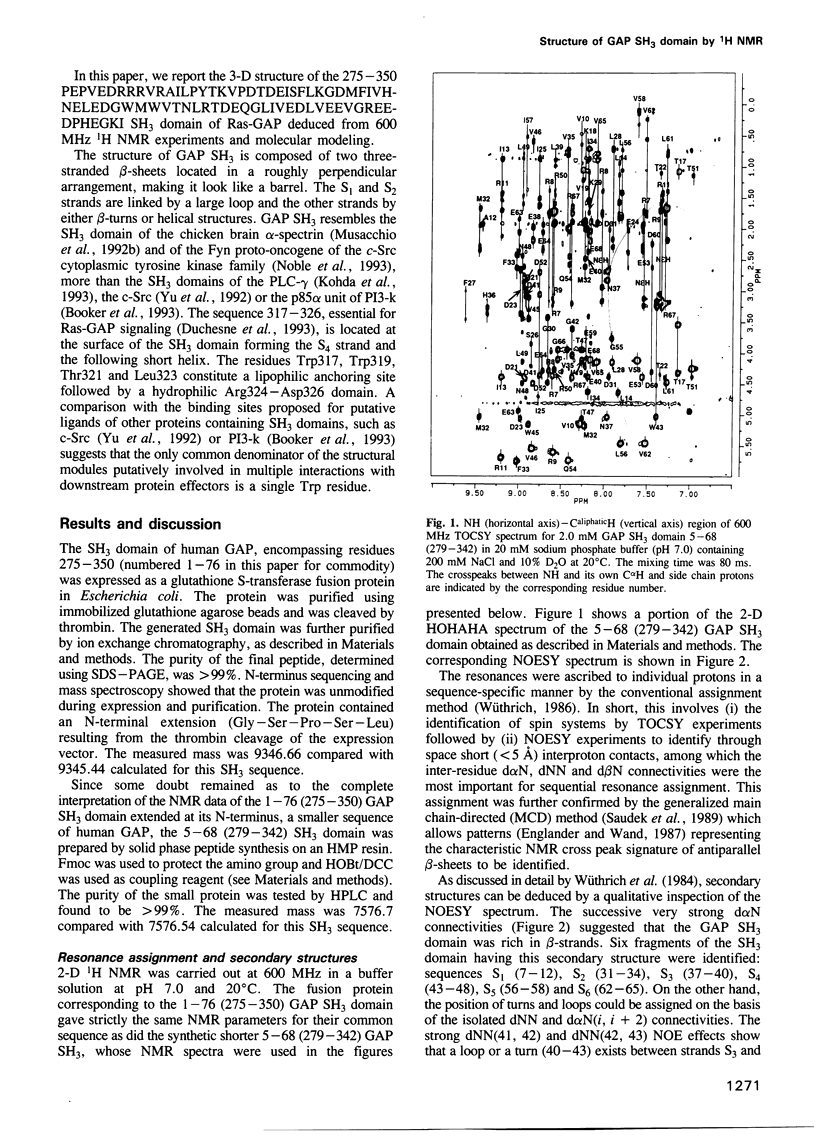
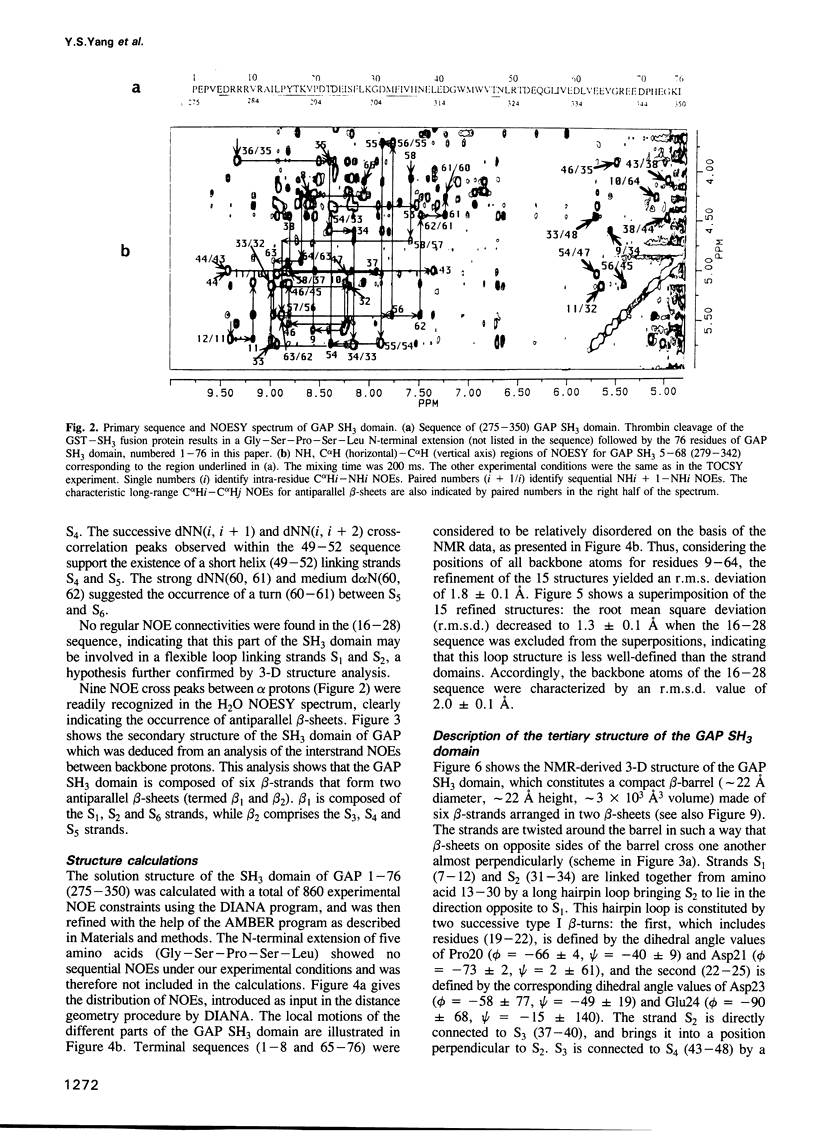
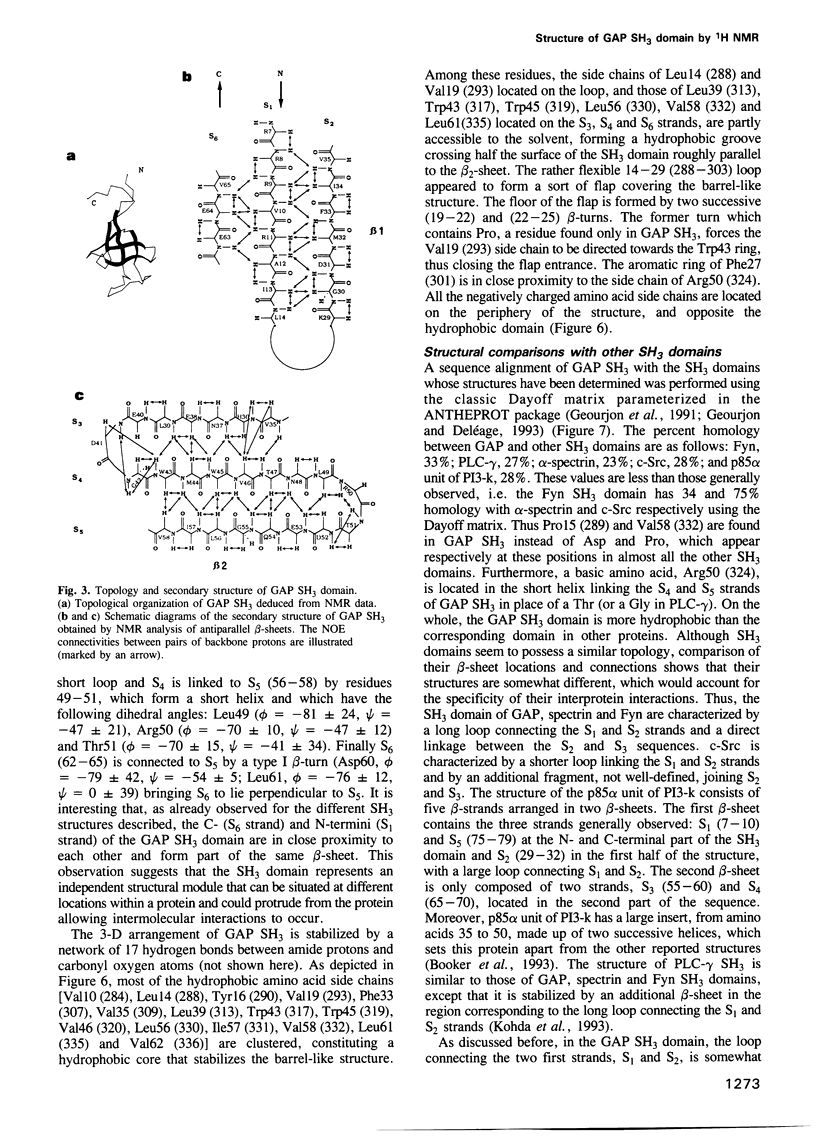
Abstract
Src homology 3 (SH3) domains are found in numerous cytoplasmic proteins involved in intracellular signal transduction. We used 2-D 1H NMR to determine the structure of the SH3 domain of the guanosine triphosphatase-activating protein (GAP), an essential component of the Ras signaling pathway. The structure of the GAP SH3 domain (275-350) was found to be a compact beta-barrel made of six antiparallel beta-strands arranged in two roughly perpendicular beta-sheets with the acidic residues located at the surface of the protein. The Trp317, Trp319, Thr321 and Leu323 residues belonging to the sequence (317-326), which was shown to be essential for Ras signaling, formed two nearby lipophilic bulges followed by a hydrophilic domain (Arg324-Asp326). These structural data could be used to characterize the still unidentified downstream components of GAP, which are involved in Ras signaling, and to rationally design inhibitors of this pathway.
Full text
PDF
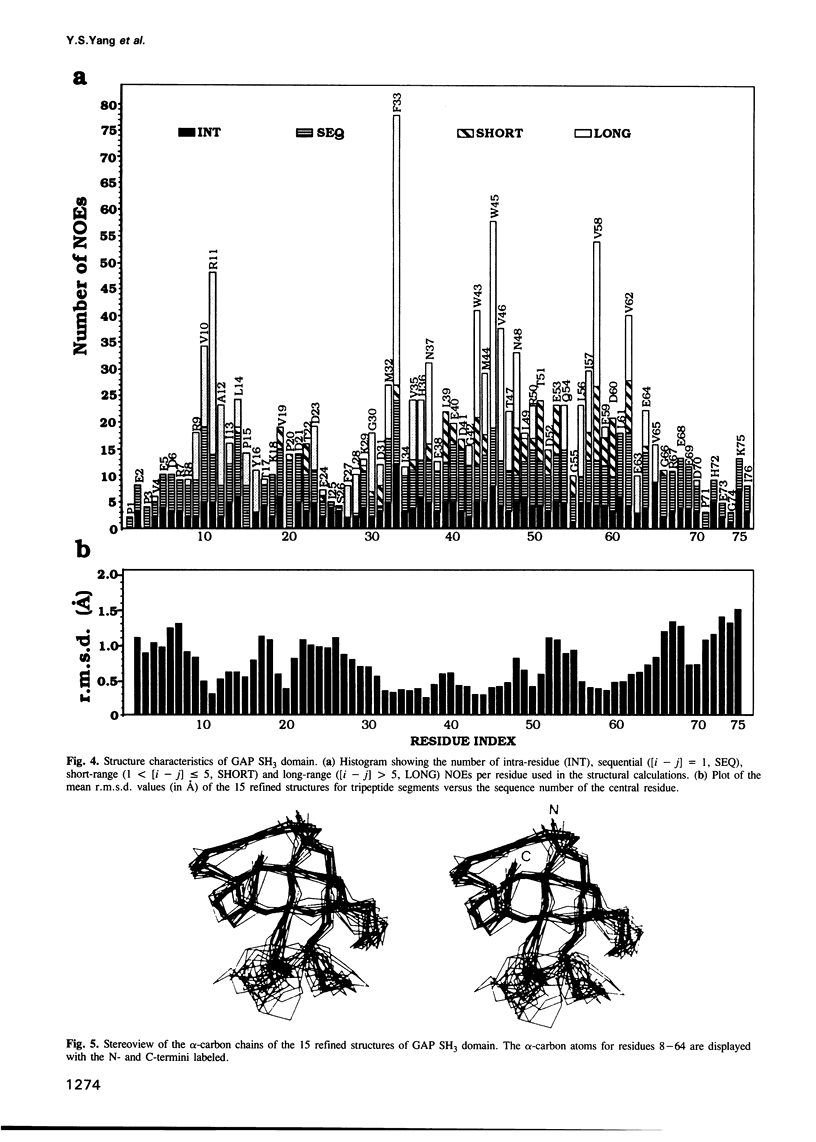
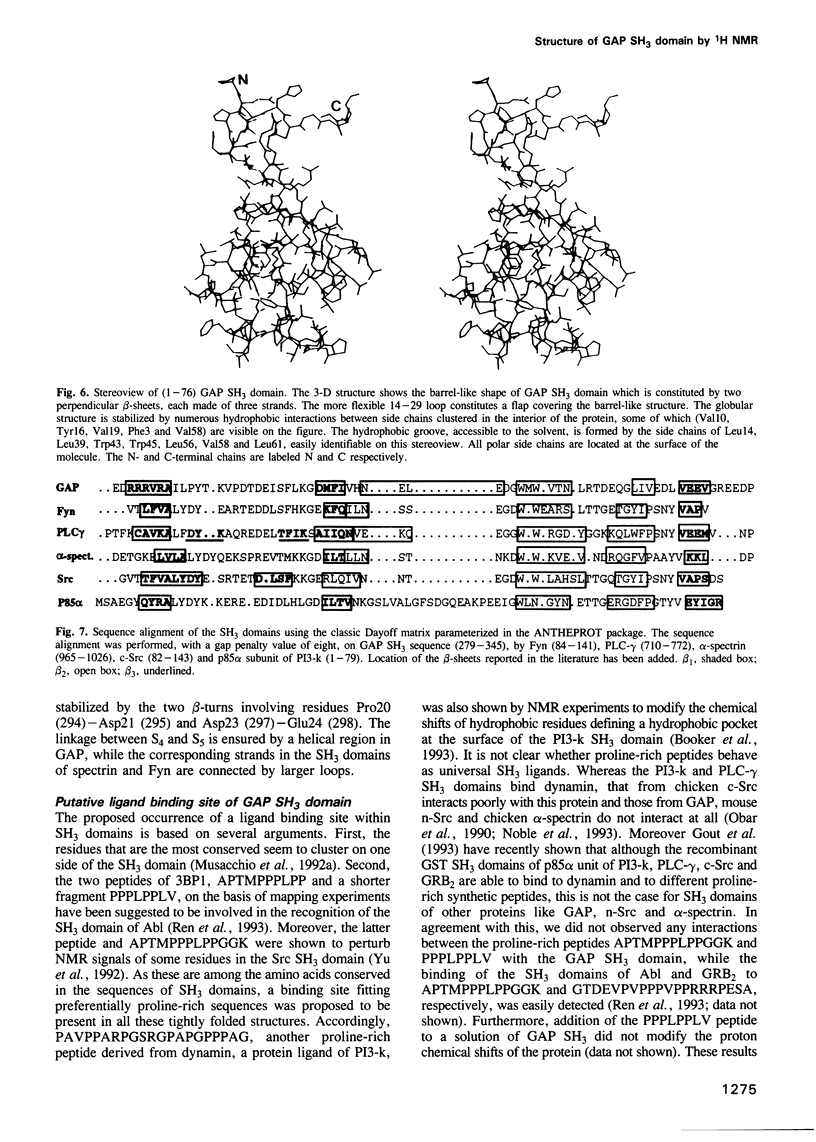
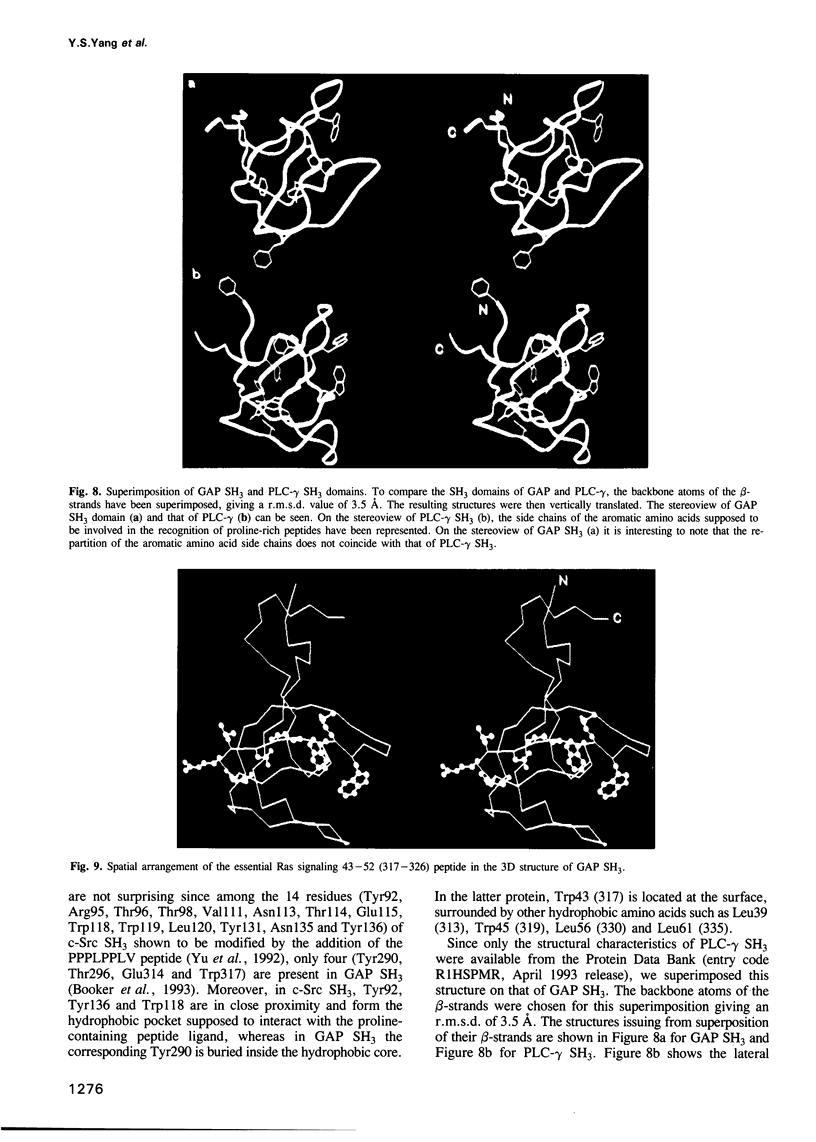
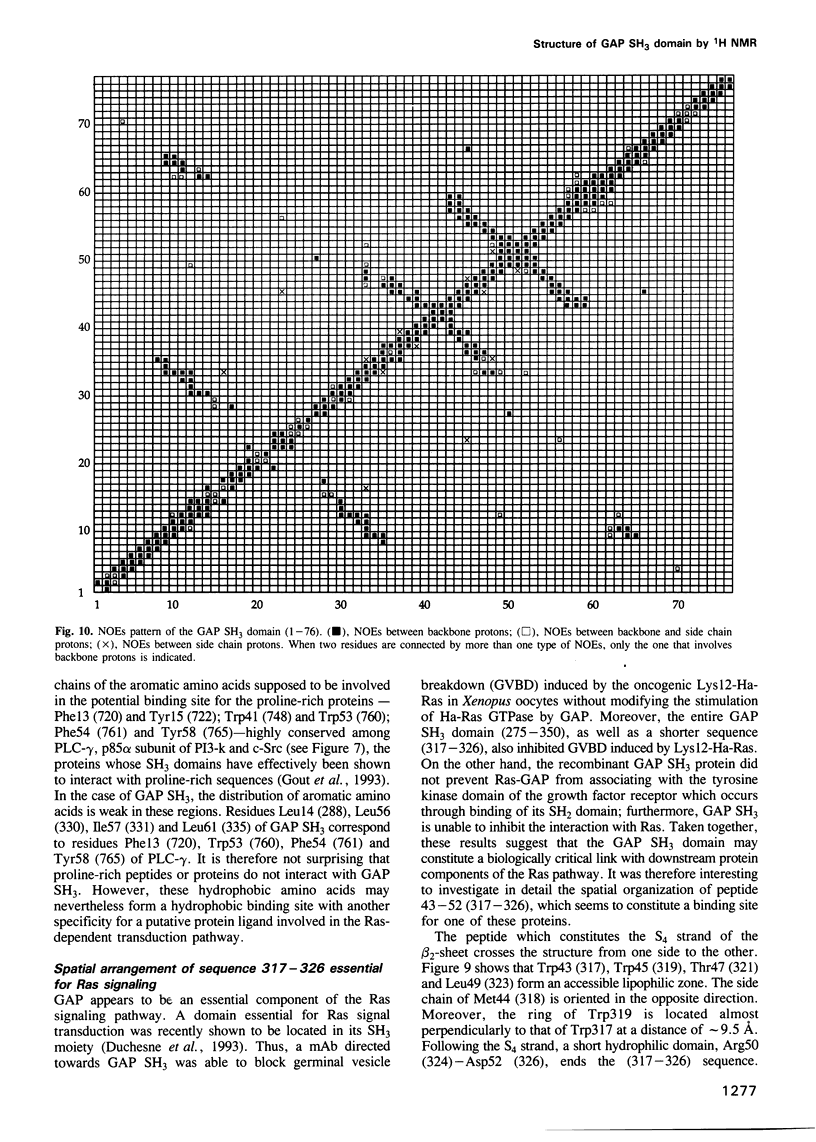


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bollag G., McCormick F. Regulators and effectors of ras proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:601–632. