Abstract
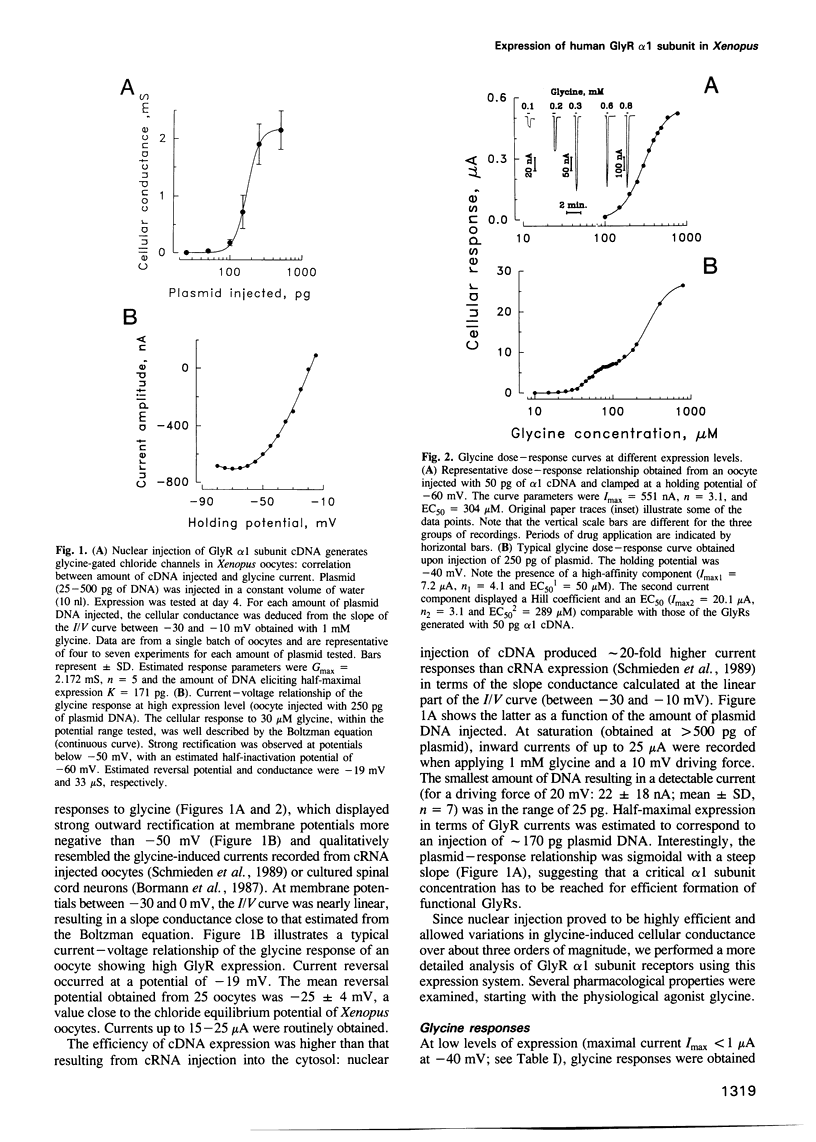
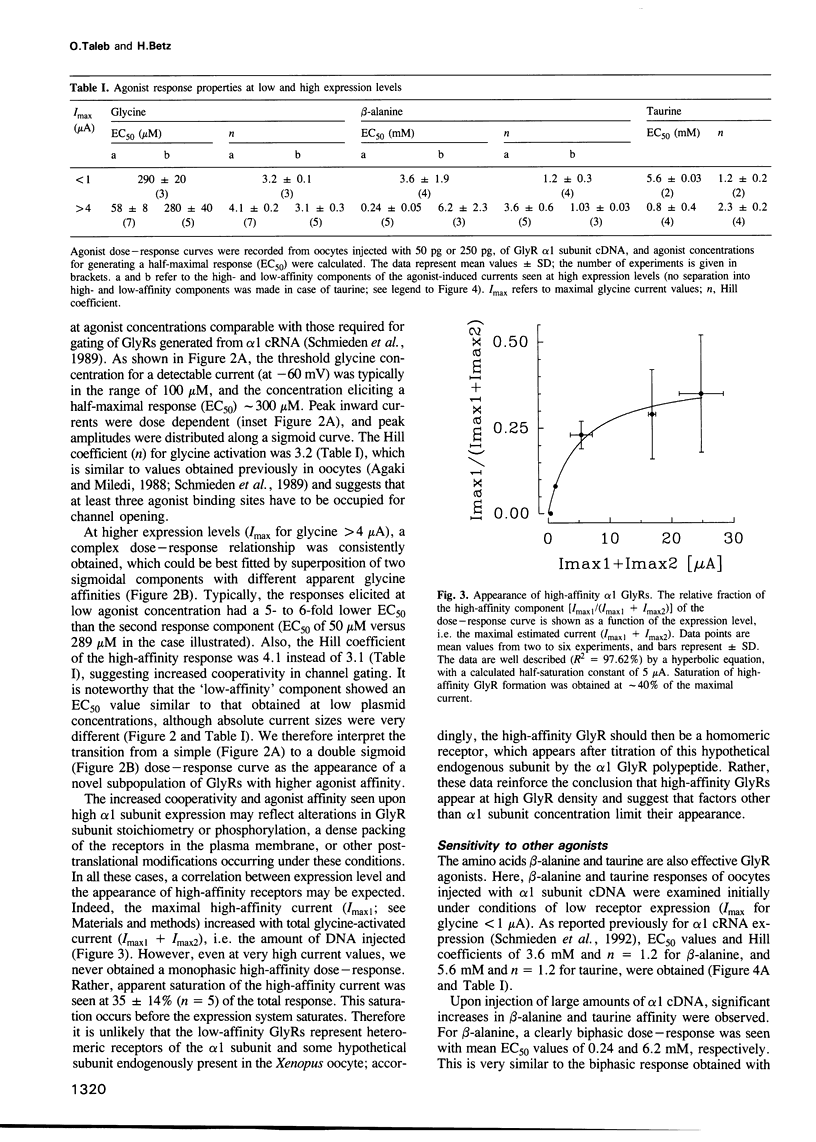
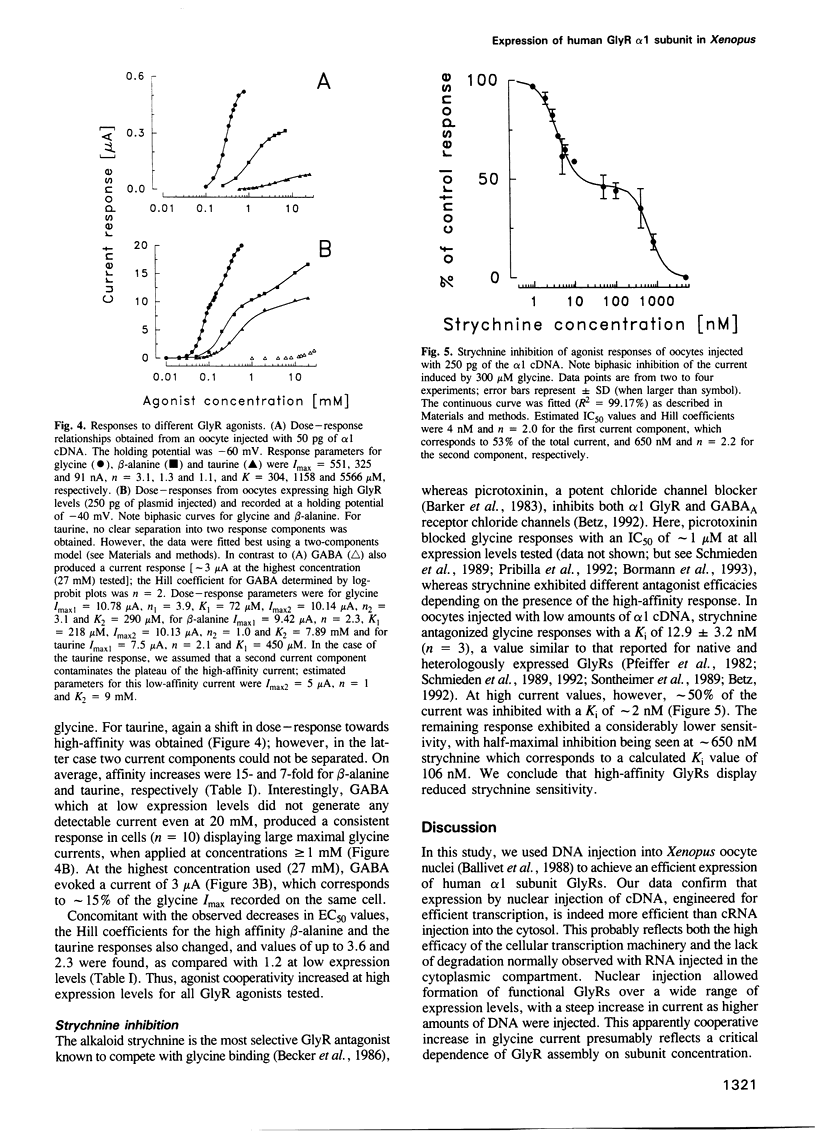
The inhibitory glycine receptor (GlyR) is a ligand-gated chloride channel, which mediates post-synaptic inhibition in spinal cord and other brain regions. Heterologous expression of the ligand binding alpha subunits of the GlyR generates functional agonist-gated chloride channels that mimic most of the pharmacological properties of the receptor in vivo. Here, nuclear injection into Xenopus oocytes of a human alpha 1 subunit cDNA, engineered for efficient expression, was used to create GlyR channels over a wide density range, resulting in whole-cell glycine currents of 10 nA to 25 microA. Notably, the pharmacology of these channels changed at high expression levels, with the appearance of a novel receptor subpopulation of 5- to 6-fold higher apparent agonist affinity at current values > 4 microA. The low-affinity receptors were readily blocked by nM concentrations of the competitive antagonist strychnine, whereas the high-affinity receptors were more resistant to antagonism by this alkaloid. Picrotoxinin, a chloride channel blocker, inhibited both GlyR populations with equal potency. Our data suggest that receptor interactions, occurring at high receptor density, modify the agonist response of the GlyR. This phenomenon may contribute to neurotransmitter efficacy at fast synapses.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akagi H., Hirai K., Hishinuma F. Cloning of a glycine receptor subtype expressed in rat brain and spinal cord during a specific period of neuronal development. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):160–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80383-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akagi H., Miledi R. Heterogeneity of glycine receptors and their messenger RNAs in rat brain and spinal cord. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):270–273. doi: 10.1126/science.2845580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschuler R. A., Betz H., Parakkal M. H., Reeks K. A., Wenthold R. J. Identification of glycinergic synapses in the cochlear nucleus through immunocytochemical localization of the postsynaptic receptor. Brain Res. 1986 Mar 26;369(1-2):316–320. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90542-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballivet M., Nef P., Couturier S., Rungger D., Bader C. R., Bertrand D., Cooper E. Electrophysiology of a chick neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes after cDNA injection. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):847–852. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., McBurney R. N., Mathers D. A. Convulsant-induced depression of amino acid responses in cultured mouse spinal neurones studied under voltage clamp. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec;80(4):619–629. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10051.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Ransom B. R. Amino acid pharmacology of mammalian central neurones grown in tissue culture. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:331–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. M., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Schmitt B., Betz H. The glycine receptor deficiency of the mutant mouse spastic: evidence for normal glycine receptor structure and localization. J Neurosci. 1986 May;6(5):1358–1364. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-05-01358.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. M., Schmieden V., Tarroni P., Strasser U., Betz H. Isoform-selective deficit of glycine receptors in the mouse mutant spastic. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):283–289. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90295-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz H. Ligand-gated ion channels in the brain: the amino acid receptor superfamily. Neuron. 1990 Oct;5(4):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90077-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz H. Structure and function of inhibitory glycine receptors. Q Rev Biophys. 1992 Nov;25(4):381–394. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann J., Hamill O. P., Sakmann B. Mechanism of anion permeation through channels gated by glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid in mouse cultured spinal neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:243–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann J., Rundström N., Betz H., Langosch D. Residues within transmembrane segment M2 determine chloride conductance of glycine receptor homo- and hetero-oligomers. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3729–3737. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Thiéry J., Tung Y., Kittel C. On the cooperativity of biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):335–341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber D. S., Funch P. G., Korn H. Evidence that receptors mediating central synaptic potentials extend beyond the postsynaptic density. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3504–3508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D., Pfeiffer F., Simler R., Betz H. Purification and characterization of the glycine receptor of pig spinal cord. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 12;24(4):990–994. doi: 10.1021/bi00325a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Pribilla I., Prior P., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Taleb O., Betz H. Cloning and expression of the 58 kd beta subunit of the inhibitory glycine receptor. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):963–970. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90149-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Rienitz A., Schmitt B., Methfessel C., Zensen M., Beyreuther K., Gundelfinger E. D., Betz H. The strychnine-binding subunit of the glycine receptor shows homology with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):215–220. doi: 10.1038/328215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Schmieden V., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H., Siddique T., Mohandas T. K., Becker C. M., Betz H. Alpha subunit variants of the human glycine receptor: primary structures, functional expression and chromosomal localization of the corresponding genes. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):771–776. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemare E., Honoré E., Pradier L., Lesage F., Schweitz H., Attali B., Barhanin J., Lazdunski M. Effects of the level of mRNA expression on biophysical properties, sensitivity to neurotoxins, and regulation of the brain delayed-rectifier K+ channels Kv1.2. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 15;31(49):12463–12468. doi: 10.1021/bi00164a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. V. The Combinations of Haemoglobin with Oxygen and with Carbon Monoxide. I. Biochem J. 1913 Oct;7(5):471–480. doi: 10.1042/bj0070471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch W., Betz H., Becker C. M. Primary cultures of mouse spinal cord express the neonatal isoform of the inhibitory glycine receptor. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90258-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré E., Attali B., Romey G., Lesage F., Barhanin J., Lazdunski M. Different types of K+ channel current are generated by different levels of a single mRNA. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2465–2471. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05311.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hymel L., Striessnig J., Glossmann H., Schindler H. Purified skeletal muscle 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor forms phosphorylation-dependent oligomeric calcium channels in planar bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4290–4294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B. Perfection of a synaptic receptor: kinetics and energetics of the acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch J., Langosch D., Prior P., Littauer U. Z., Schmitt B., Betz H. The 93-kDa glycine receptor-associated protein binds to tubulin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22242–22245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch J., Wolters I., Triller A., Betz H. Gephyrin antisense oligonucleotides prevent glycine receptor clustering in spinal neurons. Nature. 1993 Dec 23;366(6457):745–748. doi: 10.1038/366745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhse J., Kuryatov A., Maulet Y., Malosio M. L., Schmieden V., Betz H. Alternative splicing generates two isoforms of the alpha 2 subunit of the inhibitory glycine receptor. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 20;283(1):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80557-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhse J., Laube B., Magalei D., Betz H. Assembly of the inhibitory glycine receptor: identification of amino acid sequence motifs governing subunit stoichiometry. Neuron. 1993 Dec;11(6):1049–1056. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90218-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhse J., Schmieden V., Betz H. A single amino acid exchange alters the pharmacology of neonatal rat glycine receptor subunit. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):867–873. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90346-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhse J., Schmieden V., Betz H. Identification and functional expression of a novel ligand binding subunit of the inhibitory glycine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22317–22320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langosch D., Thomas L., Betz H. Conserved quaternary structure of ligand-gated ion channels: the postsynaptic glycine receptor is a pentamer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7394–7398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Methfessel C., Witzemann V., Takahashi T., Mishina M., Numa S., Sakmann B. Patch clamp measurements on Xenopus laevis oocytes: currents through endogenous channels and implanted acetylcholine receptor and sodium channels. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Dec;407(6):577–588. doi: 10.1007/BF00582635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer F., Graham D., Betz H. Purification by affinity chromatography of the glycine receptor of rat spinal cord. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9389–9393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribilla I., Takagi T., Langosch D., Bormann J., Betz H. The atypical M2 segment of the beta subunit confers picrotoxinin resistance to inhibitory glycine receptor channels. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4305–4311. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05529.