Abstract
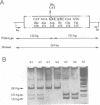
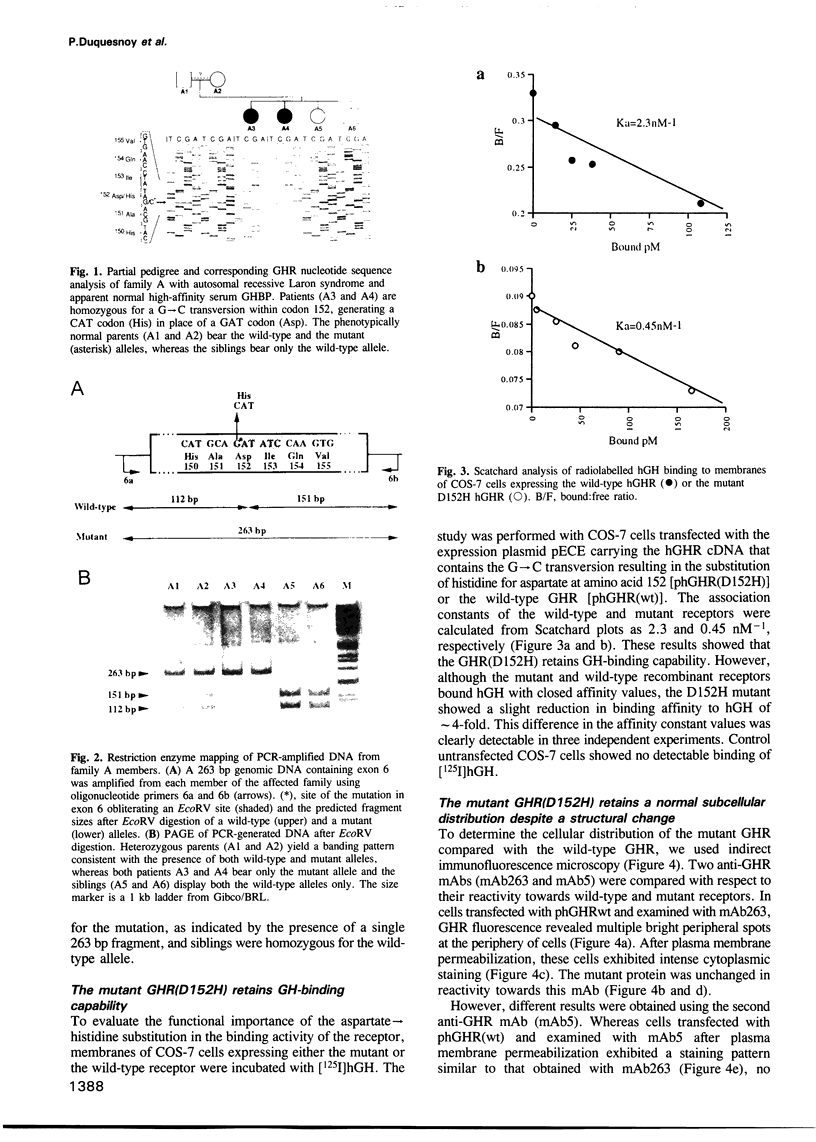
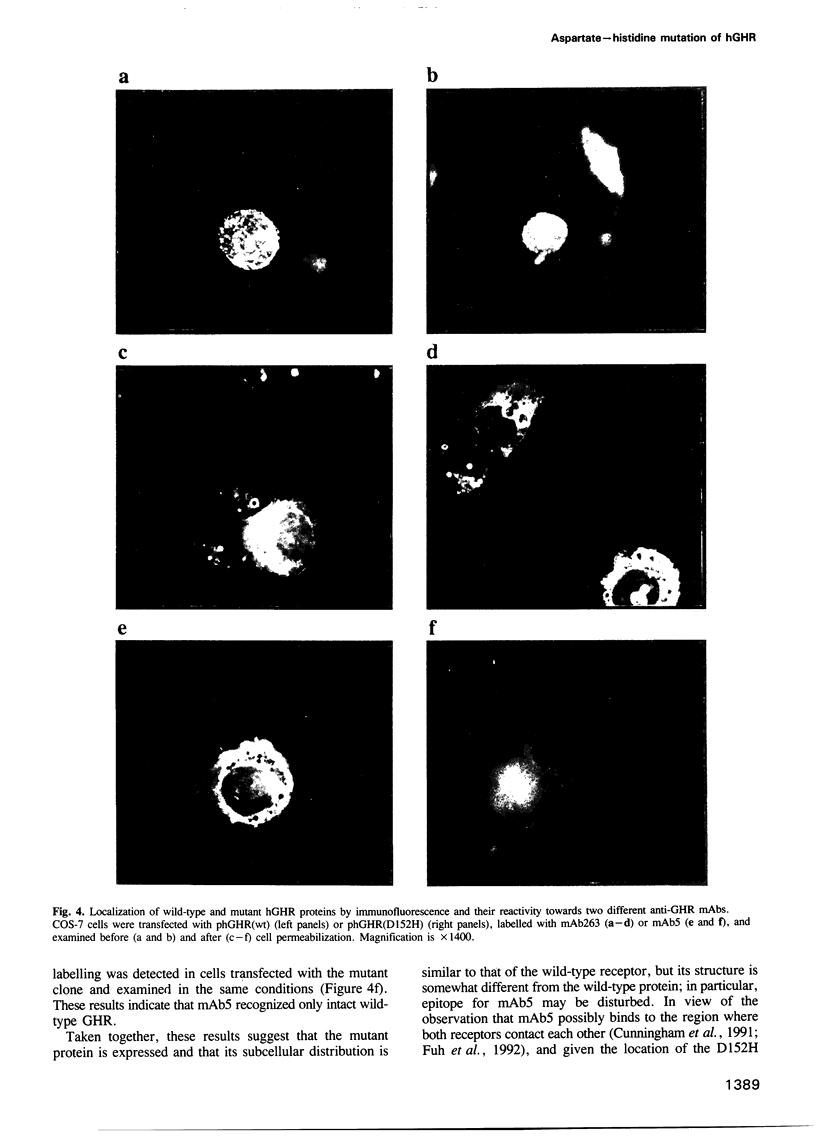
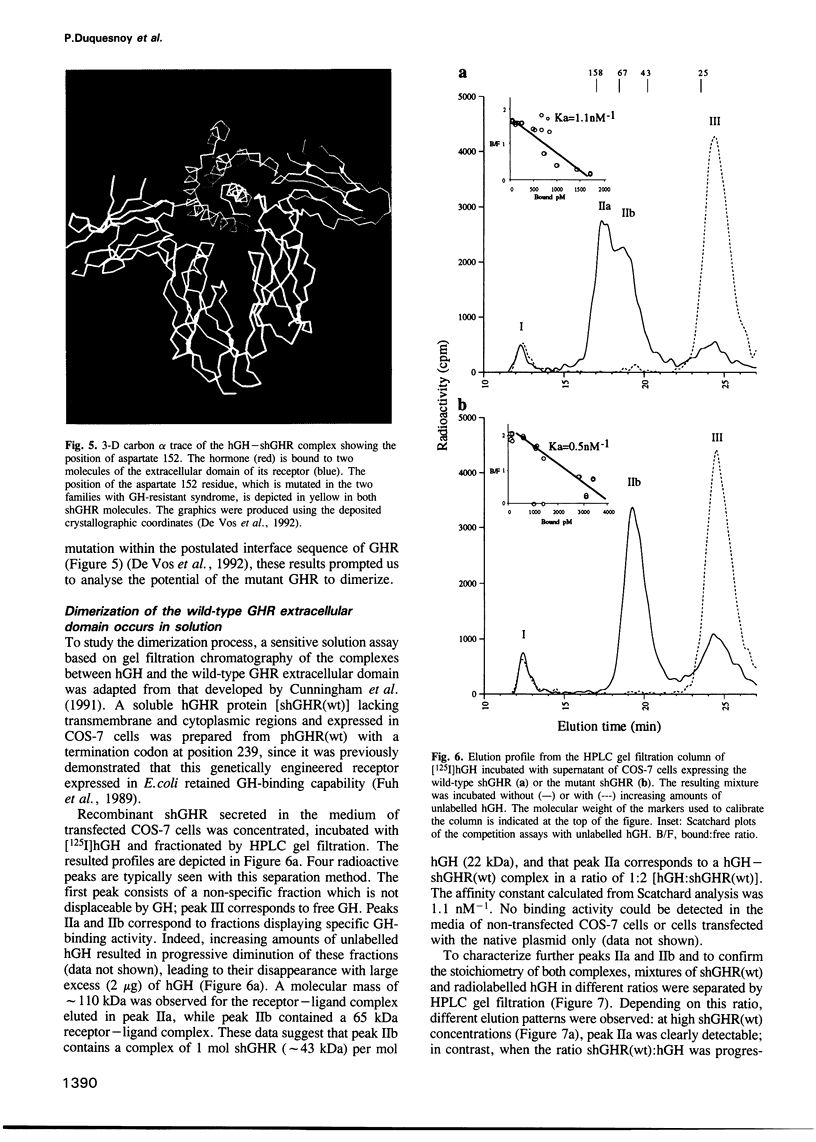
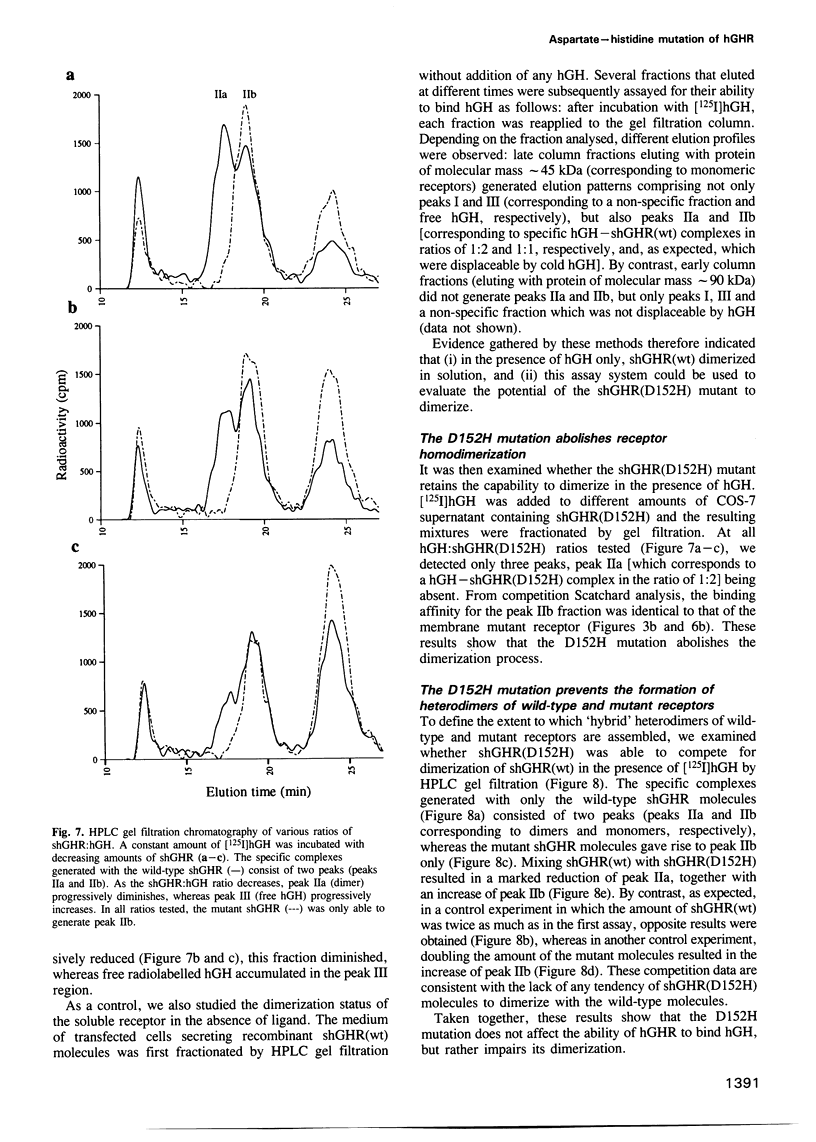
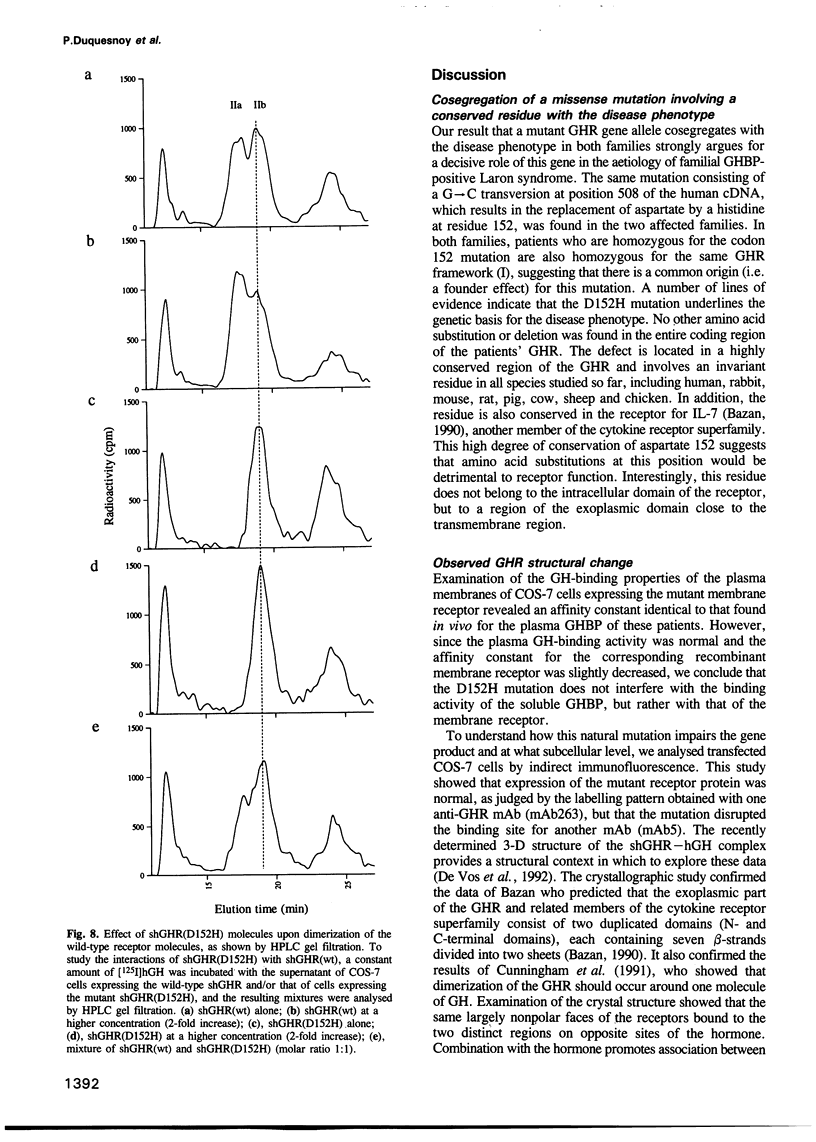
Growth hormone (GH) elicits a variety of biological activities mainly mediated by the GH receptor (GHR), a transmembrane protein that, based on in vitro studies, seemed to function as a homodimer. To test this hypothesis directly, we investigated patients displaying the classic features of Laron syndrome (familial GH resistance characterized by severe dwarfism and metabolic dysfunction), except for the presence of normal binding activity of the plasma GH-binding protein, a molecule that derives from the exoplasmic-coding domain of the GHR gene. In two unrelated families, the same GHR mutation was identified, resulting in the substitution of a highly conserved aspartate residue by histidine at position 152 (D152H) of the exoplasmic domain, within the postulated interface sequence involved in homodimerization. The recombinant mutated receptor protein was correctly expressed at the plasma membrane. It displayed subnormal GH-binding activity, a finding in agreement with the X-ray crystal structure data inferring this aspartate residue outside the GH-binding domain. However, mAb-based studies suggested the critical role of aspartate 152 in the proper folding of the interface area. We show that a recombinant soluble form of the mutant receptor is unable to dimerize, the D152H substitution also preventing the formation of heterodimers of wild-type and mutant molecules. These results provide in vivo evidence that monomeric receptors are inactive and that receptor dimerization is involved in the primary signalling of the GH-associated growth-promoting and metabolic actions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams T. E., Baker L., Fiddes R. J., Brandon M. R. The sheep growth hormone receptor: molecular cloning and ontogeny of mRNA expression in the liver. