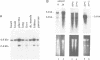Abstract
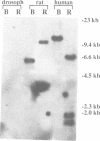
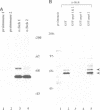
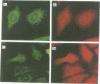
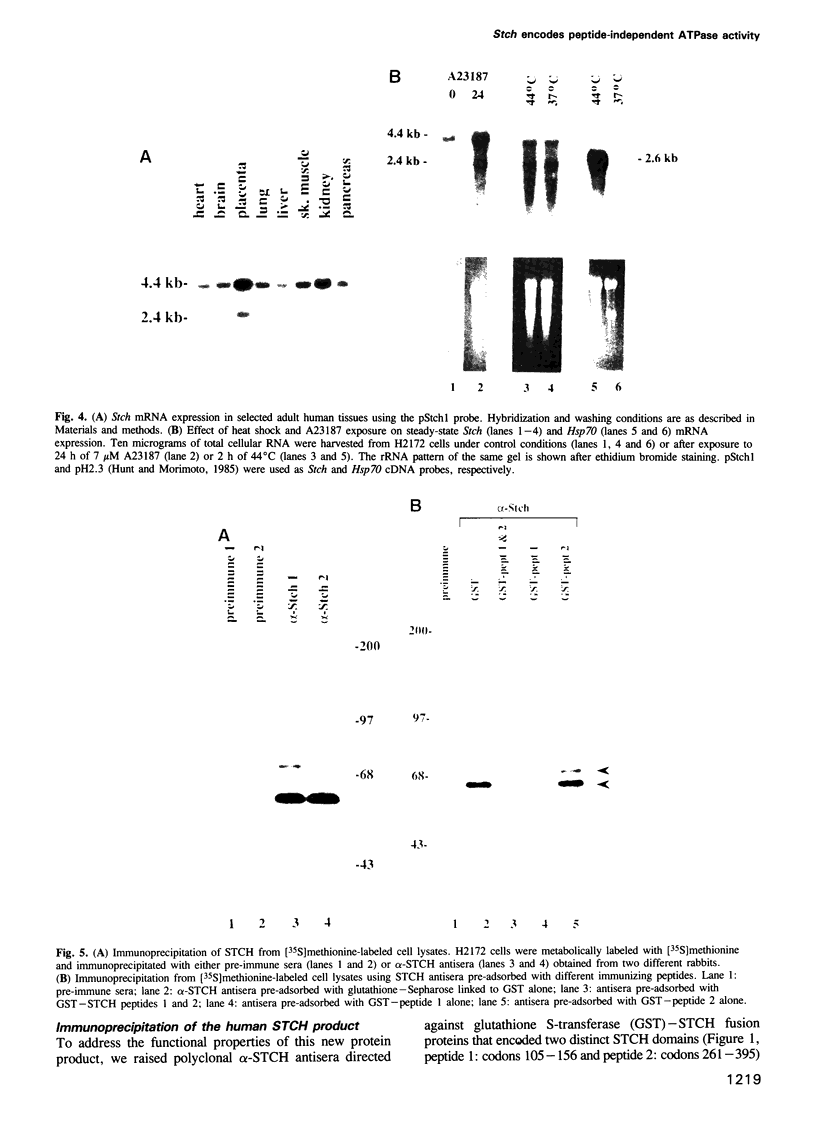
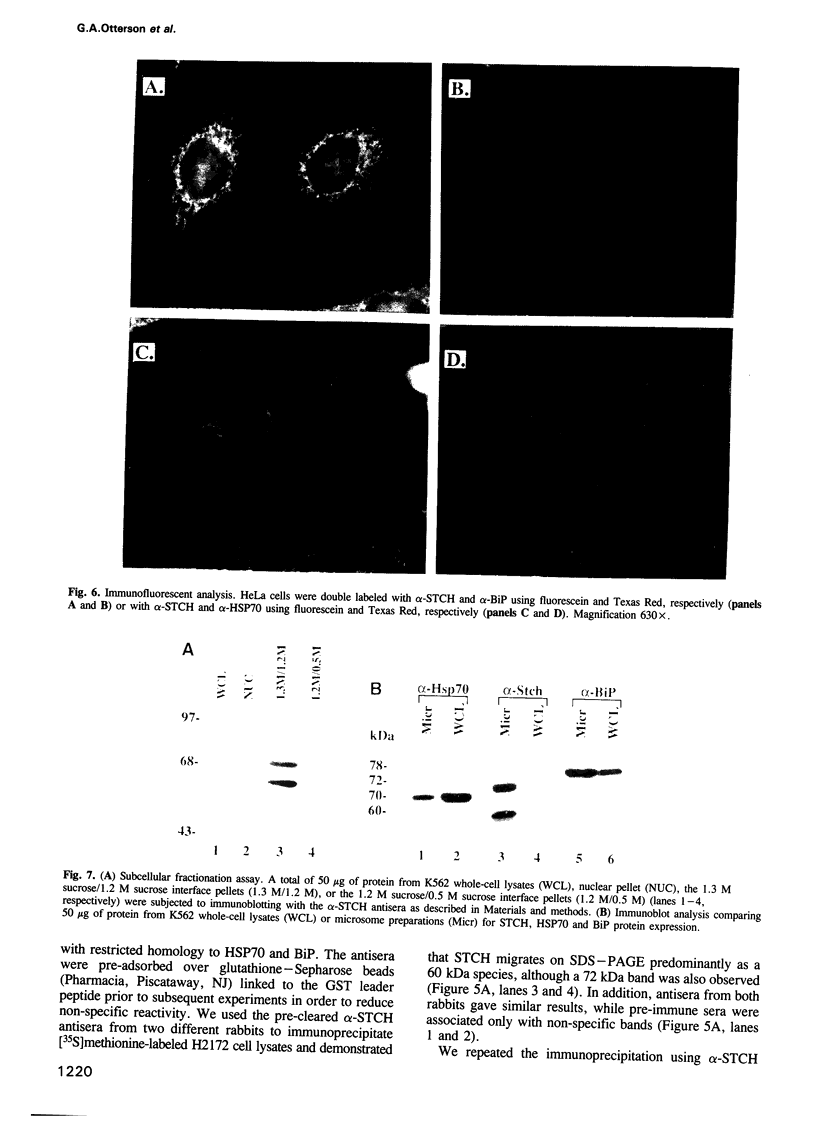
The stress70 protein chaperone family plays a central role in the processing of cytosolic and secretory proteins. We have cloned a human cDNA, designated Stch, that is conserved in rat tissues and which encodes a novel microsome-associated member of the stress70 protein chaperone family. Stch mRNA is constitutively expressed in all human cell types and is induced by incubation with the calcium ionophore A23187, but not by exposure to heat shock. Inspection of the predicted amino acid sequence reveals that the STCH product contains a unique hydrophobic leader sequence and shares homology within the amino terminal domains of the stress70 gene family, but has a 50 residue insertion within the ATP-binding domains and truncates the carboxyl terminal peptide-binding region. Immunofluorescent and subcellular analyses show that STCH migrates predominantly as a 60 kDa species and is enriched in a membrane-bound microsome fraction. In contrast to purified BiP and dnaK, however, STCH demonstrates ATPase activity that is independent of peptide stimulation. Stch, therefore, encodes a calcium-inducible, microsome-associated ATPase activity with properties similar to a proteolytically cleaved N-terminal HSC70/BiP fragment. This truncated stress70 molecule may allow increased diversity in cellular responses to protein processing requirements.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Major heat shock gene of Drosophila and the Escherichia coli heat-inducible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):848–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bole D. G., Hendershot L. M., Kearney J. F. Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein with nascent heavy chains in nonsecreting and secreting hybridomas. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1558–1566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bork P., Sander C., Valencia A. An ATPase domain common to prokaryotic cell cycle proteins, sugar kinases, actin, and hsp70 heat shock proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7290–7294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappell T. G., Konforti B. B., Schmid S. L., Rothman J. E. The ATPase core of a clathrin uncoating protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):746–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirico W. J., Waters M. G., Blobel G. 70K heat shock related proteins stimulate protein translocation into microsomes. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):805–810. doi: 10.1038/332805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Koch B. D., Werner-Washburne M., Craig E. A., Schekman R. A subfamily of stress proteins facilitates translocation of secretory and mitochondrial precursor polypeptides. