Abstract
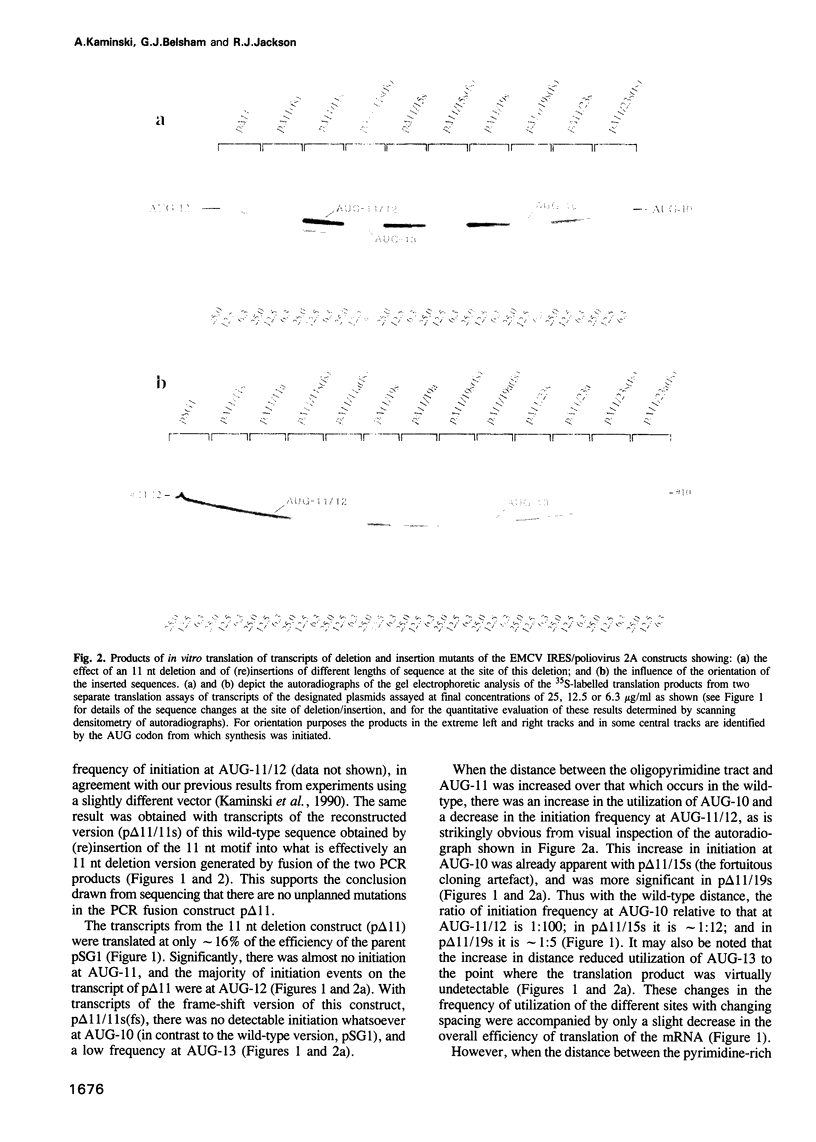
The initiation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA translation is by internal ribosome entry almost exclusively at the 11th AUG codon from the 5'-end, which is the central of the three AUG codons in the sequence..[sequence: see text].., and is located some 25 nt downstream from an oligopyrimidine tract conserved amongst related viruses. As the sequences between the oligopyrimidine tract and AUG-10/11 are poorly conserved and thus possibly serve only as a spacer, the influence of this spacer length on initiation frequency at the three AUG codons was examined in vitro and in vivo. Deletion of 11 residues resulted in initiation almost exclusively at AUG-12 but at significantly reduced overall efficiency. Insertion of eight residues caused a 15-fold increase in initiation frequency at AUG-10 and a decrease at AUG-11. Longer insertions reduced overall efficiency without changing the initiation site preferences. With the wild-type spacing, complete substitution of the oligopyrimidine tract by purines caused a 30-35% decrease in initiation efficiency, and partial substitution only a 10-15% decrease. Thus the internal initiation mechanism selects the initiation site partly on the basis of its distance from upstream elements, of which the oligopyrimidine tract is not the most critical, but for reasons not yet understood a preference for AUG-11 is superimposed on this selection.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agol V. I. The 5'-untranslated region of picornaviral genomes. Adv Virus Res. 1991;40:103–180. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60278-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsham G. J., Brangwyn J. K. A region of the 5' noncoding region of foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA directs efficient internal initiation of protein synthesis within cells: involvement with the role of L protease in translational control. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5389–5395. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5389-5395.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsham G. J. Dual initiation sites of protein synthesis on foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA are selected following internal entry and scanning of ribosomes in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1105–1110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05150.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Digard P., Inglis S. C. Characterization of an efficient coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal: requirement for an RNA pseudoknot. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasso M. C., Jackson R. J. Efficient initiation of mammalian mRNA translation at a CUG codon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6485–6497. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasso M. C., Jackson R. J. On the fidelity of mRNA translation in the nuclease-treated rabbit reticulocyte lysate system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3129–3144. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasso M. C., Milburn S. C., Hershey J. W., Jackson R. J. Selection of the 5'-proximal translation initiation site is influenced by mRNA and eIF-2 concentrations. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 26;187(2):361–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke G. M., Hoffman M. A., Palmenberg A. C. Sequence and structural elements that contribute to efficient encephalomyocarditis virus RNA translation. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1602–1609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1602-1609.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller A. A., Semler B. L. Linker scanning mutagenesis of the internal ribosome entry site of poliovirus RNA. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5075–5086. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5075-5086.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt S. L., Kaminski A., Jackson R. J. The influence of viral coding sequences on the efficiency of internal initiation of translation of cardiovirus RNAs. Virology. 1993 Dec;197(2):801–807. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka N., Kohara M., Hagino-Yamagishi K., Abe S., Komatsu T., Tago K., Arita M., Nomoto A. Construction of less neurovirulent polioviruses by introducing deletions into the 5' noncoding sequence of the genome. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5354–5363. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5354-5363.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka N., Yonekawa H., Nomoto A. Nucleotide sequences important for translation initiation of enterovirus RNA. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4867–4873. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4867-4873.