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Oct 22;73(2-3):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90126-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre A., Donnadieu M., Job J. C., Chaussain J. L. Nanisme de type Laron: hétérogénéité de l'anomalie biochimique chez trois enfants et leurs parents. C R Acad Sci III. 1990;311(9):315–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amselem S., Duquesnoy P., Attree O., Novelli G., Bousnina S., Postel-Vinay M. C., Goossens M. Laron dwarfism and mutations of the growth hormone-receptor gene. N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 12;321(15):989–995. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910123211501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amselem S., Duquesnoy P., Duriez B., Dastot F., Sobrier M. L., Valleix S., Goossens M. Spectrum of growth hormone receptor mutations and associated haplotypes in Laron syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Apr;2(4):355–359. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.4.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amselem S., Sobrier M. L., Duquesnoy P., Rappaport R., Postel-Vinay M. C., Gourmelen M., Dallapiccola B., Goossens M. Recurrent nonsense mutations in the growth hormone receptor from patients with Laron dwarfism. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):1098–1102. doi: 10.1172/JCI115071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann G., Shaw M. A., Winter R. J. Absence of the plasma growth hormone-binding protein in Laron-type dwarfism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Oct;65(4):814–816. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-4-814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach W. R., Horner D. L., Logan J. S. The growth hormone-binding protein in rat serum is an alternatively spliced form of the rat growth hormone receptor. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1199–1205. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Structural design and molecular evolution of a cytokine receptor superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6934–6938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg M. A., Argente J., Chernausek S., Gracia R., Guevara-Aguirre J., Hopp M., Pérez-Jurado L., Rosenbloom A., Toledo S. P., Francke U. Diverse growth hormone receptor gene mutations in Laron syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 May;52(5):998–1005. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg M. A., Guevara-Aguirre J., Rosenbloom A. L., Rosenfeld R. G., Francke U. Mutation creating a new splice site in the growth hormone receptor genes of 37 Ecuadorean patients with Laron syndrome. Hum Mutat. 