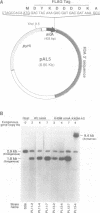
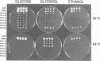
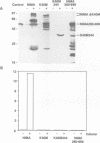
Abstract
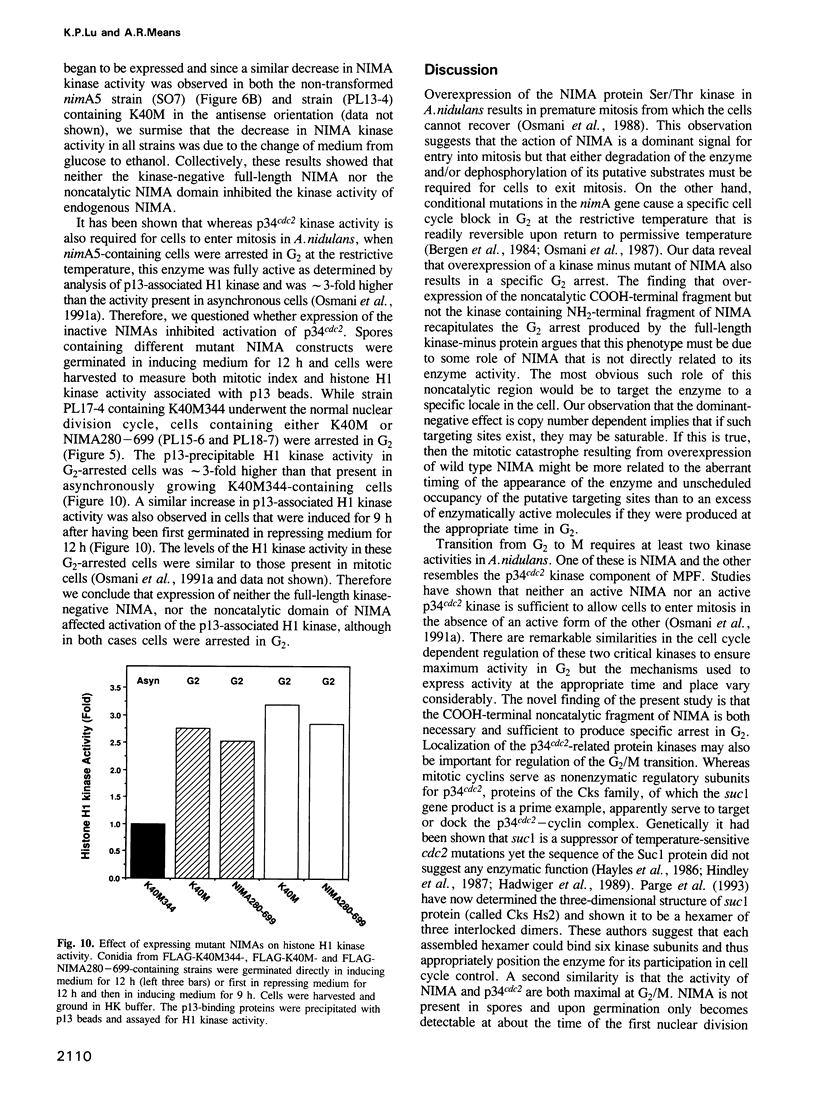
Temperature-sensitive mutation of the nimA gene of Aspergillus nidulans causes a reversible G2 arrest, whereas overexpression of nimA causes premature entry into mitosis from which the cells cannot exit. The nimA gene encodes a Ser/Thr-specific protein kinase (NIMA) which contains an extended COOH-terminal noncatalytic domain. To evaluate the role of this enzyme in nuclear division control, we introduced various mutant nimA cDNAs under the control of the inducible alcohol dehydrogenase gene promoter into a strain of Aspergillus nidulans containing a temperature-sensitive nimA mutation (nimA5). While expression of the wild type NIMA complemented the nimA5 mutation and induced a premature mitotic arrest when overexpressed, expression of a kinase-negative NIMA containing a single amino acid mutation in the putative ATP-binding site could not rescue the nimA5 mutation but resulted in a specific G2 arrest when overexpressed. An identical phenotype was observed with cells expressing only the noncatalytic COOH-terminal domain of NIMA, whereas overexpression of the inactive kinase domain was without effect. The G2 arrest produced by overexpression of the full-length inactive or COOH-terminal NIMA molecules did not prevent activation of the endogenous NIMA or H1 kinase activity precipitable by p13 beads. We suggest that this dominant-negative phenotype results from competitive inhibition of the association of active NIMA with a cellular target(s) and that appropriate targeting is essential for the mitotic function of the NIMA kinase.
