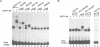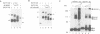Abstract
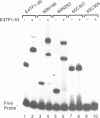
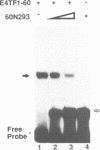
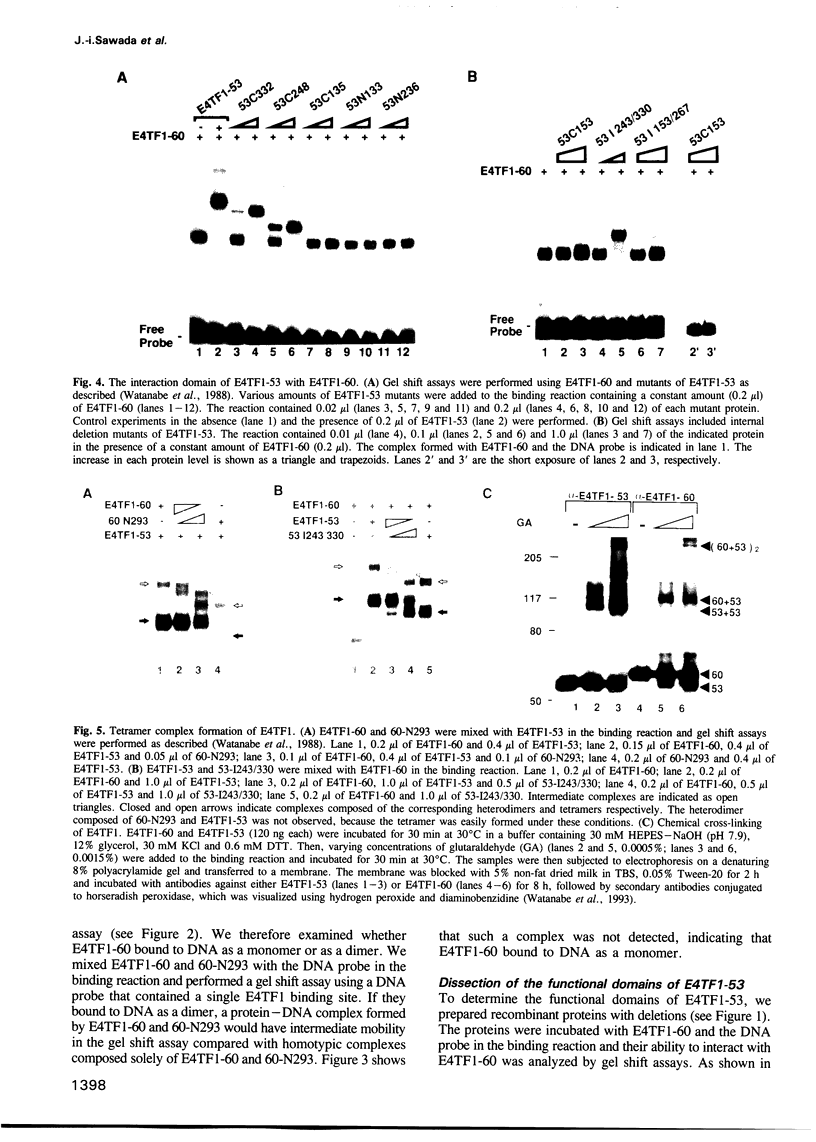
Transcription factor E4TF1 is composed of two types of subunit, an ets-related DNA binding protein, E4TF1-60, and its associated proteins with four tandemly repeated Notch-ankyrin motifs, E4TF1-53 and E4TF1-47. To determine the functional domains, we constructed various mutants of the subunits. E4TF1-60 bound to DNA as a monomer. The ets domain and its N-terminal flanking region were necessary to recognize the specific DNA sequence. The 48 amino acids at the E4TF1-60 C-terminus were required for interaction with the other type of subunit. E4TF1-53 and E4TF1-47 share the N-terminal 332 amino acids but differ at the C-termini. They interacted with E4TF1-60 through the N-terminal flanking region to form a heterodimer. E4TF1-53 dimerized with itself, whereas E4TF1-47 did not. The C-terminal region specific for E4TF1-53 was required for the dimerization. Therefore, heterodimers composed of E4TF1-53 and E4TF1-60 were further dimerized, resulting in the formation of a tetrameric complex, which stimulated transcription in vitro. Heterodimers of E4TF1-47 and E4TF1-60 weakly stimulated transcription in vitro. The results indicated that the tetrameric complex formation of E4TF1 subunits was necessary to activate transcription efficiently in vitro.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolwig G. M., Bruder J. T., Hearing P. Different binding site requirements for binding and activation for the bipartite enhancer factor EF-1A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6555–6564. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Allegretto E. A., Karin M., Green M. R. A family of immunologically related transcription factors that includes multiple forms of ATF and AP-1. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1216–1226. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inomata Y., Kawaguchi H., Hiramoto M., Wada T., Handa H. Direct purification of multiple ATF/E4TF3 polypeptides from HeLa cell crude nuclear extracts using DNA affinity latex particles. Anal Biochem. 1992 Oct;206(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(05)80018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Rashid D., Davis N., Bose H. R., Jr, Verma I. M. Direct association of pp40/I kappa B beta with rel/NF-kappa B transcription factors: role of ankyrin repeats in the inhibition of DNA binding activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4333–4337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. Transcriptional regulation by dimerization: two sides to an incestuous relationship. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):9–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90207-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarco K. L., McKnight S. L. Purification of a set of cellular polypeptides that bind to the purine-rich cis-regulatory element of herpes simplex virus immediate early genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1372–1383. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarco K., Thompson C. C., Byers B. P., Walton E. M., McKnight S. L. Identification of Ets- and notch-related subunits in GA binding protein. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):789–792. doi: 10.1126/science.1876836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Hai T. Y., SivaRaman L., Thimmappaya B., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Green M. R. A cellular protein, activating transcription factor, activates transcription of multiple E1A-inducible adenovirus early promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8355–8359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Bennett V. Analysis of cDNA for human erythrocyte ankyrin indicates a repeated structure with homology to tissue-differentiation and cell-cycle control proteins. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):36–42. doi: 10.1038/344036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. C., Brown T. A., McKnight S. L. Convergence of Ets- and notch-related structural motifs in a heteromeric DNA binding complex. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):762–768. doi: 10.1126/science.1876833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virbasius J. V., Virbasius C. A., Scarpulla R. C. Identity of GABP with NRF-2, a multisubunit activator of cytochrome oxidase expression, reveals a cellular role for an ETS domain activator of viral promoters. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):380–392. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada T., Watanabe H., Usuda Y., Handa H. Different biological activities of the hetero- and homodimers formed by the 47- and 43-kilodalton proteins of transcription factor ATF/E4TF3. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):557–564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.557-564.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Imai T., Sharp P. A., Handa H. Identification of two transcription factors that bind to specific elements in the promoter of the adenovirus early-region 4. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1290–1300. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Sawada J., Yano K., Yamaguchi K., Goto M., Handa H. cDNA cloning of transcription factor E4TF1 subunits with Ets and notch motifs. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1385–1391. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Wada T., Handa H. Transcription factor E4TF1 contains two subunits with different functions. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):841–847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08181.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoganathan T., Bhat N. K., Sells B. H. A positive regulator of the ribosomal protein gene, beta factor, belongs to the ETS oncoprotein family. Biochem J. 1992 Oct 15;287(Pt 2):349–353. doi: 10.1042/bj2870349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]