Abstract
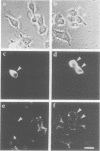
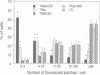
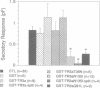
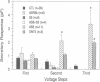
There is accumulating evidence that small GTPases of the rab family regulate intracellular vesicle traffic along biosynthetic and endocytotic pathways in eukaryotic cells. It has been suggested that Rab3a, which is associated with synaptic vesicles in neurons and with secretory granules in adrenal chromaffin cells, might regulate exocytosis. We report here that overexpression in PC12 cells of Rab3a mutant proteins defective in either GTP hydrolysis or in guanine nucleotide binding inhibited exocytosis, as measured by a double indirect immunofluorescence assay. Moreover, injection of the purified mutant proteins into bovine adrenal chromaffin cells also inhibited exocytosis, as monitored by membrane capacitance measurements. Finally, the electrophysiological approach showed that bovine chromaffin cells which were intracellularly injected with antisense oligonucleotides targeted to the rab3a messenger exhibited an increasing potential to respond to repetitive stimulations. In contrast, control cells showed a phenomenon of desensitization. These results provide clear evidence that Rab3a is involved in regulated exocytosis and suggest that Rab3a is a regulatory factor that prevents exocytosis from occurring unless secretion is triggered. Furthermore, it is proposed that Rab3a is involved in adaptive processes such as response habituation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Wegenhorst U., Stecher B., Spicher K., Rosenthal W., Gratz M. Exocytosis from permeabilized bovine adrenal chromaffin cells is differently modulated by guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate and guanosine 5'-[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate. Evidence for the involvement of various guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):321–326. doi: 10.1042/bj2840321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki S., Kikuchi A., Hata Y., Isomura M., Takai Y. Regulation of reversible binding of smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein, to synaptic plasma membranes and vesicles by its specific regulatory protein, GDP dissociation inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13007–13015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly E., McCaffrey M., Touchot N., Zahraoui A., Goud B., Bornens M. Phosphorylation of two small GTP-binding proteins of the Rab family by p34cdc2. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):715–718. doi: 10.1038/350715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., García-Arrarás J. E., Elferink L. A., Peterson K., Fleming A. M., Hazuka C. D., Scheller R. H. The syntaxin family of vesicular transport receptors. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):863–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Collingridge G. L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):31–39. doi: 10.1038/361031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bommert K., Charlton M. P., DeBello W. M., Chin G. J., Betz H., Augustine G. J. Inhibition of neurotransmitter release by C2-domain peptides implicates synaptotagmin in exocytosis. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):163–165. doi: 10.1038/363163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brondyk W. H., McKiernan C. J., Burstein E. S., Macara I. G. Mutants of Rab3A analogous to oncogenic Ras mutants. Sensitivity to Rab3A-GTPase activating protein and Rab3A-guanine nucleotide releasing factor. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9410–9415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucci C., Parton R. G., Mather I. H., Stunnenberg H., Simons K., Hoflack B., Zerial M. The small GTPase rab5 functions as a regulatory factor in the early endocytic pathway. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):715–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90306-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein E. S., Brondyk W. H., Macara I. G. Amino acid residues in the Ras-like GTPase Rab3A that specify sensitivity to factors that regulate the GTP/GDP cycling of Rab3A. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22715–22718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein E. S., Linko-Stentz K., Lu Z. J., Macara I. G. Regulation of the GTPase activity of the ras-like protein p25rab3A. Evidence for a rab3A-specific GAP. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2689–2692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein E. S., Macara I. G. Characterization of a guanine nucleotide-releasing factor and a GTPase-activating protein that are specific for the ras-related protein p25rab3A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1154–1158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darchen F., Zahraoui A., Hammel F., Monteils M. P., Tavitian A., Scherman D. Association of the GTP-binding protein Rab3A with bovine adrenal chromaffin granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5692–5696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBello W. M., Betz H., Augustine G. J. Synaptotagmin and neurotransmitter release. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):947–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink L. A., Peterson M. R., Scheller R. H. A role for synaptotagmin (p65) in regulated exocytosis. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90059-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Mignery G. A., Baumert M., Perin M. S., Hanson T. J., Burger P. M., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. rab3 is a small GTP-binding protein exclusively localized to synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1988–1992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Südhof T. C., Jahn R. A small GTP-binding protein dissociates from synaptic vesicles during exocytosis. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):79–81. doi: 10.1038/349079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. Ras-related proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2116664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess S. D., Doroshenko P. A., Augustine G. J. A functional role for GTP-binding proteins in synaptic vesicle cycling. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1169–1172. doi: 10.1126/science.8438167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikawa H. P., Saisu H., Ishizuka T., Sekine Y., Tsugita A., Odani S., Abe T. A complex of rab3A, SNAP-25, VAMP/synaptobrevin-2 and syntaxins in brain presynaptic terminals. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 13;330(2):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johannes L., Arnheiter H., Meier E. Switch in antiviral specificity of a GTPase upon translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1653–1657. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1653-1657.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Archer B. T., 3rd, Robinson K., Mignery G. A., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. rab3A attachment to the synaptic vesicle membrane mediated by a conserved polyisoprenylated carboxy-terminal sequence. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90078-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karniguian A., Zahraoui A., Tavitian A. Identification of small GTP-binding rab proteins in human platelets: thrombin-induced phosphorylation of rab3B, rab6, and rab8 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7647–7651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law G. J., Northrop A. J., Mason W. T. rab3-peptide stimulates exocytosis from mast cells via a pertussis toxin-sensitive mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 25;333(1-2):56–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80374-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Stahl P. D. Structure-function relationship of the small GTPase rab5. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24475–24480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littleton J. T., Stern M., Schulze K., Perin M., Bellen H. J. Mutational analysis of Drosophila synaptotagmin demonstrates its essential role in Ca(2+)-activated neurotransmitter release. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1125–1134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90733-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lledo P. M., Vernier P., Vincent J. D., Mason W. T., Zorec R. Inhibition of Rab3B expression attenuates Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis in rat anterior pituitary cells. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):540–544. doi: 10.1038/364540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean C. M., Law G. J., Edwardson J. M. Stimulation of exocytotic membrane fusion by modified peptides of the rab3 effector domain: re-evaluation of the role of rab3 in regulated exocytosis. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 1;294(Pt 2):325–328. doi: 10.1042/bj2940325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Kikuchi A., Araki S., Hata Y., Kondo J., Teranishi Y., Takai Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel type of regulatory protein (GDI) for smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4116–4122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Kikuchi A., Kondo J., Hishida T., Teranishi Y., Takai Y. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of a GTP-binding protein family with molecular weights of 25,000 from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11071–11074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. ras GTPase activating protein: signal transmitter and signal terminator. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90976-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden P. N., Koshland D. E., Jr Habituation in the single cell: diminished secretion of norepinephrine with repetitive depolarization of PC12 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):2031–2035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKiernan C. J., Brondyk W. H., Macara I. G. The Rab3A GTPase interacts with multiple factors through the same effector domain. Mutational analysis of cross-linking of Rab3A to a putative target protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24449–24452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Marty A. Discrete changes of cell membrane capacitance observed under conditions of enhanced secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6712–6716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Zucker R. S. Multiple calcium-dependent processes related to secretion in bovine chromaffin cells. Neuron. 1993 Jan;10(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90238-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhauser A. F., Monck J. R., Balch W. E., Fernandez J. M. Exocytotic fusion is activated by Rab3a peptides. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):270–273. doi: 10.1038/360270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padfield P. J., Balch W. E., Jamieson J. D. A synthetic peptide of the rab3a effector domain stimulates amylase release from permeabilized pancreatic acini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1656–1660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R. GTP-binding proteins in intracellular transport. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;2(2):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90161-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popov S. V., Poo M. M. Synaptotagmin: a calcium-sensitive inhibitor of exocytosis? Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1247–1249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90352-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Janeczko R., Esteban M. Isolation and characterization of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):482–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.482-488.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Kikuchi A., Araki S., Hata Y., Isomura M., Kuroda S., Takai Y. Purification and characterization from bovine brain cytosol of a protein that inhibits the dissociation of GDP from and the subsequent binding of GTP to smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2333–2337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senyshyn J., Balch W. E., Holz R. W. Synthetic peptides of the effector-binding domain of rab enhance secretion from digitonin-permeabilized chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 31;309(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80735-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirataki H., Kaibuchi K., Sakoda T., Kishida S., Yamaguchi T., Wada K., Miyazaki M., Takai Y. Rabphilin-3A, a putative target protein for smg p25A/rab3A p25 small GTP-binding protein related to synaptotagmin. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2061–2068. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Zerial M. Rab proteins and the road maps for intracellular transport. Neuron. 1993 Nov;11(5):789–799. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontag Jean-Marie, Aunis Dominique, Bader Marie-France. Two GTP-binding Proteins Control Calcium-dependent Exocytosis in Chromaffin Cells. Eur J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;4(1):98–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1992.tb00112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenmark H., Parton R. G., Steele-Mortimer O., Lütcke A., Gruenberg J., Zerial M. Inhibition of rab5 GTPase activity stimulates membrane fusion in endocytosis. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1287–1296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Whiteheart S. W., Brunner M., Erdjument-Bromage H., Geromanos S., Tempst P., Rothman J. E. SNAP receptors implicated in vesicle targeting and fusion. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):318–324. doi: 10.1038/362318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Baumert M., Perin M. S., Jahn R. A synaptic vesicle membrane protein is conserved from mammals to Drosophila. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1475–1481. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90193-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale E. J., Bourne J. R., Khosravi-Far R., Der C. J., Balch W. E. GTP-binding mutants of rab1 and rab2 are potent inhibitors of vesicular transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):749–761. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touchot N., Chardin P., Tavitian A. Four additional members of the ras gene superfamily isolated by an oligonucleotide strategy: molecular cloning of YPT-related cDNAs from a rat brain library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8210–8214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich O., Stenmark H., Alexandrov K., Huber L. A., Kaibuchi K., Sasaki T., Takai Y., Zerial M. Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor as a general regulator for the membrane association of rab proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18143–18150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volknandt W., Pevsner J., Elferink L. A., Schilling J., Scheller R. H. A synaptic vesicle specific GTP-binding protein from ray electric organ. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Oct;11(3-4):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walworth N. C., Goud B., Kabcenell A. K., Novick P. J. Mutational analysis of SEC4 suggests a cyclical mechanism for the regulation of vesicular traffic. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1685–1693. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. Cell biology. Bridging the gap. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):297–298. doi: 10.1038/362297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahraoui A., Touchot N., Chardin P., Tavitian A. The human Rab genes encode a family of GTP-binding proteins related to yeast YPT1 and SEC4 products involved in secretion. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12394–12401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorec R., Sikdar S. K., Mason W. T. Increased cytosolic calcium stimulates exocytosis in bovine lactotrophs. Direct evidence from changes in membrane capacitance. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Mar;97(3):473–497. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Rüden L., Neher E. A Ca-dependent early step in the release of catecholamines from adrenal chromaffin cells. Science. 1993 Nov 12;262(5136):1061–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.8235626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]