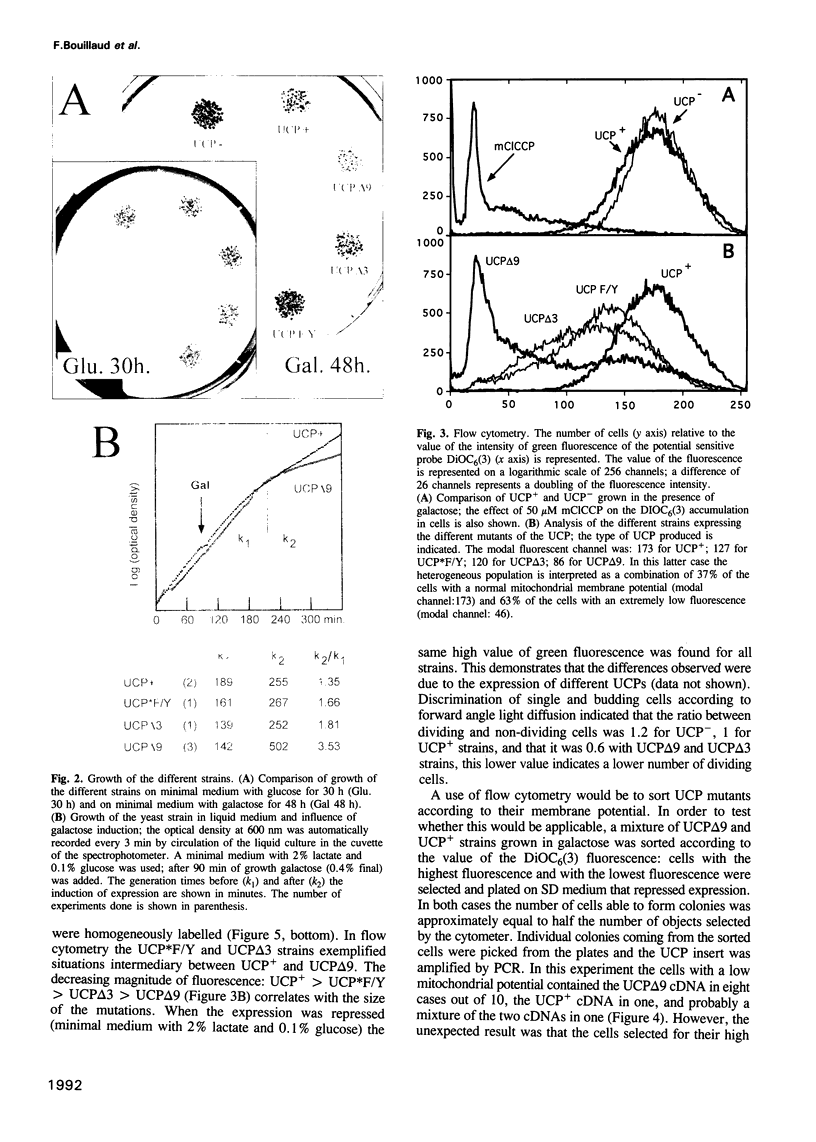
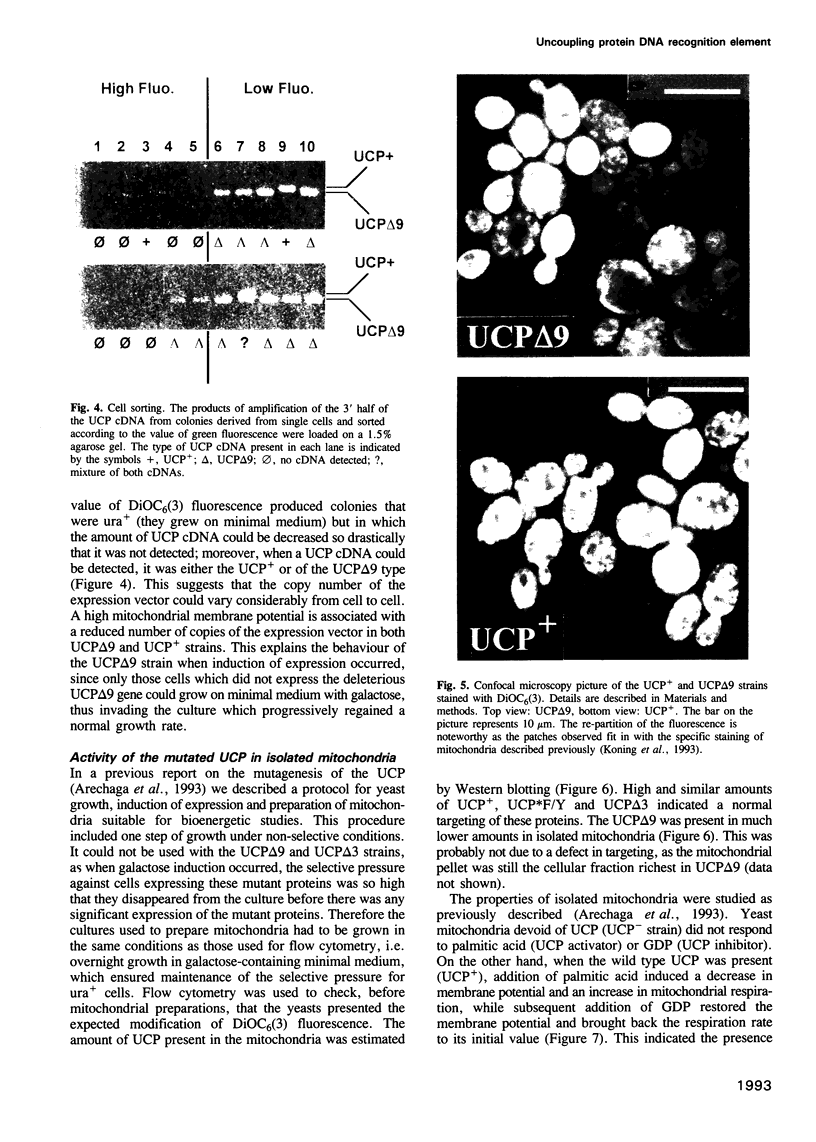
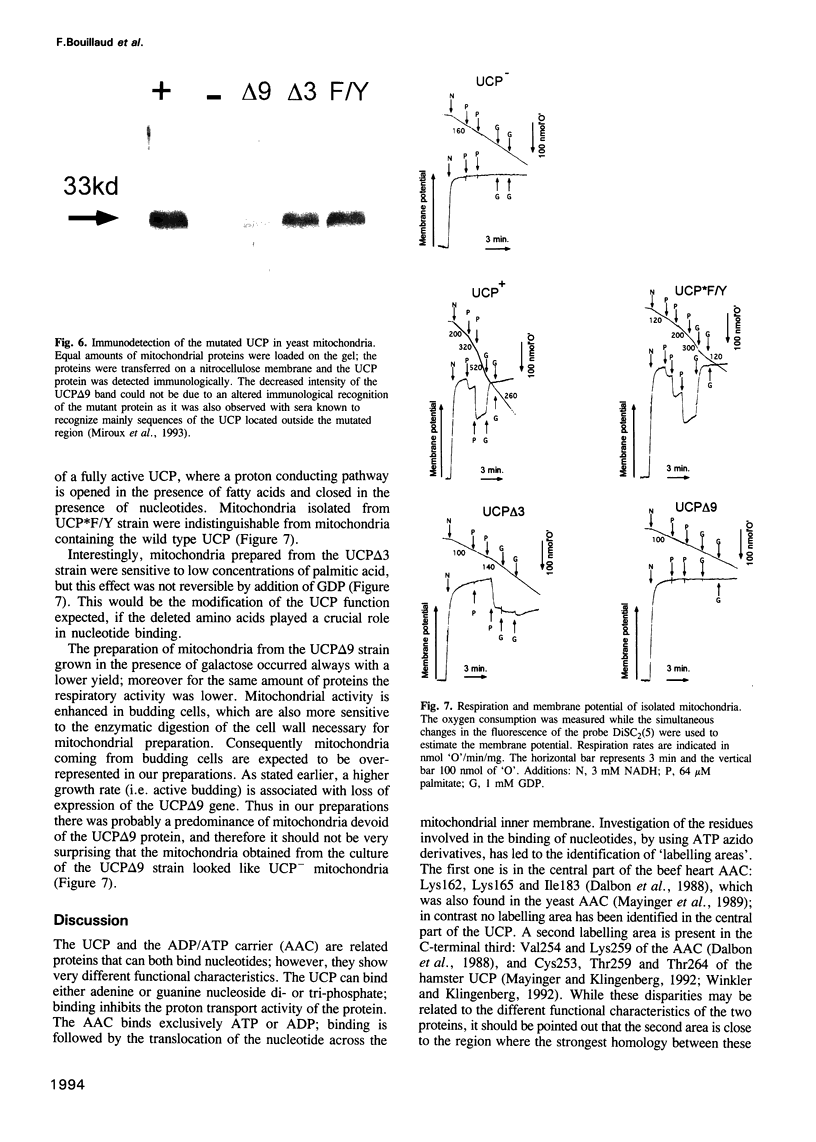
Abstract
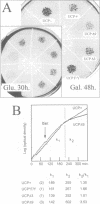
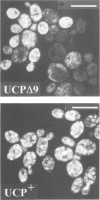
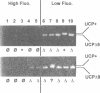
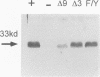
The uncoupling protein (UCP) is uniquely expressed in brown adipose tissue, which is a thermogenic organ of mammals. The UCP uncouples mitochondrial respiration from ATP production by introducing a proton conducting pathway through the mitochondrial inner membrane. The activity of the UCP is regulated: nucleotide binding to the UCP inhibits proton conductance whereas free fatty acids increase it. The similarities between the UCP, the ADP/ATP carrier and the DNA recognition element found in the DNA binding domain of the estrogen receptor suggested that these proteins could share common features in their respective interactions with free nucleotides or DNA, and thus defined a putative 'nucleotide recognition element' in the UCP. This article provides demonstration of the validity of this hypothesis. The putative nucleotide recognition element corresponding to the amino acids 261-269 of the UCP was gradually destroyed, and these mutant proteins were expressed in yeast. Flow cytometry, measuring the mitochondrial membrane potential in vivo, showed increased uncoupling activities of these mutant proteins, and was corroborated with studies with isolated mitochondria. The deletion of the three amino acids Phe267, Lys268 and Gly269, resulted in a mutant where proton leak could be activated by fatty acids but not inhibited by nucleotides.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arechaga I., Raimbault S., Prieto S., Levi-Meyrueis C., Zaragoza P., Miroux B., Ricquier D., Bouillaud F., Rial E. Cysteine residues are not essential for uncoupling protein function. Biochem J. 1993 Dec 15;296(Pt 3):693–700. doi: 10.1042/bj2960693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bathgate B., Freebairn E. M., Greenland A. J., Reid G. A. Functional expression of the rat brown adipose tissue uncoupling protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(3):363–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01479.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. DNA binding specificity of steroid receptors. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1065–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouillaud F., Casteilla L., Ricquier D. A conserved domain in mitochondrial transporters is homologous to a zinc-finger knuckle of nuclear hormone receptors. Mol Biol Evol. 1992 Sep;9(5):970–975. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouillaud F., Weissenbach J., Ricquier D. Complete cDNA-derived amino acid sequence of rat brown fat uncoupling protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1487–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteilla L., Blondel O., Klaus S., Raimbault S., Diolez P., Moreau F., Bouillaud F., Ricquier D. Stable expression of functional mitochondrial uncoupling protein in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5124–5128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullin C., Pompon D. Synthesis of functional mouse cytochromes P-450 P1 and chimeric P-450 P3-1 in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1988 May 30;65(2):203–217. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90457-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbon P., Brandolin G., Boulay F., Hoppe J., Vignais P. V. Mapping of the nucleotide-binding sites in the ADP/ATP carrier of beef heart mitochondria by photolabeling with 2-azido[alpha-32P]adenosine diphosphate. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):5141–5149. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández M., Nicholls D. G., Rial E. The uncoupling protein from brown-adipose-tissue mitochondria. Chymotrypsin-induced structural and functional modifications. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 4;164(3):675–680. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glab N., Petit P. X., Slonimski P. P. Mitochondrial dysfunction in yeast expressing the cytoplasmic male sterility T-urf13 gene from maize: analysis at the population and individual cell level. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Jan;236(2-3):299–308. doi: 10.1007/BF00277126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härd T., Kellenbach E., Boelens R., Maler B. A., Dahlman K., Freedman L. P., Carlstedt-Duke J., Yamamoto K. R., Gustafsson J. A., Kaptein R. Solution structure of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):157–160. doi: 10.1126/science.2115209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jezek P., Garlid K. D. New substrates and competitive inhibitors of the Cl- translocating pathway of the uncoupling protein of brown adipose tissue mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19303–19311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katiyar S. S., Shrago E. Differential interaction of fatty acids and fatty acyl CoA esters with the purified/reconstituted brown adipose tissue mitochondrial uncoupling protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 29;175(3):1104–1111. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91679-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingenberg M. Mechanism and evolution of the uncoupling protein of brown adipose tissue. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):108–112. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90194-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koning A. J., Lum P. Y., Williams J. M., Wright R. DiOC6 staining reveals organelle structure and dynamics in living yeast cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1993;25(2):111–128. doi: 10.1002/cm.970250202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mai M. S., Allison W. S. Inhibition of an oligomycin-sensitive ATPase by cationic dyes, some of which are atypical uncouplers of intact mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Mar;221(2):467–476. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90165-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayinger P., Klingenberg M. Labeling of two different regions of the nucleotide binding site of the uncoupling protein from brown adipose tissue mitochondria with two ATP analogs. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 3;31(43):10536–10543. doi: 10.1021/bi00158a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayinger P., Winkler E., Klingenberg M. The ADP/ATP carrier from yeast (AAC-2) is uniquely suited for the assignment of the binding center by photoaffinity labeling. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 27;244(2):421–426. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80576-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner-White E. J., Coggins J. R., Anton I. A. Evidence for an ancestral core structure in nucleotide-binding proteins with the type A motif. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 5;221(3):751–754. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80170-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miroux B., Casteilla L., Klaus S., Raimbault S., Grandin S., Clément J. M., Ricquier D., Bouillaud F. Antibodies selected from whole antiserum by fusion proteins as tools for the study of the topology of mitochondrial membrane proteins. Evidence that the N-terminal extremity of the sixth alpha-helix of the uncoupling protein is facing the matrix. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13603–13609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miroux B., Frossard V., Raimbault S., Ricquier D., Bouillaud F. The topology of the brown adipose tissue mitochondrial uncoupling protein determined with antibodies against its antigenic sites revealed by a library of fusion proteins. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3739–3745. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06051.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdza-Inglis D. L., Patel H. V., Freeman K. B., Jezek P., Orosz D. E., Garlid K. D. Functional reconstitution of rat uncoupling protein following its high level expression in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11871–11875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G., Lindberg O. Brown-adipose-tissue mitochondria. The influence of albumin and nucleotides on passive ion permeabilities. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Sep 3;37(3):523–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit P. X., O'Connor J. E., Grunwald D., Brown S. C. Analysis of the membrane potential of rat- and mouse-liver mitochondria by flow cytometry and possible applications. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 12;194(2):389–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pompon D. cDNA cloning and functional expression in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae of beta-naphthoflavone-induced rabbit liver P-450 LM4 and LM6. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 1;177(2):285–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rial E., Poustie A., Nicholls D. G. Brown-adipose-tissue mitochondria: the regulation of the 32000-Mr uncoupling protein by fatty acids and purine nucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 1;137(1-2):197–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricquier D., Casteilla L., Bouillaud F. Molecular studies of the uncoupling protein. FASEB J. 1991 Jun;5(9):2237–2242. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.9.1860614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe J. W., Chapman L., Finch J. T., Rhodes D. The crystal structure of the estrogen receptor DNA-binding domain bound to DNA: how receptors discriminate between their response elements. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90390-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe J. W., Rhodes D. Beyond zinc fingers: steroid hormone receptors have a novel structural motif for DNA recognition. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Aug;16(8):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90121-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler E., Klingenberg M. Photoaffinity labeling of the nucleotide-binding site of the uncoupling protein from hamster brown adipose tissue. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jan 15;203(1-2):295–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb19859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]