Abstract
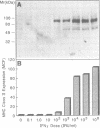
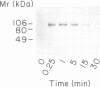
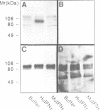
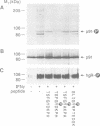
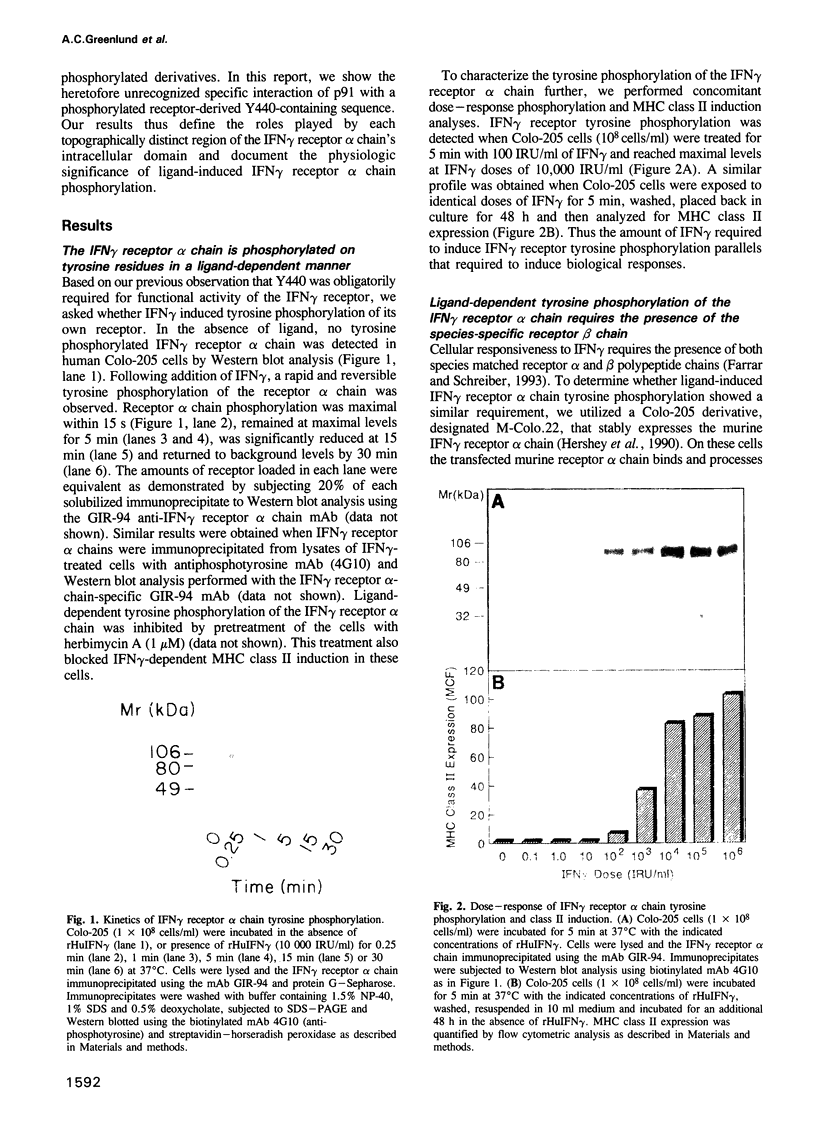
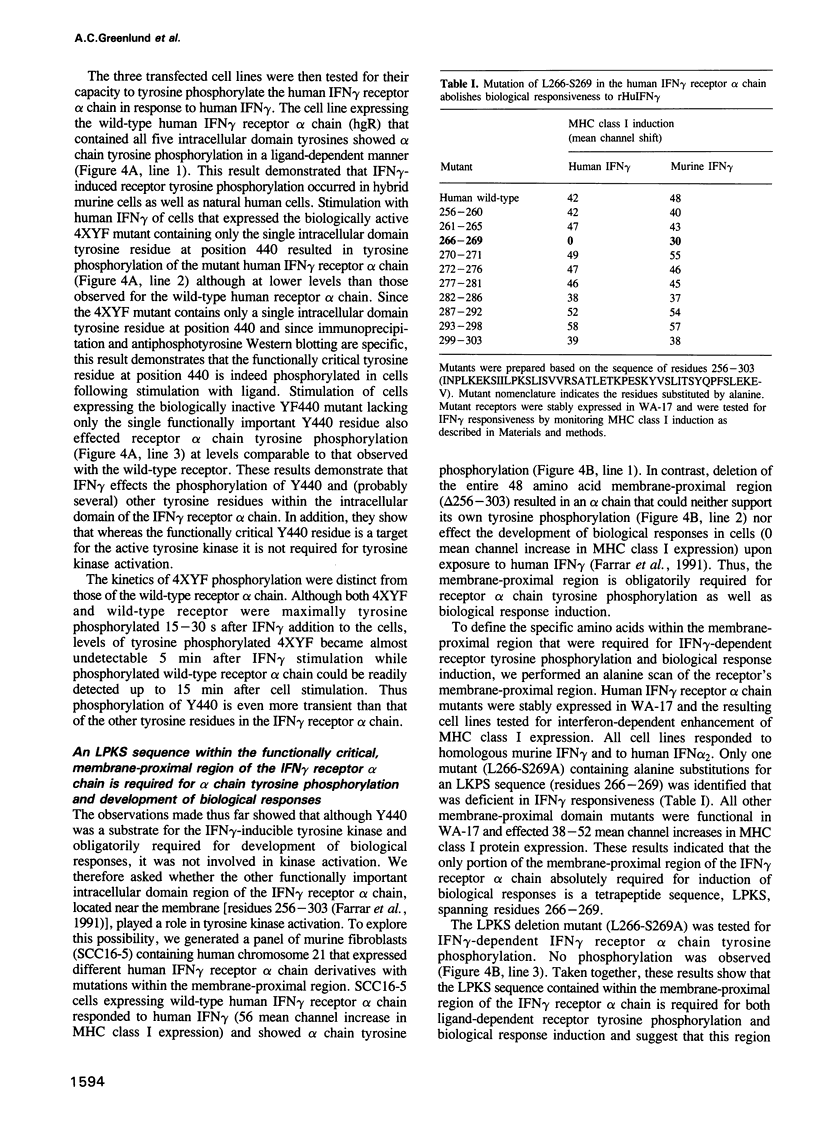
Herein we report that interferon-gamma (IFN gamma) induces the rapid and reversible tyrosine phosphorylation of the IFN gamma receptor. Using a panel of receptor intracellular domain mutants, we show that a membrane-proximal LPKS sequence (residues 266-269) is required for ligand-induced tyrosine kinase activation and/or kinase-receptor association and biological responsiveness, and a functionally critical membrane-distal tyrosine residue (Y440) is a target of the activated enzyme. The biological significance of Y440 phosphorylation was demonstrated by showing that a receptor-derived nonapeptide corresponding to receptor residues 436-444 and containing phosphorylated Y440 bound specifically to p91, blocked p91 phosphorylation and inhibited the generation of an active p91-containing transcription factor complex. In contrast, nonphosphorylated wild-type, phosphorylated mutant, or phosphorylated irrelevant peptides did not. Moreover, the phosphorylated Y440-containing peptide did not interact with a related but distinct latent transcription factor (p113) which is activatible by IFN alpha but not IFN gamma. These results thus document the specific and inducible association of p91 with the phosphorylated IFN gamma receptor and thereby elucidate the mechanism by which ligand couples the IFN gamma receptor to its signal transduction system.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguet M., Dembić Z., Merlin G. Molecular cloning and expression of the human interferon-gamma receptor. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu M., Pace J. L., Pinson D. M., Hayes M. P., Trotta P. P., Russell S. W. Purification and partial characterization of a receptor protein for mouse interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6282–6286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. R., Jung V., Schwartz B., Wang P., Pestka S. Structural analysis of the human interferon gamma receptor: a small segment of the intracellular domain is specifically required for class I major histocompatibility complex antigen induction and antiviral activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11317–11321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Mirkovitch J., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of GAF, an IFN-gamma-regulated DNA-binding factor. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):927–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dighe A. S., Farrar M. A., Schreiber R. D. Inhibition of cellular responsiveness to interferon-gamma (IFN gamma) induced by overexpression of inactive forms of the IFN gamma receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10645–10653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druker B. J., Mamon H. J., Roberts T. M. Oncogenes, growth factors, and signal transduction. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 16;321(20):1383–1391. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911163212007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar M. A., Campbell J. D., Schreiber R. D. Identification of a functionally important sequence in the C terminus of the interferon-gamma receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11706–11710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar M. A., Fernandez-Luna J., Schreiber R. D. Identification of two regions within the cytoplasmic domain of the human interferon-gamma receptor required for function. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19626–19635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar M. A., Schreiber R. D. The molecular cell biology of interferon-gamma and its receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:571–611. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fountoulakis M., Zulauf M., Lustig A., Garotta G. Stoichiometry of interaction between interferon gamma and its receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Sep 15;208(3):781–787. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y. A transcription factor with SH2 and SH3 domains is directly activated by an interferon alpha-induced cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase(s). Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90106-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Schindler C., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr The proteins of ISGF-3, the interferon alpha-induced transcriptional activator, define a gene family involved in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7840–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Zhang J. J. Transcription factor p91 interacts with the epidermal growth factor receptor and mediates activation of the c-fos gene promoter. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1135–1145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90734-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga R., Ishizaka-Ikeda E., Nagata S. Growth and differentiation signals mediated by different regions in the cytoplasmic domain of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1079–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90729-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlund A. C., Schreiber R. D., Goeddel D. V., Pennica D. Interferon-gamma induces receptor dimerization in solution and on cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18103–18110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Mori H., Doi T., Taniguchi T. A restricted cytoplasmic region of IL-2 receptor beta chain is essential for growth signal transduction but not for ligand binding and internalization. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90607-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmi S., Böhni R., Stark G., Di Marco F., Aguet M. A novel member of the interferon receptor family complements functionality of the murine interferon gamma receptor in human cells. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):803–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90355-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey G. K., McCourt D. W., Schreiber R. D. Ligand-induced phosphorylation of the human interferon-gamma receptor. Dependence on the presence of a functionally active receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17868–17875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey G. K., Schreiber R. D. Biosynthetic analysis of the human interferon-gamma receptor. Identification of N-linked glycosylation intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11981–11988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibino Y., Mariano T. M., Kumar C. S., Kozak C. A., Pestka S. Expression and reconstitution of a biologically active mouse interferon gamma receptor in hamster cells. Chromosomal location of an accessory factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6948–6951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., David M., Finbloom D. S., Larner A. C. In vitro activation of the transcription factor gamma interferon activation factor by gamma interferon: evidence for a tyrosine phosphatase/kinase signaling cascade. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1634–1640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., David M., Larner A. C., Finbloom D. S. In vitro activation of a transcription factor by gamma interferon requires a membrane-associated tyrosine kinase and is mimicked by vanadate. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3984–3989. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen J. W., Collard J. G., Tulp A., Cox D., Millington-Ward A., Pearson P. Construction and analysis of an EMBL-3 phage library containing partially digested human chromosome 21-specific DNA inserts (15-20 kb). Cytometry. 1986 Sep;7(5):411–417. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990070504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung V., Rashidbaigi A., Jones C., Tischfield J. A., Shows T. B., Pestka S. Human chromosomes 6 and 21 are required for sensitivity to human interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4151–4155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao C., Merlin G., Ballotti R., Metzler M., Aguet M. Rapid increase of the human IFN-gamma receptor phosphorylation in response to human IFN-gamma and phorbol myristate acetate. Involvement of different serine/threonine kinases. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4257–4264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariano T. M., Kozak C. A., Langer J. A., Pestka S. The mouse immune interferon receptor gene is located on chromosome 10. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5812–5814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura O., Cleveland J. L., Ihle J. N. Inactivation of erythropoietin receptor function by point mutations in a region having homology with other cytokine receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1788–1795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Narazaki M., Hibi M., Yawata H., Yasukawa K., Hamaguchi M., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Critical cytoplasmic region of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130 is conserved in the cytokine receptor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11349–11353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Briscoe J., Laxton C., Guschin D., Ziemiecki A., Silvennoinen O., Harpur A. G., Barbieri G., Witthuhn B. A., Schindler C. The protein tyrosine kinase JAK1 complements defects in interferon-alpha/beta and -gamma signal transduction. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):129–135. doi: 10.1038/366129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse R. N., Feinman R., Shuai K., Darnell J. E., Jr, Ravetch J. V. Interferon gamma-induced transcription of the high-affinity Fc receptor for IgG requires assembly of a complex that includes the 91-kDa subunit of transcription factor ISGF3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4314–4318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Wiegmann K., Scheurich P., Krönke M., Merlin G., Aguet M., Knowles B. B., Ucer U. High affinity human IFN-gamma-binding capacity is encoded by a single receptor gene located in proximity to c-ros on human chromosome region 6q16 to 6q22. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):856–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raziuddin A., Sarkar F. H., Dutkowski R., Shulman L., Ruddle F. H., Gupta S. L. Receptors for human alpha and beta interferon but not for gamma interferon are specified by human chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Fu X. Y., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr Proteins of transcription factor ISGF-3: one gene encodes the 91-and 84-kDa ISGF-3 proteins that are activated by interferon alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7836–7839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Shuai K., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of a latent cytoplasmic transcription factor. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):809–813. doi: 10.1126/science.1496401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan K. C., Calderon J., Schreiber R. D. Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for the human IFN-gamma receptor. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4231–4237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Schindler C., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Activation of transcription by IFN-gamma: tyrosine phosphorylation of a 91-kD DNA binding protein. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1281555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soh J., Donnelly R. J., Kotenko S., Mariano T. M., Cook J. R., Wang N., Emanuel S., Schwartz B., Miki T., Pestka S. Identification and sequence of an accessory factor required for activation of the human interferon gamma receptor. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):793–802. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90354-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watling D., Guschin D., Müller M., Silvennoinen O., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Rogers N. C., Schindler C., Stark G. R., Ihle J. N. Complementation by the protein tyrosine kinase JAK2 of a mutant cell line defective in the interferon-gamma signal transduction pathway. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):166–170. doi: 10.1038/366166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. C., Finbloom D. S. Interferon gamma rapidly induces in human monocytes a DNA-binding factor that recognizes the gamma response region within the promoter of the gene for the high-affinity Fc gamma receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11964–11968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Silvennoinen O., Yi T., Tang B., Miura O., Ihle J. N. JAK2 associates with the erythropoietin receptor and is tyrosine phosphorylated and activated following stimulation with erythropoietin. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90414-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]