1992;1(1):24–32. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380010105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan C. R., Maheshwari H. G., Norman M. R., Morrell D. J., Preece M. A. Laron-type dwarfism with apparently normal high affinity serum growth hormone-binding protein. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1991 Aug;35(2):179–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1991.tb03518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnside J., Liou S. S., Cogburn L. A. Molecular cloning of the chicken growth hormone receptor complementary deoxyribonucleic acid: mutation of the gene in sex-linked dwarf chickens. Endocrinology. 1991 Jun;128(6):3183–3192. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-6-3183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cioffi J. A., Wang X., Kopchick J. J. Porcine growth hormone receptor cDNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6451–6451. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Jhurani P., Ng P., Wells J. A. Receptor and antibody epitopes in human growth hormone identified by homolog-scanning mutagenesis. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1330–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.2466339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Ultsch M., De Vos A. M., Mulkerrin M. G., Clauser K. R., Wells J. A. Dimerization of the extracellular domain of the human growth hormone receptor by a single hormone molecule. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):821–825. doi: 10.1126/science.1948064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Wells J. A. High-resolution epitope mapping of hGH-receptor interactions by alanine-scanning mutagenesis. Science. 1989 Jun 2;244(4908):1081–1085. doi: 10.1126/science.2471267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Wells J. A. Rational design of receptor-specific variants of human growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3407–3411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Trivedi B. Absence of serum growth hormone binding protein in patients with growth hormone receptor deficiency (Laron dwarfism). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4636–4640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M. B. Effect of growth hormone on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Endocr Rev. 1987 May;8(2):115–131. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-2-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Aldrich T. H., Valenzuela D. M., Wong V. V., Furth M. E., Squinto S. P., Yancopoulos G. D. The receptor for ciliary neurotrophic factor. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.1648265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duquesnoy P., Sobrier M. L., Amselem S., Goossens M. Defective membrane expression of human growth hormone (GH) receptor causes Laron-type GH insensitivity syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10272–10276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C. K., 3rd, Ghiasuddin S. M., Schepper J. M., Yunger L. M., Kelley K. W. A newly defined property of somatotropin: priming of macrophages for production of superoxide anion. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):769–771. doi: 10.1126/science.2829357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elders M. J., Garland J. T., Daughaday W. A., Fisher D. A., Whitney J. E., Hughes E. R. Laron's dwarfism: studies on the nature of the defect. J Pediatr. 1973 Aug;83(2):253–263. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80485-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuh G., Cunningham B. C., Fukunaga R., Nagata S., Goeddel D. V., Wells J. A. Rational design of potent antagonists to the human growth hormone receptor. Science. 1992 Jun 19;256(5064):1677–1680. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5064.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuh G., Mulkerrin M. G., Bass S., McFarland N., Brochier M., Bourell J. H., Light D. R., Wells J. A. The human growth hormone receptor. Secretion from Escherichia coli and disulfide bonding pattern of the extracellular binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3111–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Thut C. J., VandeBos T., Gimpel S. D., Delaney P. B., King J., Price V., Cosman D., Beckmann M. P. Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor is structurally related to the IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2839–2848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Leung D. W., Meacham L. R., Galgani J. P., Hellmiss R., Keret R., Rotwein P. S., Parks J. S., Laron Z., Wood W. I. Characterization of the human growth hormone receptor gene and demonstration of a partial gene deletion in two patients with Laron-type dwarfism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8083–8087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Friend D., Ziegler S. F., Jerzy R., Falk B. A., Gimpel S., Cosman D., Dower S. K., March C. J., Namen A. E. Cloning of the human and murine interleukin-7 receptors: demonstration of a soluble form and homology to a new receptor superfamily. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):941–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90342-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser S. D., McGrath M. F., Collier R. J., Krivi G. G. Cloning and in vivo expression of bovine growth hormone receptor mRNA. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Sep 10;72(3):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90143-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. P., Friesen H. G. The nature and regulation of the receptors for pituitary growth hormone. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:469–482. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaksson O. G., Edén S., Jansson J. O. Mode of action of pituitary growth hormone on target cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:483–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka-Ikeda E., Fukunaga R., Wood W. I., Goeddel D. V., Nagata S. Signal transduction mediated by growth hormone receptor and its chimeric molecules with the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):123–127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kou K., Lajara R., Rotwein P. Amino acid substitutions in the intracellular part of the growth hormone receptor in a patient with the Laron syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Jan;76(1):54–59. doi: 10.1210/jcem.76.1.8421103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laron Z., Pertzelan A., Karp M., Kowadlo-Silbergeld A., Daughaday W. H. Administration of growth hormone to patients with familial dwarfism with high plasma immunoreactive growth hormone: measurement of sulfation factor, metabolic and linear growth responses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Aug;33(2):332–342. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-2-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laron Z., Pertzelan A., Mannheimer S. Genetic pituitary dwarfism with high serum concentation of growth hormone--a new inborn error of metabolism? Isr J Med Sci. 1966 Mar-Apr;2(2):152–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Spencer S. A., Cachianes G., Hammonds R. G., Collins C., Henzel W. J., Barnard R., Waters M. J., Wood W. I. Growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein: purification, cloning and expression. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):537–543. doi: 10.1038/330537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews L. S., Enberg B., Norstedt G. Regulation of rat growth hormone receptor gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9905–9910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage M. O., Blum W. F., Ranke M. B., Postel-Vinay M. C., Cotterill A. M., Hall K., Chatelain P. G., Preece M. A., Rosenfeld R. G. Clinical features and endocrine status in patients with growth hormone insensitivity (Laron syndrome). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Dec;77(6):1465–1471. doi: 10.1210/jcem.77.6.7505286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Kuniyoshi J., Talamantes F. Mouse serum growth hormone (GH) binding protein has GH receptor extracellular and substituted transmembrane domains. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jun;3(6):984–990. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-6-984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watowich S. S., Yoshimura A., Longmore G. D., Hilton D. J., Yoshimura Y., Lodish H. F. Homodimerization and constitutive activation of the erythropoietin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2140–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura A., Longmore G., Lodish H. F. Point mutation in the exoplasmic domain of the erythropoietin receptor resulting in hormone-independent activation and tumorigenicity. Nature. 1990 Dec 13;348(6302):647–649. doi: 10.1038/348647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Ultsch M., Kossiakoff A. A. Human growth hormone and extracellular domain of its receptor: crystal structure of the complex. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):306–312. doi: 10.1126/science.1549776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]