1982 Sep;165(1):63–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00304583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]