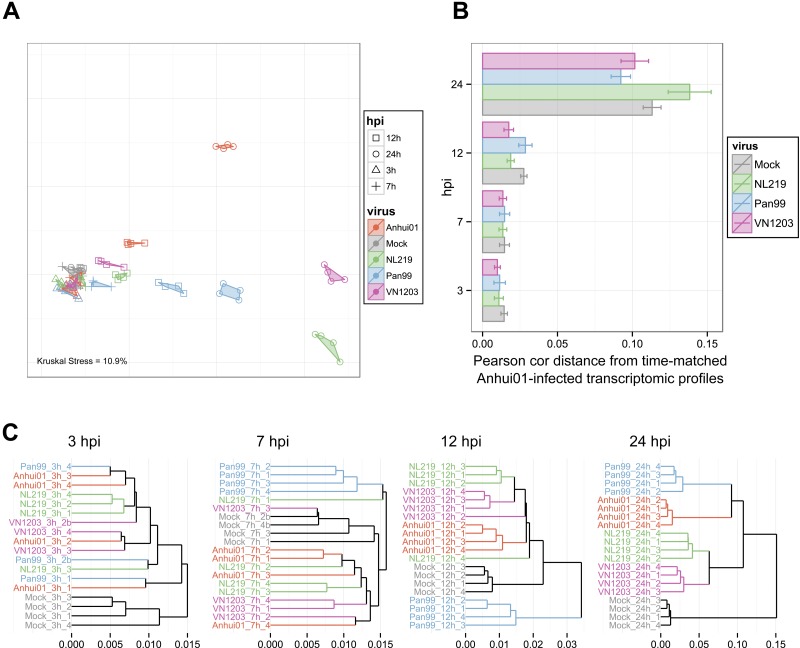
FIG 2 .
The host response to H7N9 infection is specific but closer to that to H3N2 than to the response to other avian-origin IAVs at late time points. (A) Similarities in transcriptomic responses are depicted using nonparametric multidimensional scaling (MDS). Each RNA sample is represented as a single point colored by viral treatment and with a different shape according to the time point. Euclidian distance was calculated using the whole normalized transcriptomic data, such that proximity indicates similarity, whereas distance indicates dissimilarity, of gene expression profiles. Kruskal’s stress quantifies the quality of the representations as a fraction of the information lost during the dimensionality reduction procedure. (B) Average distances between Anhui01-infected samples and time-matched infected or mock samples quantifying whole-transcriptome diversity after infection. Pearson correlation distance (Pearson cor distance) is defined as 1 − Pearson correlation coefficient calculated using normalized transcriptomic data. Error bars indicate SD. Similar results were obtained with Euclidian, Manhattan, or Spearman correlation distance (data not shown). (C) Hierarchical clustering by average linkage of IAV- and mock-infected samples at each time hpi based on their gene expression profiles. Distances were calculated using Pearson correlation distance, but similar clustering was observed with other distance metrics.