Abstract
Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases have been proposed to play a critical role in receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)-mediated signal transduction pathways. Although genetic and biochemical studies of RTK pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila melanogaster and mammals have revealed remarkable similarities, a genetic requirement for MAP kinases in RTK signaling has not been established. During retinal development in Drosophila, the sevenless (Sev) RTK is required for development of the R7 photoreceptor cell. Components of the signal transduction pathway activated by Sev in the R7 precursor include proteins encoded by the gap1, drk, Sos, ras1 and raf loci. In this report we present evidence that a Drosophila MAP kinase, ERK-A, is encoded by the rolled locus and is required downstream of raf in the Sev signal transduction pathway.
Full text
PDF
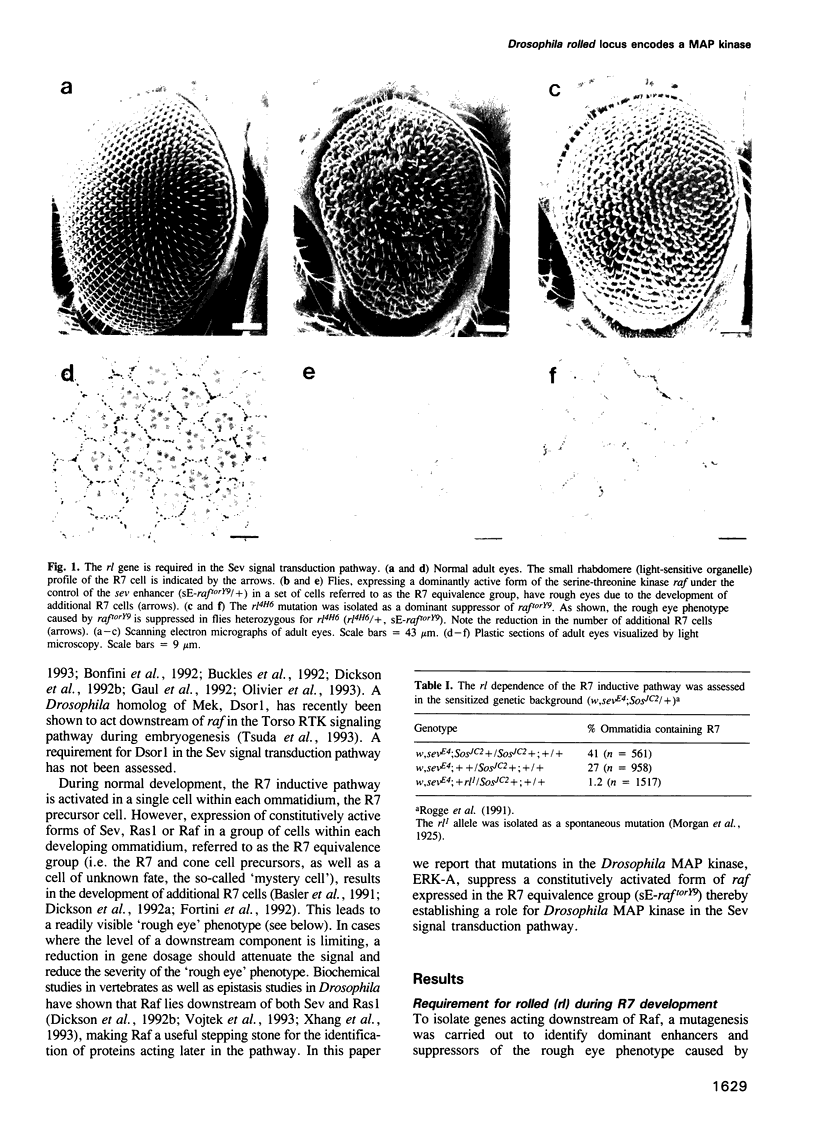

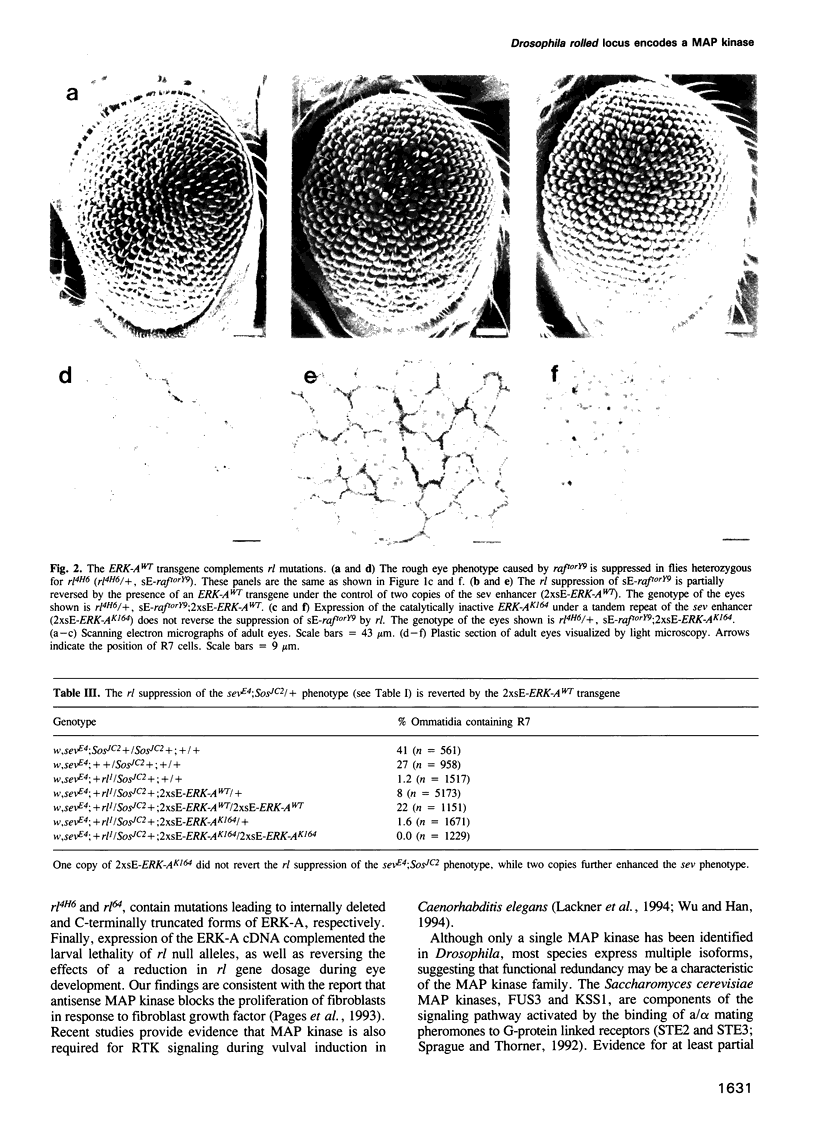

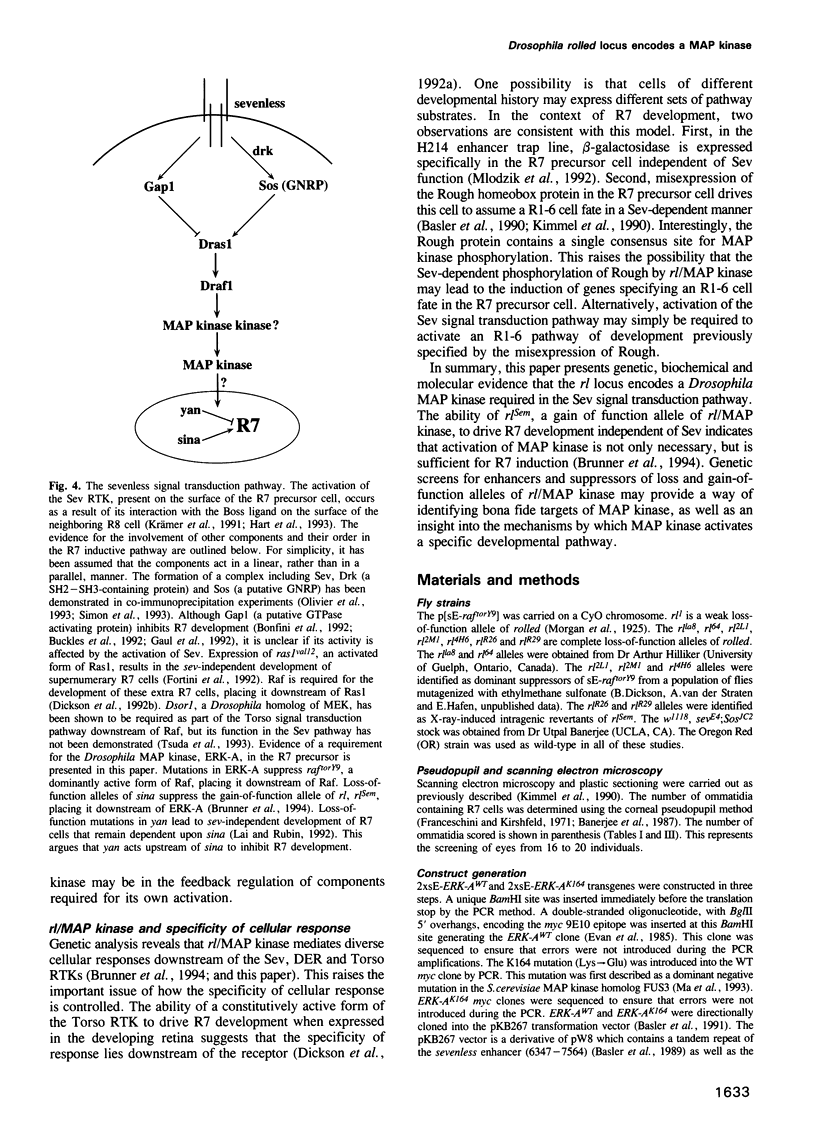


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Krebs E. G. The mitogen-activated protein kinase activator. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;4(6):992–999. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90131-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Li P., Marsden L. A., Williams N., Roberts T. M., Sturgill T. W. Raf-1 is a potential substrate for mitogen-activated protein kinase in vivo. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 15;277(Pt 2):573–576. doi: 10.1042/bj2770573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee U., Renfranz P. J., Pollock J. A., Benzer S. Molecular characterization and expression of sevenless, a gene involved in neuronal pattern formation in the Drosophila eye. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90569-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Christen B., Hafen E. Ligand-independent activation of the sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase changes the fate of cells in the developing Drosophila eye. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1069–1081. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90262-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Siegrist P., Hafen E. The spatial and temporal expression pattern of sevenless is exclusively controlled by gene-internal elements. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2381–2386. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08367.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Yen D., Tomlinson A., Hafen E. Reprogramming cell fate in the developing Drosophila retina: transformation of R7 cells by ectopic expression of rough. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):728–739. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs W. H., 3rd, Zipursky S. L. Primary structure, expression, and signal-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of a Drosophila homolog of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6295–6299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5889–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfini L., Karlovich C. A., Dasgupta C., Banerjee U. The Son of sevenless gene product: a putative activator of Ras. Science. 