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booker G. W., Gout I., Downing A. K., Driscoll P. C., Boyd J., Waterfield M. D., Campbell I. D. Solution structure and ligand-binding site of the SH3 domain of the p85 alpha subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):813–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90259-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4682–4689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun W., Go N. Calculation of protein conformations by proton-proton distance constraints. A new efficient algorithm. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 5;186(3):611–626. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Dionne C. A., Kaplow J., Mudd R., Friesel R., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J., Jaye M. Characterization and cDNA cloning of phospholipase C-gamma, a major substrate for heparin-binding growth factor 1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor)-activated tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4770–4777. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchesne M., Schweighoffer F., Parker F., Clerc F., Frobert Y., Thang M. N., Tocqué B. Identification of the SH3 domain of GAP as an essential sequence for Ras-GAP-mediated signaling. Science. 1993 Jan 22;259(5094):525–528. doi: 10.1126/science.7678707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan S. E., Giddings B. W., Brooks M. W., Buday L., Sizeland A. M., Weinberg R. A. Association of Sos Ras exchange protein with Grb2 is implicated in tyrosine kinase signal transduction and transformation. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):45–51. doi: 10.1038/363045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englander S. W., Wand A. J. Main-chain-directed strategy for the assignment of 1H NMR spectra of proteins. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):5953–5958. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geourjon C., Deléage G. Interactive and graphic coupling between multiple alignments, secondary structure predictions and motif/pattern scanning into proteins. Comput Appl Biosci. 1993 Feb;9(1):87–91. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/9.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geourjon C., Deléage G., Roux B. ANTHEPROT: an interactive graphics software for analyzing protein structures from sequences. J Mol Graph. 1991 Sep;9(3):188-90, 167. doi: 10.1016/0263-7855(91)80008-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gout I., Dhand R., Hiles I. D., Fry M. J., Panayotou G., Das P., Truong O., Totty N. F., Hsuan J., Booker G. W. The GTPase dynamin binds to and is activated by a subset of SH3 domains. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):25–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli: an improved thrombin cleavage and purification procedure of fusion proteins with glutathione S-transferase. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 1;192(2):262–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90534-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güntert P., Braun W., Wüthrich K. Efficient computation of three-dimensional protein structures in solution from nuclear magnetic resonance data using the program DIANA and the supporting programs CALIBA, HABAS and GLOMSA. J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 5;217(3):517–530. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90754-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohda D., Hatanaka H., Odaka M., Mandiyan V., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Inagaki F. Solution structure of the SH3 domain of phospholipase C-gamma. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):953–960. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90583-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama S., Yu H., Dalgarno D. C., Shin T. B., Zydowsky L. D., Schreiber S. L. Structure of the PI3K SH3 domain and analysis of the SH3 family. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):945–952. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90582-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N., Batzer A., Daly R., Yajnik V., Skolnik E., Chardin P., Bar-Sagi D., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. Guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor hSos1 binds to Grb2 and links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras signalling. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):85–88. doi: 10.1038/363085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion D., Wüthrich K. Application of phase sensitive two-dimensional correlated spectroscopy (COSY) for measurements of 1H-1H spin-spin coupling constants in proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 29;113(3):967–974. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. A novel viral oncogene with structural similarity to phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):272–275. doi: 10.1038/332272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morellet N., Jullian N., De Rocquigny H., Maigret B., Darlix J. L., Roques B. P. Determination of the structure of the nucleocapsid protein NCp7 from the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by 1H NMR. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3059–3065. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05377.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio A., Gibson T., Lehto V. P., Saraste M. SH3--an abundant protein domain in search of a function. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 27;307(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80901-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio A., Noble M., Pauptit R., Wierenga R., Saraste M. Crystal structure of a Src-homology 3 (SH3) domain. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):851–855. doi: 10.1038/359851a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble M. E., Musacchio A., Saraste M., Courtneidge S. A., Wierenga R. K. Crystal structure of the SH3 domain in human Fyn; comparison of the three-dimensional structures of SH3 domains in tyrosine kinases and spectrin. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2617–2624. doi: 10.2210/pdb1shf/pdb. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obar R. A., Collins C. A., Hammarback J. A., Shpetner H. S., Vallee R. B. Molecular cloning of the microtubule-associated mechanochemical enzyme dynamin reveals homology with a new family of GTP-binding proteins. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):256–261. doi: 10.1038/347256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R., Mayer B. J., Cicchetti P., Baltimore D. Identification of a ten-amino acid proline-rich SH3 binding site. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.8438166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saudek V., Atkinson R. A., Williams R. J., Ramponi G. Identification and description of alpha-helical regions in horse muscle acylphosphatase by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90377-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Lee C. H., Batzer A., Vicentini L. M., Zhou M., Daly R., Myers M. J., Jr, Backer J. M., Ullrich A., White M. F. The SH2/SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 interacts with tyrosine-phosphorylated IRS1 and Shc: implications for insulin control of ras signalling. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1929–1936. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., Wong G., Halenbeck R., Rubinfeld B., Martin G. A., Ladner M., Long C. M., Crosier W. J., Watt K., Koths K. Molecular cloning of two types of GAP complementary DNA from human placenta. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1697–1700. doi: 10.1126/science.3201259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Kominos D., Robertson S. C., Pant N., Baltimore D., Birge R. B., Cowburn D., Hanafusa H., Mayer B. J., Overduin M. Crystal structure of the phosphotyrosine recognition domain SH2 of v-src complexed with tyrosine-phosphorylated peptides. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):646–653. doi: 10.1038/358646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Billeter M., Braun W. Polypeptide secondary structure determination by nuclear magnetic resonance observation of short proton-proton distances. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):715–740. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Billeter M., Braun W. Pseudo-structures for the 20 common amino acids for use in studies of protein conformations by measurements of intramolecular proton-proton distance constraints with nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 5;169(4):949–961. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80144-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Rosen M. K., Shin T. B., Seidel-Dugan C., Brugge J. S., Schreiber S. L. Solution structure of the SH3 domain of Src and identification of its ligand-binding site. Science. 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1665–1668. doi: 10.1126/science.1280858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]