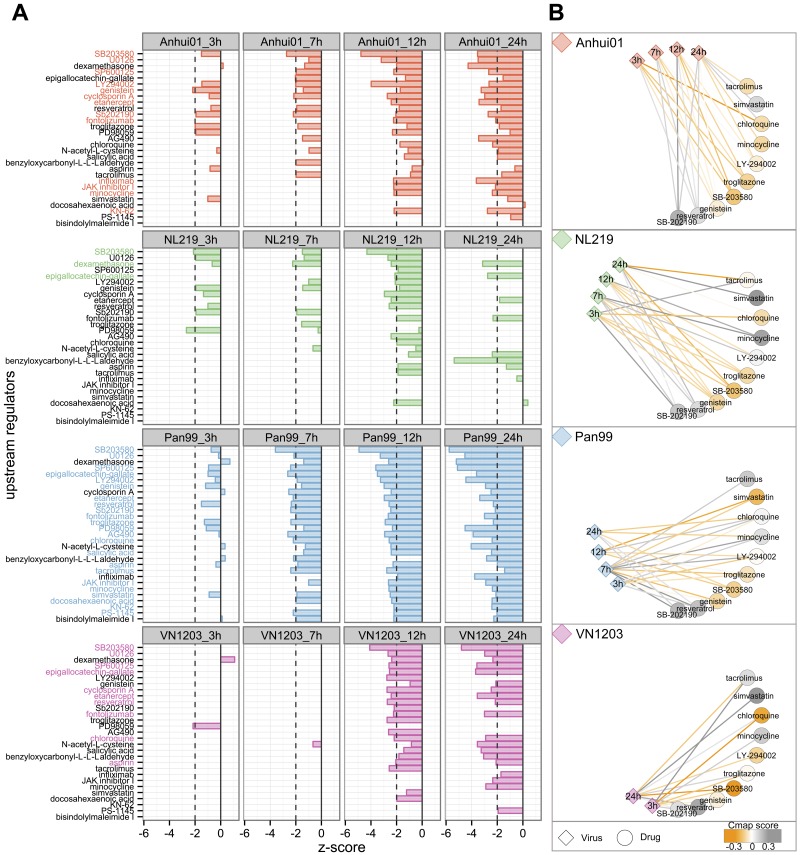
FIG 4 .
Potential antiviral prediction based on transcriptomic profiles after IAV infection. (A) Prediction based on expression of known targets for molecules within the IPA database. A negative z score indicates that the regulator is known to downregulate the same genes that were significantly upregulated after infection and/or to upregulate genes that were downregulated after infection. Dashed lines depict the limit of significance (|z score| > 2). For each virus, z scores were calculated using log2FC expression of DE genes at each time point, and molecules with significant negative z scores for at least 2 time points were selected for this representation (29 drugs). Potential antivirals were defined as drugs with a z score < −2 for at least 2 time points and no positive z score (molecules highlighted in color). Twenty-six regulators were predicted to have an effect opposite to that of infection for at least one IAV. Molecules were ranked from most- to least-negative mean z score across all conditions. (B) The Connectivity Map (Cmap) was used to confirm potential anti-IAV effects of regulators predicted in IPA. Gene expression profiles for 10 molecules (out of the 26) were found in the Cmap database and compared with IAV-infected profiles. Cmap scores go from −1 to 1, with positive scores for drugs inducing changes similar to the viral signature and negative scores for opposite changes. Relationships between viral signatures and drugs were depicted in a network with a circular layout. Edges between virus and drugs are colored based on the Cmap scores comparing drug and viral profiles at each time point. Drugs are colored based on the mean of the Cmap scores for all time points. Drugs colored in orange induced gene expression changes that are the reverse of those for IAVs after cell treatment. Note that the Cmap query requires a list of up- and downregulated genes and was therefore not performed for VN1203 at 7 and 12 hpi, for which there were too few downregulated genes.