1992 Jan 31;255(5044):603–606. doi: 10.1126/science.1736363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckles G. R., Smith Z. D., Katz F. N. mip causes hyperinnervation of a retinotopic map in Drosophila by excessive recruitment of R7 photoreceptor cells. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1015–1029. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90124-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Rubin G. M. seven in absentia, a gene required for specification of R7 cell fate in the Drosophila eye. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):561–577. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90452-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Sarnecki C., Blenis J. Nuclear localization and regulation of erk- and rsk-encoded protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):915–927. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L. Definition of a consensus sequence for peptide substrate recognition by p44mpk, the meiosis-activated myelin basic protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15180–15184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courchesne W. E., Kunisawa R., Thorner J. A putative protein kinase overcomes pheromone-induced arrest of cell cycling in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1107–1119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90509-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Erikson R. L. Extracellular signals and reversible protein phosphorylation: what to Mek of it all. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90411-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Haser W., Haystead T. A., Vincent L. A., Roberts T. M., Sturgill T. W. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase by v-Raf in NIH 3T3 cells and in vitro. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1404–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.1326789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson B., Sprenger F., Hafen E. Prepattern in the developing Drosophila eye revealed by an activated torso--sevenless chimeric receptor. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2327–2339. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson B., Sprenger F., Morrison D., Hafen E. Raf functions downstream of Ras1 in the Sevenless signal transduction pathway. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):600–603. doi: 10.1038/360600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitri P. Cytogenetic analysis of the second chromosome heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1991 Mar;127(3):553–564. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.3.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolph P. J., Ranganathan R., Colley N. J., Hardy R. W., Socolich M., Zuker C. S. Arrestin function in inactivation of G protein-coupled receptor rhodopsin in vivo. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1910–1916. doi: 10.1126/science.8316831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Grisafi P. L., Fink G. R. FUS3 encodes a cdc2+/CDC28-related kinase required for the transition from mitosis into conjugation. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):649–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90668-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortini M. E., Simon M. A., Rubin G. M. Signalling by the sevenless protein tyrosine kinase is mimicked by Ras1 activation. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):559–561. doi: 10.1038/355559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franceschini N., Kirschfeld K. Les phénoménes de pseudopupille dans l'oeil compose de Drosophila. Kybernetik. 1971 Nov;9(5):159–182. doi: 10.1007/BF02215177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaul U., Mardon G., Rubin G. M. A putative Ras GTPase activating protein acts as a negative regulator of signaling by the Sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1007–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90073-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Sharrocks A. D., Shaw P. E. Phosphorylation of transcription factor p62TCF by MAP kinase stimulates ternary complex formation at c-fos promoter. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):414–417. doi: 10.1038/358414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Identification of substrate recognition determinants for human ERK1 and ERK2 protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22159–22163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Seth A., Raden D. L., Bowman D. S., Fay F. S., Davis R. J. Serum-induced translocation of mitogen-activated protein kinase to the cell surface ruffling membrane and the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):1089–1101. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Basler K., Edstroem J. E., Rubin G. M. Sevenless, a cell-specific homeotic gene of Drosophila, encodes a putative transmembrane receptor with a tyrosine kinase domain. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):55–63. doi: 10.1126/science.2882603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart A. C., Krämer H., Zipursky S. L. Extracellular domain of the boss transmembrane ligand acts as an antagonist of the sev receptor. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):732–736. doi: 10.1038/361732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Marais R., John S., Wynne J., Dalton S., Treisman R. Functional analysis of a growth factor-responsive transcription factor complex. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):395–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90238-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilliker A. J. Genetic analysis of the centromeric heterochromatin of chromosome 2 of Drosophila melanogaster: deficiency mapping of EMS-induced lethal complementation groups. Genetics. 1976 Aug;83(4):765–782. doi: 10.1093/genetics/83.4.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Leevers S. J., Gómez N., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. J. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90361-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel B. E., Heberlein U., Rubin G. M. The homeo domain protein rough is expressed in a subset of cells in the developing Drosophila eye where it can specify photoreceptor cell subtype. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):712–727. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolch W., Heidecker G., Lloyd P., Rapp U. R. Raf-1 protein kinase is required for growth of induced NIH/3T3 cells. Nature. 