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):800–805. doi: 10.1038/332800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domanico S. Z., DeNagel D. C., Dahlseid J. N., Green J. M., Pierce S. K. Cloning of the gene encoding peptide-binding protein 74 shows that it is a new member of the heat shock protein 70 family. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3598–3610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaherty K. M., DeLuca-Flaherty C., McKay D. B. Three-dimensional structure of the ATPase fragment of a 70K heat-shock cognate protein. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):623–628. doi: 10.1038/346623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flajnik M. F., Canel C., Kramer J., Kasahara M. Which came first, MHC class I or class II? Immunogenetics. 1991;33(5-6):295–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00216688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn G. C., Chappell T. G., Rothman J. E. Peptide binding and release by proteins implicated as catalysts of protein assembly. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):385–390. doi: 10.1126/science.2756425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn G. C., Pohl J., Flocco M. T., Rothman J. E. Peptide-binding specificity of the molecular chaperone BiP. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):726–730. doi: 10.1038/353726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower L. E. Heat shock, stress proteins, chaperones, and proteotoxicity. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90611-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C., Morimoto R. I. Conserved features of eukaryotic hsp70 genes revealed by comparison with the nucleotide sequence of human hsp70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6455–6459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Slater M. R., Craig E. A. Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains a complex multigene family related to the major heat shock-inducible gene of Drosophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1388–1398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassenbrock C. K., Kelly R. B. Interaction of heavy chain binding protein (BiP/GRP78) with adenine nucleotides. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1461–1467. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03529.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudo F., Johnson L. Condition with nutrition: a community program that works. Hosp Food Nutr Focus. 