Abstract
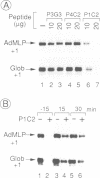
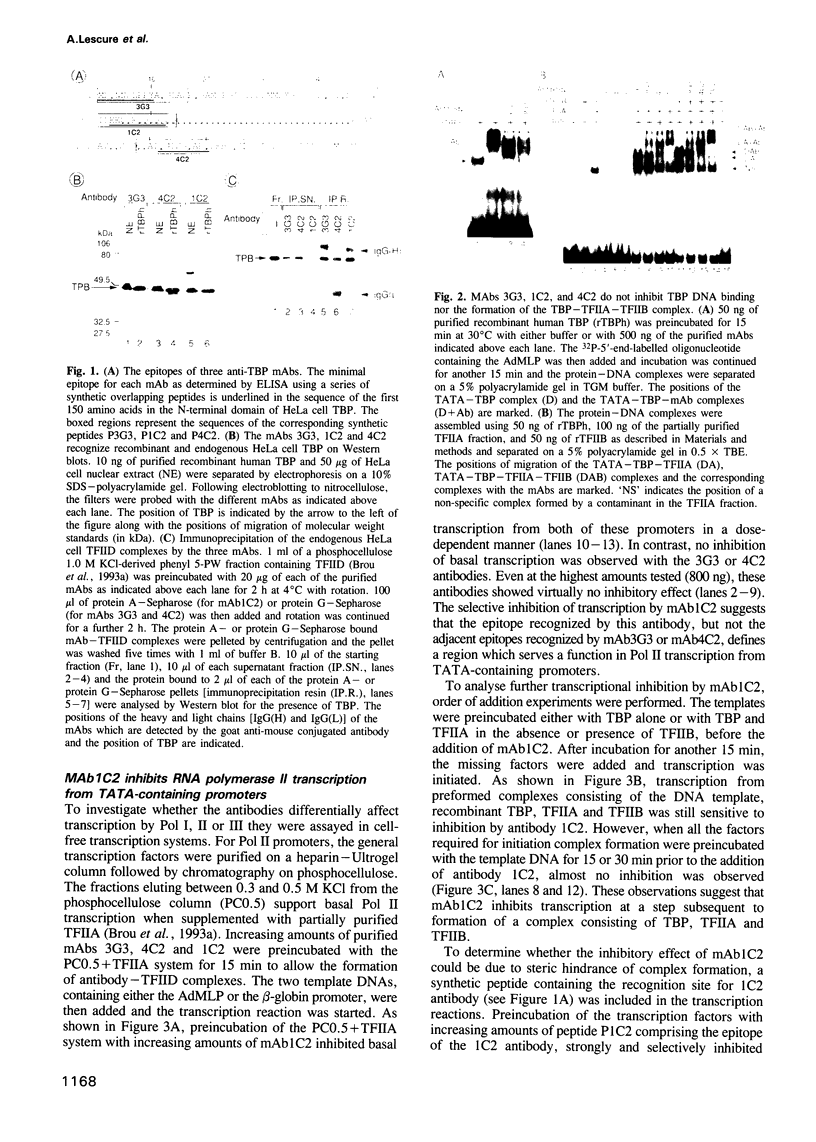
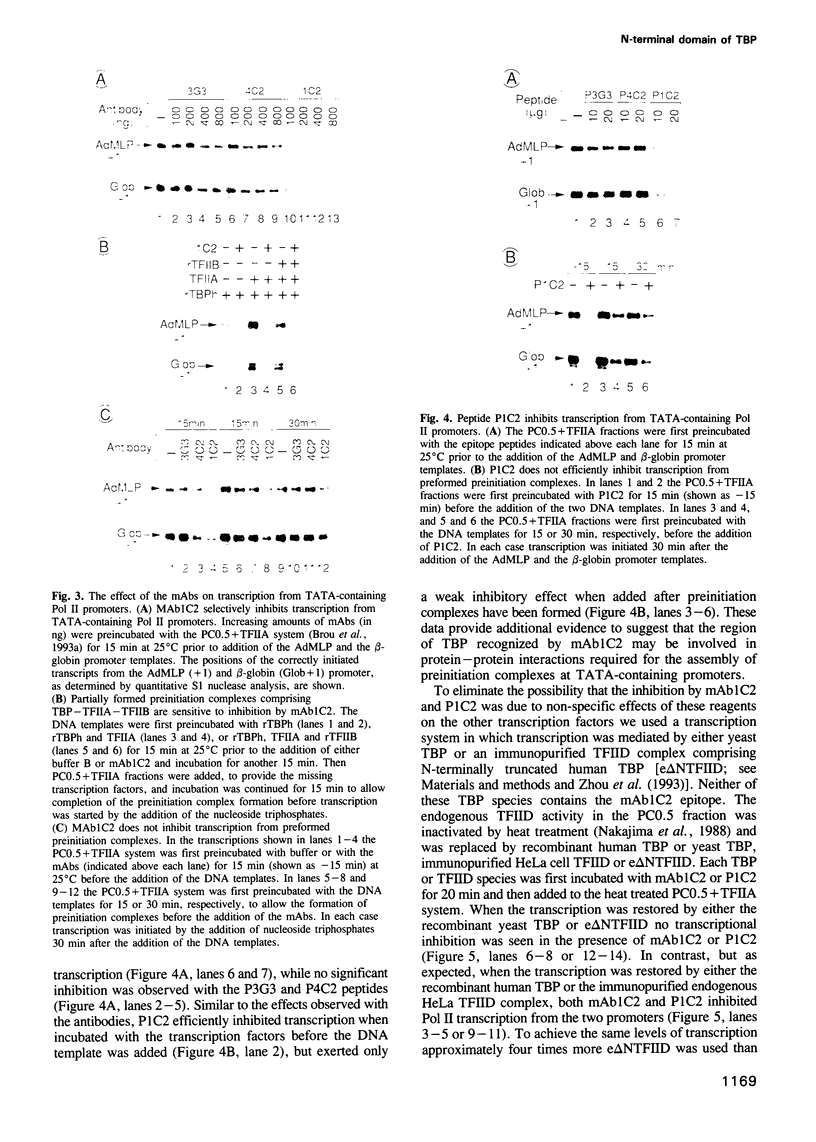
In eukaryotes, the TATA box binding protein (TBP) is an integral component of the transcription initiation complexes of all three classes of nuclear RNA polymerases. In this study we have investigated the role of the N-terminal region of human TBP in transcription initiation from RNA polymerase (Pol) I, II and III promoters by using three monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). Each antibody recognizes a distinct epitope in the N-terminal domain of human TBP. We demonstrate that these antibodies differentially affect transcription from distinct classes of promoters. One antibody, mAb1C2, and a synthetic peptide comprising its epitope selectively inhibited in vitro transcription from TATA-containing, but not from TATA-less promoters, irrespective of whether they were transcribed by Pol II or Pol III. Transcription by Pol I, on the other hand, was not affected. Two other antibodies and their respective epitope peptides did not affect transcription from any of the promoters tested. Order of addition experiments indicate that mAb1C2 did not prevent binding of TBP to the TATA box or the formation of the TBP-TFIIA-TFIIB complex but rather inhibited a subsequent step of preinitiation complex formation. These data suggest that a defined region within the N-terminal domain of human TBP may be involved in specific protein-protein interactions required for the assembly of functional preinitiation complexes on TATA-containing, but not on TATA-less promoters.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beattie J., Fawcett H. A., Flint D. J. The use of multiple-pin peptide synthesis in an analysis of the continuous epitopes recognised by various anti-(recombinant bovine growth hormone) sera. Comparison with predicted regions of immunogenicity and location within the three-dimensional structure of the molecule. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Nov 15;210(1):59–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernués J., Simmen K. A., Lewis J. D., Gunderson S. I., Polycarpou-Schwarz M., Moncollin V., Egly J. M., Mattaj I. W. Common and unique transcription factor requirements of human U1 and U6 snRNA genes. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3573–3585. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brou C., Chaudhary S., Davidson I., Lutz Y., Wu J., Egly J. M., Tora L., Chambon P. Distinct TFIID complexes mediate the effect of different transcriptional activators. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):489–499. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brou C., Wu J., Ali S., Scheer E., Lang C., Davidson I., Chambon P., Tora L. Different TBP-associated factors are required for mediating the stimulation of transcription in vitro by the acidic transactivator GAL-VP16 and the two nonacidic activation functions of the estrogen receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 11;21(1):5–12. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton N., Cavallini B., Kanno M., Moncollin V., Egly J. M. Expression in Escherichia coli: purification and properties of the yeast general transcription factor TFIID. Protein Expr Purif. 1991 Oct-Dec;2(5-6):432–441. doi: 10.1016/1046-5928(91)90105-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carcamo J., Buckbinder L., Reinberg D. The initiator directs the assembly of a transcription factor IID-dependent transcription complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8052–8056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang C. M., Ge H., Wang Z., Hoffmann A., Roeder R. G. Unique TATA-binding protein-containing complexes and cofactors involved in transcription by RNA polymerases II and III. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2749–2762. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05936.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Tanese N., Tjian R. The TATA-binding protein and associated factors are integral components of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor, SL1. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):965–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90039-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Bradsher J. N., Conaway J. W. Mechanism of assembly of the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex. Evidence for a functional interaction between the carboxyl-terminal domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II and a high molecular mass form of the TATA factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8464–8467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormack B. P., Strubin M., Ponticelli A. S., Struhl K. Functional differences between yeast and human TFIID are localized to the highly conserved region. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90167-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard D., Tora L., Egly J. M., Grummt I. A TBP-containing multiprotein complex (TIF-IB) mediates transcription specificity of murine RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 11;21(18):4180–4186. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.18.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase III (C) and its transcription factors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):412–416. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90166-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel S., Thompson J. A., Jacob W. F., Cohen R., Safer B. Identification and characterization of an adenovirus 2 major late promoter CAP sequence DNA-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10309–10319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Tjian R. A highly conserved domain of TFIID displays species specificity in vivo. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90166-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. Roles of TFIID in transcriptional initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1067–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90027-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha I., Roberts S., Maldonado E., Sun X., Kim L. U., Green M., Reinberg D. Multiple functional domains of human transcription factor IIB: distinct interactions with two general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):1021–1032. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N. TBP, a universal eukaryotic transcription factor? Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1291–1308. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Dynlacht B. D., Peterson M. G., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Isolation and characterization of the Drosophila gene encoding the TATA box binding protein, TFIID. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1179–1186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90682-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Weinzierl R. O., Gill G., Chen J. L., Dynlacht B. D., Tjian R. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of Drosophila TAF110 reveal properties expected of coactivators. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):247–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90664-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Yamamoto T., Ohkuma Y., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Analysis of structure-function relationships of yeast TATA box binding factor TFIID. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1171–1178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90681-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Sentenac A. The TATA-binding protein participates in TFIIIB assembly on tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6451–6454. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Joazeiro C. A., Pisano M., Geiduschek E. P., Colbert T., Hahn S., Blanco J. A. The role of the TATA-binding protein in the assembly and function of the multisubunit yeast RNA polymerase III transcription factor, TFIIIB. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1055–1064. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90399-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keaveney M., Berkenstam A., Feigenbutz M., Vriend G., Stunnenberg H. G. Residues in the TATA-binding protein required to mediate a transcriptional response to retinoic acid in EC cells. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):562–566. doi: 10.1038/365562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Flanagan P. M., Chasman D. I., Ponticelli A. S., Struhl K., Kornberg R. D. Yeast and human TFIIDs are interchangeable for the response to acidic transcriptional activators in vitro. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):296–303. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Nikolov D. B., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of a TATA element. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):520–527. doi: 10.1038/365520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Geiger J. H., Hahn S., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of a yeast TBP/TATA-box complex. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):512–520. doi: 10.1038/365512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koleske A. J., Buratowski S., Nonet M., Young R. A. A novel transcription factor reveals a functional link between the RNA polymerase II CTD and TFIID. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):883–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90298-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuddus R., Schmidt M. C. Effect of the non-conserved N-terminus on the DNA binding activity of the yeast TATA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1789–1796. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Grummt I. Dual role of the nucleolar transcription factor UBF: trans-activator and antirepressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7340–7344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Stefanovsky V., Grummt I. The nucleolar transcription activator UBF relieves Ku antigen-mediated repression of mouse ribosomal gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 11;21(9):2057–2063. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.9.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. K., DeJong J., Hashimoto S., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. TFIIA induces conformational changes in TFIID via interactions with the basic repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5189–5196. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lescure A., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W., Krol A., Carbon P. A factor with Sp1 DNA-binding specificity stimulates Xenopus U6 snRNA in vivo transcription by RNA polymerase III. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 20;228(2):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90828-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Schmidt M. C., Kao C. C., Berk A. J. Two distinct domains in the yeast transcription factor IID and evidence for a TATA box-induced conformational change. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):63–74. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Tanaka M., Sullivan M. L., Hernandez N. A TBP complex essential for transcription from TATA-less but not TATA-containing RNA polymerase III promoters is part of the TFIIIB fraction. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1029–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90397-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncollin V., Miyamoto N. G., Zheng X. M., Egly J. M. Purification of a factor specific for the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2577–2584. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncollin V., Schaeffer L., Chalut C., Egly J. M. Expression in Escherichia coli: purification and properties of the recombinant human general transcription factor rTFIIB. Protein Expr Purif. 1992 Oct;3(5):374–379. doi: 10.1016/s1046-5928(05)80038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Yoon J. B., Gerster T., Roeder R. G. Oct-1 and Oct-2 potentiate functional interactions of a transcription factor with the proximal sequence element of small nuclear RNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3247–3261. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Clarkson S. G. Nucleotide sequence of genes coding for tRNAPhe and tRNATyr from a repeating unit of X. laevis DNA. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90509-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolov D. B., Hu S. H., Lin J., Gasch A., Hoffmann A., Horikoshi M., Chua N. H., Roeder R. G., Burley S. K. Crystal structure of TFIID TATA-box binding protein. Nature. 1992 Nov 5;360(6399):40–46. doi: 10.1038/360040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima Y., Okada N., Tani T., Itoh Y., Itoh M. Nucleotide sequences of mouse genomic loci including a gene or pseudogene for U6 (4.8S) nuclear RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):5145–5158. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Functional domains and upstream activation properties of cloned human TATA binding protein. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1625–1630. doi: 10.1126/science.2363050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponglikitmongkol M., White J. H., Chambon P. Synergistic activation of transcription by the human estrogen receptor bound to tandem responsive elements. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2221–2231. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon D., Schroeder S., Wang C. K., Yamamoto T., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G., Weil P. A. The conserved carboxy-terminal domain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae TFIID is sufficient to support normal cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4809–4821. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Diverse transcriptional functions of the multisubunit eukaryotic TFIID complex. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):679–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Transcription from a TATA-less promoter requires a multisubunit TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1935–1945. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranish J. A., Lane W. S., Hahn S. Isolation of two genes that encode subunits of the yeast transcription factor IIA. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1127–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.1546313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P., Hahn S. Dominant negative mutations in yeast TFIID define a bipartite DNA-binding region. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. rRNA synthesis in the nucleolus. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90298-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W. Three in one and one in three: it all depends on TBP. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90042-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G. The complexities of eukaryotic transcription initiation: regulation of preinitiation complex assembly. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):402–408. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90164-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Meisterernst M., Pognonec P., Roeder R. G. Cooperative interaction of an initiator-binding transcription initiation factor and the helix-loop-helix activator USF. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):245–248. doi: 10.1038/354245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski C. L., Henry R. W., Lobo S. M., Hernandez N. Targeting TBP to a non-TATA box cis-regulatory element: a TBP-containing complex activates transcription from snRNA promoters through the PSE. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1535–1548. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Grummt I. Transcription complex formation at the mouse rDNA promoter involves the stepwise association of four transcription factors and RNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24588–24595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Rosenbauer H., Grummt I. Trans-acting factors involved in species-specificity and control of mouse ribosomal gene transcription. 1991 May 29-Jun 12Mol Cell Biochem. 104(1-2):137–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00229813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seipel K., Georgiev O., Schaffner W. Different activation domains stimulate transcription from remote ('enhancer') and proximal ('promoter') positions. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4961–4968. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05603.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. TATA-binding protein is a classless factor. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):819–821. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmen K. A., Bernués J., Lewis J. D., Mattaj I. W. Cofractionation of the TATA-binding protein with the RNA polymerase III transcription factor TFIIIB. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 25;20(22):5889–5898. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.22.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart A. K., Fisher T. S., Pugh B. F. The TATA-binding protein and associated factors are components of pol III transcription factor TFIIIB. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1015–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90396-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Coactivators for a proline-rich activator purified from the multisubunit human TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2212–2224. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tora L., White J., Brou C., Tasset D., Webster N., Scheer E., Chambon P. The human estrogen receptor has two independent nonacidic transcriptional activation functions. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usheva A., Maldonado E., Goldring A., Lu H., Houbavi C., Reinberg D., Aloni Y. Specific interaction between the nonphosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II and the TATA-binding protein. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):871–881. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90297-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldschmidt R., Wanandi I., Seifart K. H. Identification of transcription factors required for the expression of mammalian U6 genes in vitro. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2595–2603. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07801.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. The immunoglobulin heavy-chain B-lymphocyte enhancer efficiently stimulates transcription in non-lymphoid cells. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):553–560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04246.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis L., Reinberg D. Transcription by RNA polymerase II: initiator-directed formation of transcription-competent complexes. FASEB J. 1992 Nov;6(14):3300–3309. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.14.1426767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. H., Brou C., Wu J., Burton N., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Evidence for a factor required for transcriptional stimulation by the chimeric acidic activator GAL-VP16 in HeLa cell extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7674–7678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Jackson S. P. Mechanism of TATA-binding protein recruitment to a TATA-less class III promoter. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1041–1053. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90398-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Jackson S. P. The TATA-binding protein: a central role in transcription by RNA polymerases I, II and III. Trends Genet. 1992 Aug;8(8):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley S. R., Kraus R. J., Mertz J. E. Functional binding of the "TATA" box binding component of transcription factor TFIID to the -30 region of TATA-less promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5814–5818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Matthes H., Garnier J. M., Chambon P. Cloning, expression, and transcriptional properties of the human enhancer factor TEF-1. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):551–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90088-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenzie-Gregory B., Khachi A., Garraway I. P., Smale S. T. Mechanism of initiator-mediated transcription: evidence for a functional interaction between the TATA-binding protein and DNA in the absence of a specific recognition sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3841–3849. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q. A., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. J. Requirement for acidic amino acid residues immediately N-terminal to the conserved domain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae TFIID. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1843–1852. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07710.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q., Boyer T. G., Berk A. J. Factors (TAFs) required for activated transcription interact with TATA box-binding protein conserved core domain. Genes Dev. 1993 Feb;7(2):180–187. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.2.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q., Lieberman P. M., Boyer T. G., Berk A. J. Holo-TFIID supports transcriptional stimulation by diverse activators and from a TATA-less promoter. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1964–1974. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]