1991 Jan 31;349(6308):426–428. doi: 10.1038/349426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer H., Cagan R. L., Zipursky S. L. Interaction of bride of sevenless membrane-bound ligand and the sevenless tyrosine-kinase receptor. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):207–212. doi: 10.1038/352207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackner M. R., Kornfeld K., Miller L. M., Horvitz H. R., Kim S. K. A MAP kinase homolog, mpk-1, is involved in ras-mediated induction of vulval cell fates in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(2):160–173. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Z. C., Rubin G. M. Negative control of photoreceptor development in Drosophila by the product of the yan gene, an ETS domain protein. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):609–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90430-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. M., Cobb M. H., Blackshear P. J. Evidence that extracellular signal-regulated kinases are the insulin-activated Raf-1 kinase kinases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1088–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenormand P., Sardet C., Pagès G., L'Allemain G., Brunet A., Pouysségur J. Growth factors induce nuclear translocation of MAP kinases (p42mapk and p44mapk) but not of their activator MAP kinase kinase (p45mapkk) in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):1079–1088. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mlodzik M., Hiromi Y., Goodman C. S., Rubin G. M. The presumptive R7 cell of the developing Drosophila eye receives positional information independent of sevenless, boss and sina. Mech Dev. 1992 Mar;37(1-2):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90013-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodie S. A., Willumsen B. M., Weber M. J., Wolfman A. Complexes of Ras.GTP with Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.8503013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rapp U., Roberts T. M. Signal transduction from membrane to cytoplasm: growth factors and membrane-bound oncogene products increase Raf-1 phosphorylation and associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8855–8859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivier J. P., Raabe T., Henkemeyer M., Dickson B., Mbamalu G., Margolis B., Schlessinger J., Hafen E., Pawson T. A Drosophila SH2-SH3 adaptor protein implicated in coupling the sevenless tyrosine kinase to an activator of Ras guanine nucleotide exchange, Sos. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90170-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagès G., Lenormand P., L'Allemain G., Chambard J. C., Meloche S., Pouysségur J. Mitogen-activated protein kinases p42mapk and p44mapk are required for fibroblast proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8319–8323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. Mitogen-activated protein kinases: versatile transducers for cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jun;17(6):233–238. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Hughes K., Franklin C. C., Kraft A. S., Leevers S. J., Woodgett J. R. Co-purification of mitogen-activated protein kinases with phorbol ester-induced c-Jun kinase activity in U937 leukaemic cells. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):407–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinke R., Zipursky S. L. Cell-cell interaction in the Drosophila retina: the bride of sevenless gene is required in photoreceptor cell R8 for R7 cell development. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogge R. D., Karlovich C. A., Banerjee U. Genetic dissection of a neurodevelopmental pathway: Son of sevenless functions downstream of the sevenless and EGF receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90207-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogge R., Cagan R., Majumdar A., Dulaney T., Banerjee U. Neuronal development in the Drosophila retina: the sextra gene defines an inhibitory component in the developmental pathway of R7 photoreceptor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5271–5275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Gonzalez F. A., Gupta S., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Signal transduction within the nucleus by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24796–24804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Bowtell D. D., Dodson G. S., Laverty T. R., Rubin G. M. Ras1 and a putative guanine nucleotide exchange factor perform crucial steps in signaling by the sevenless protein tyrosine kinase. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):701–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Dodson G. S., Rubin G. M. An SH3-SH2-SH3 protein is required for p21Ras1 activation and binds to sevenless and Sos proteins in vitro. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90169-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., D'Arcangelo G., Halegoua S., Brugge J. S. Ras is essential for nerve growth factor- and phorbol ester-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of MAP kinases. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1031–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90075-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda L., Inoue Y. H., Yoo M. A., Mizuno M., Hata M., Lim Y. M., Adachi-Yamada T., Ryo H., Masamune Y., Nishida Y. A protein kinase similar to MAP kinase activator acts downstream of the raf kinase in Drosophila. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):407–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A. B., Hollenberg S. M., Cooper J. A. Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90307-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. G., Paradis H., Agarwal S., Charest D. L., Pelech S. L., Roberts T. M. Raf-1 and p21v-ras cooperate in the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5772–5776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y., Han M. Suppression of activated Let-60 ras protein defines a role of Caenorhabditis elegans Sur-1 MAP kinase in vulval differentiation. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(2):147–159. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. F., Settleman J., Kyriakis J. M., Takeuchi-Suzuki E., Elledge S. J., Marshall M. S., Bruder J. T., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Normal and oncogenic p21ras proteins bind to the amino-terminal regulatory domain of c-Raf-1. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):308–313. doi: 10.1038/364308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]