1988 Jan;4(5):1-5, 8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mensa-Wilmot K., Seaby R., Alfano C., Wold M. C., Gomes B., McMacken R. Reconstitution of a nine-protein system that initiates bacteriophage lambda DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2853–2861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mues G. I., Munn T. Z., Raese J. D. A human gene family with sequence homology to Drosophila melanogaster Hsp70 heat shock genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):874–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):899–907. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. An Hsp70-like protein in the ER: identity with the 78 kd glucose-regulated protein and immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normington K., Kohno K., Kozutsumi Y., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. S. cerevisiae encodes an essential protein homologous in sequence and function to mammalian BiP. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1223–1236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90059-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otterson G. A., Kratzke R. A., Lin A. Y., Johnston P. G., Kaye F. J. Alternative splicing of the RBP1 gene clusters in an internal exon that encodes potential phosphorylation sites. Oncogene. 1993 Apr;8(4):949–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Speculations on the functions of the major heat shock and glucose-regulated proteins. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):959–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90693-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippmann F., Taylor W. R., Rothbard J. B., Green N. M. A hypothetical model for the peptide binding domain of hsp70 based on the peptide binding domain of HLA. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1053–1059. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Misra L. M., Vogel J. P. KAR2, a karyogamy gene, is the yeast homolog of the mammalian BiP/GRP78 gene. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1211–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A., Vassalli P. Plasma cell immunoglobulin M molecules. Their biosynthesis, assembly, and intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):284–299. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting J., Lee A. S. Human gene encoding the 78,000-dalton glucose-regulated protein and its pseudogene: structure, conservation, and regulation. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):275–286. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissières A., Mitchell H. K., Tracy U. M. Protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: relation to chromosome puffs. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J., Garrels J. I., Thomas G. P., Lin J. J., Feramisco J. R. Biochemical characterization of the mammalian stress proteins and identification of two stress proteins as glucose- and Ca2+-ionophore-regulated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7102–7111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]