Full text
PDF



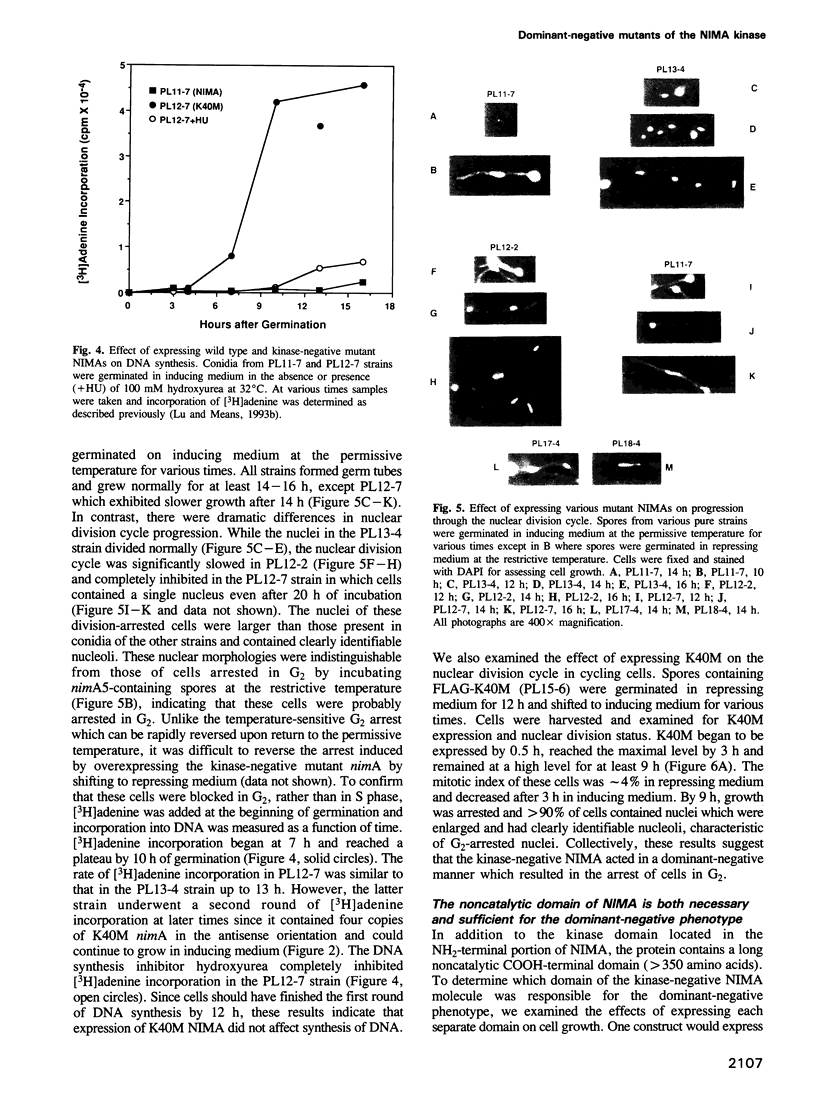



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltensperger K., Kozma L. M., Cherniack A. D., Klarlund J. K., Chawla A., Banerjee U., Czech M. P. Binding of the Ras activator son of sevenless to insulin receptor substrate-1 signaling complexes. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1950–1952. doi: 10.1126/science.8391166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Rotin D., Batzer A., Mandiyan V., Schlessinger J. SH3 domains direct cellular localization of signaling molecules. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach D., Durkacz B., Nurse P. Functionally homologous cell cycle control genes in budding and fission yeast. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):706–709. doi: 10.1038/300706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergen L. G., Upshall A., Morris N. R. S-phase, G2, and nuclear division mutants of Aspergillus nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):114–119. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.114-119.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doonan J. H., MacKintosh C., Osmani S., Cohen P., Bai G., Lee E. Y., Morris N. R. A cDNA encoding rabbit muscle protein phosphatase 1 alpha complements the Aspergillus cell cycle mutation, bimG11. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18889–18894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger J. A., Wittenberg C., Mendenhall M. D., Reed S. I. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae CKS1 gene, a homolog of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe suc1+ gene, encodes a subunit of the Cdc28 protein kinase complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2034–2041. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayles J., Aves S., Nurse P. suc1 is an essential gene involved in both the cell cycle and growth in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3373–3379. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04653.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkemeyer M., West S. R., Gertler F. B., Hoffmann F. M. A novel tyrosine kinase-independent function of Drosophila abl correlates with proper subcellular localization. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):949–960. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90498-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindley J., Phear G., Stein M., Beach D. Sucl+ encodes a predicted 13-kilodalton protein that is essential for cell viability and is directly involved in the division cycle of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):504–511. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard M. J., Cohen P. On target with a new mechanism for the regulation of protein phosphorylation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 May;18(5):172–177. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90109-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein E. J., Daly R. J., Batzer A. G., Li W., Margolis B., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Skolnik E. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Schlessinger J. The SH2 and SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 links receptor tyrosine kinases to ras signaling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90167-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu K. P., Kemp B. E., Means A. R. Identification of substrate specificity determinants for the cell cycle-regulated NIMA protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6603–6607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu K. P., Means A. R. Regulation of the cell cycle by calcium and calmodulin. Endocr Rev. 1993 Feb;14(1):40–58. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-1-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu K. P., Osmani S. A., Means A. R. Properties and regulation of the cell cycle-specific NIMA protein kinase of Aspergillus nidulans. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8769–8776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu K. P., Osmani S. A., Osmani A. H., Means A. R. Essential roles for calcium and calmodulin in G2/M progression in Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(3):621–630. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu K. P., Rasmussen C. D., May G. S., Means A. R. Cooperative regulation of cell proliferation by calcium and calmodulin in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Mar;6(3):365–374. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.3.1584213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Dominoes and clocks: the union of two views of the cell cycle. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):614–621. doi: 10.1126/science.2683077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio A., Gibson T., Lehto V. P., Saraste M. SH3--an abundant protein domain in search of a function. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 27;307(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80901-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani A. H., McGuire S. L., Osmani S. A. Parallel activation of the NIMA and p34cdc2 cell cycle-regulated protein kinases is required to initiate mitosis in A. nidulans. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani A. H., O'Donnell K., Pu R. T., Osmani S. A. Activation of the nimA protein kinase plays a unique role during mitosis that cannot be bypassed by absence of the bimE checkpoint. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2669–2679. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani S. A., May G. S., Morris N. R. Regulation of the mRNA levels of nimA, a gene required for the G2-M transition in Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1495–1504. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani S. A., Pu R. T., Morris N. R. Mitotic induction and maintenance by overexpression of a G2-specific gene that encodes a potential protein kinase. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parge H. E., Arvai A. S., Murtari D. J., Reed S. I., Tainer J. A. Human CksHs2 atomic structure: a role for its hexameric assembly in cell cycle control. Science. 1993 Oct 15;262(5132):387–395. doi: 10.1126/science.8211159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. p34cdc2: the S and M kinase? New Biol. 1990 May;2(5):389–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen C. D., Means R. L., Lu K. P., May G. S., Means A. R. Characterization and expression of the unique calmodulin gene of Aspergillus nidulans. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13767–13775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. D., McCartney S. Localization of A-kinase through anchoring proteins. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Jan;8(1):5–11. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.1.8152430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Batzer A., Li N., Lee C. H., Lowenstein E., Mohammadi M., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. The function of GRB2 in linking the insulin receptor to Ras signaling pathways. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1953–1955. doi: 10.1126/science.8316835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A. B., Hollenberg S. M., Cooper J. A. Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90307-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]