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Howell M. T., Kaminski A. The novel mechanism of initiation of picornavirus RNA translation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90302-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C., Wimmer E. A segment of the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA directs internal entry of ribosomes during in vitro translation. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2636–2643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2636-2643.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Wimmer E. Cap-independent translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: structural elements of the internal ribosomal entry site and involvement of a cellular 57-kD RNA-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1560–1572. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski A., Howell M. T., Jackson R. J. Initiation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA translation: the authentic initiation site is not selected by a scanning mechanism. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3753–3759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. A consideration of alternative models for the initiation of translation in eukaryotes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;27(4-5):385–402. doi: 10.3109/10409239209082567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuge S., Nomoto A. Construction of viable deletion and insertion mutants of the Sabin strain of type 1 poliovirus: function of the 5' noncoding sequence in viral replication. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1478–1487. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1478-1487.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn R., Luz N., Beck E. Functional analysis of the internal translation initiation site of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4625–4631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4625-4631.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerovitch K., Nicholson R., Sonenberg N. In vitro mutational analysis of cis-acting RNA translational elements within the poliovirus type 2 5' untranslated region. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5895–5901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5895-5901.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson R., Pelletier J., Le S. Y., Sonenberg N. Structural and functional analysis of the ribosome landing pad of poliovirus type 2: in vivo translation studies. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5886–5894. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5886-5894.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestova T. V., Hellen C. U., Wimmer E. Translation of poliovirus RNA: role of an essential cis-acting oligopyrimidine element within the 5' nontranslated region and involvement of a cellular 57-kilodalton protein. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6194–6204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6194-6204.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko E. V., Blinov V. M., Chernov B. K., Dmitrieva T. M., Agol V. I. Conservation of the secondary structure elements of the 5'-untranslated region of cardio- and aphthovirus RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5701–5711. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko E. V., Gmyl A. P., Maslova S. V., Svitkin Y. V., Sinyakov A. N., Agol V. I. Prokaryotic-like cis elements in the cap-independent internal initiation of translation on picornavirus RNA. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90211-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard A. E., Calenoff M. A., Simpson S., Jensen K., Lipton H. L. A single base deletion in the 5' noncoding region of Theiler's virus attenuates neurovirulence. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1951–1958. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1951-1958.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöyry T., Kinnunen L., Hovi T. Genetic variation in vivo and proposed functional domains of the 5' noncoding region of poliovirus RNA. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5313–5319. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5313-5319.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V., Newton S. E., Rowlands D. J., Clarke B. E. All foot and mouth disease virus serotypes initiate protein synthesis at two separate AUGs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3305–3315. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svitkin Y. V., Maslova S. V., Agol V. I. The genomes of attenuated and virulent poliovirus strains differ in their in vitro translation efficiencies. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesar M., Harmon S. A., Summers D. F., Ehrenfeld E. Hepatitis A virus polyprotein synthesis initiates from two alternative AUG codons. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90027-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]