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior P., Schmitt B., Grenningloh G., Pribilla I., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Maulet Y., Werner P., Langosch D., Kirsch J. Primary structure and alternative splice variants of gephyrin, a putative glycine receptor-tubulin linker protein. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1161–1170. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Spillecke F., Neumann E. Different channel properties of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor monomers and dimers reconstituted in planar membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6222–6226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieden V., Grenningloh G., Schofield P. R., Betz H. Functional expression in Xenopus oocytes of the strychnine binding 48 kd subunit of the glycine receptor. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):695–700. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03428.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieden V., Kuhse J., Betz H. Agonist pharmacology of neonatal and adult glycine receptor alpha subunits: identification of amino acid residues involved in taurine activation. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2025–2032. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05259.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt B., Knaus P., Becker C. M., Betz H. The Mr 93,000 polypeptide of the postsynaptic glycine receptor complex is a peripheral membrane protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Feb 10;26(3):805–811. doi: 10.1021/bi00377a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song Y. M., Huang L. Y. Modulation of glycine receptor chloride channels by cAMP-dependent protein kinase in spinal trigeminal neurons. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):242–245. doi: 10.1038/348242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer H., Becker C. M., Pritchett D. B., Schofield P. R., Grenningloh G., Kettenmann H., Betz H., Seeburg P. H. Functional chloride channels by mammalian cell expression of rat glycine receptor subunit. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1491–1497. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi T., Pribilla I., Kirsch J., Betz H. Coexpression of the receptor-associated protein gephyrin changes the ligand binding affinities of alpha 2 glycine receptors. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 1;303(2-3):178–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80513-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triller A., Cluzeaud F., Pfeiffer F., Betz H., Korn H. Distribution of glycine receptors at central synapses: an immunoelectron microscopy study. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):683–688. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triller A., Seitanidou T., Franksson O., Korn H. Size and shape of glycine receptor clusters in a central neuron exhibit a somato-dendritic gradient. New Biol. 1990 Jul;2(7):637–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voellmy R., Rungger D. Transcription of a Drosophila heat shock gene is heat-induced in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1776–1780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeramian E., Trautmann A., Claverie P. Acetylcholine receptors are not functionally independent. Biophys J. 1986 Aug;50(2):253–263. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83459-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Strychnine binding associated with glycine receptors of the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2832–2836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



