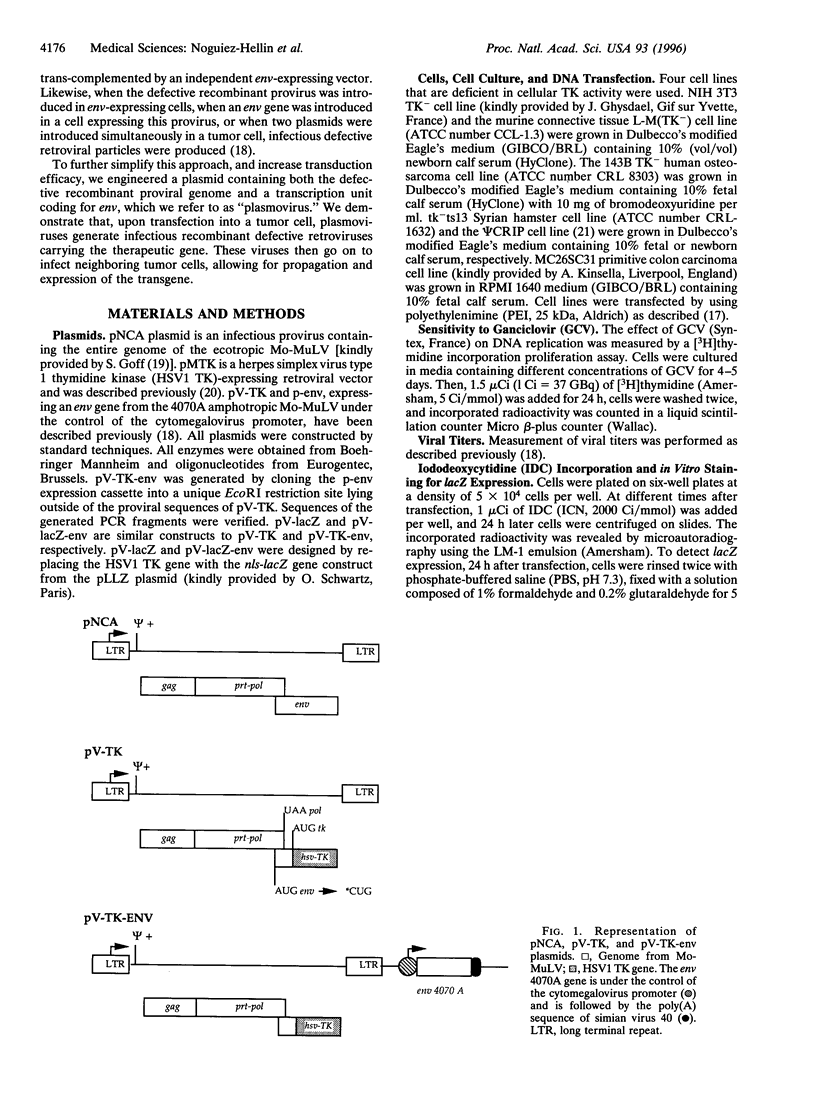
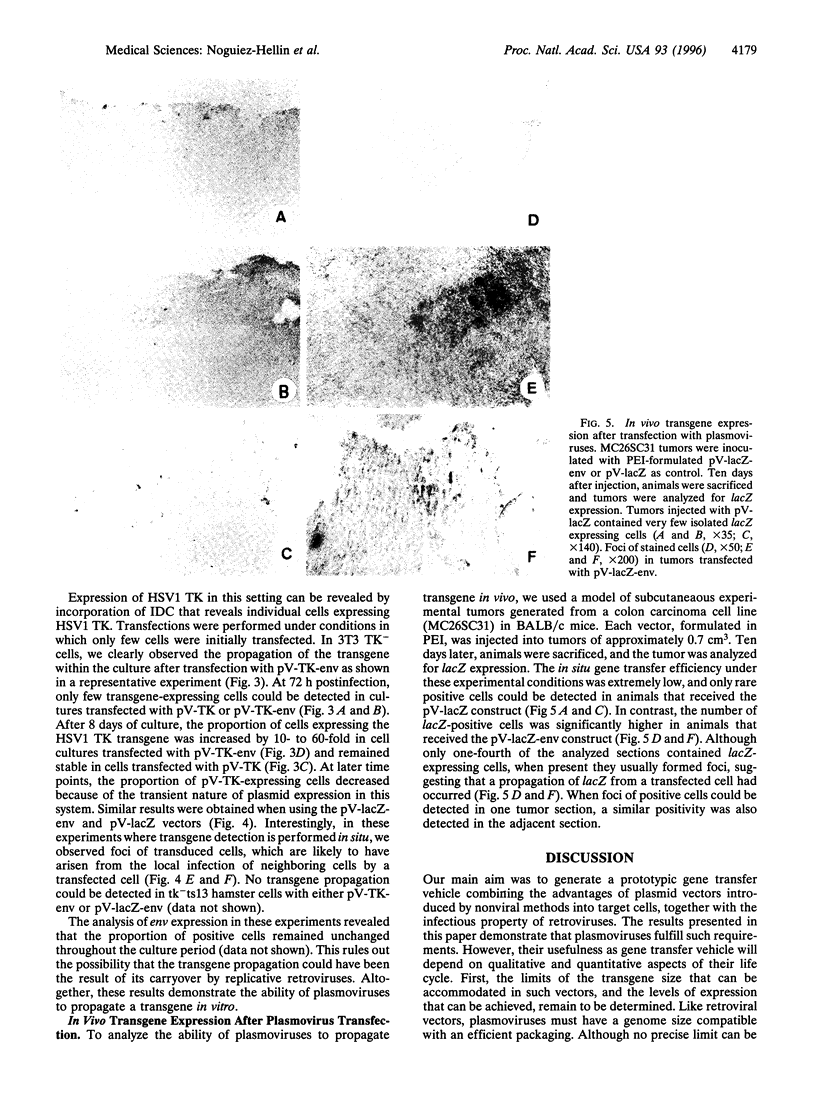
Abstract
We have generated a chimeric gene transfer vector that combines the simplicity of plasmids with the infectivity and long-term expression of retroviruses. We replaced the env gene of a Moloney murine leukemia virus-derived provirus by a foreign gene, generating a plasmid that upon transfer to tumor cells generates noninfectious retroviral particles carrying the transgene. We added to this plasmid an independent expression cassette comprising a cytomegalovirus promoter, an amphotropic retroviral envelope, and a polyadenylylation signal from simian virus 40. These constructs were designed to minimize the risk of recombination generating replication-competent retroviruses. Their only region of homology is a 157-bp sequence with 53% identity. We show that the sole transfection of this plasmid in various cell lines generates infectious but defective retroviral particles capable of efficiently infecting and expressing the transgene. The formation of infectious particles allows the transgene propagation in vitro. Eight days after transfection in vitro, the proportion of cells expressing the transgene is increased by 10-60 times. There was no evidence of replication-competent retrovirus generation in these experiments. The intratumoral injection of this plasmid, but not of the control vector lacking the env gene, led to foci of transgene-expressing cells, suggesting that the transgene had propagated in situ. Altogether, these "plasmoviruses" combine advantages of viral and non-viral vectors. They should be easy to produce in large quantity as clinical grade materials and should allow efficient and safe in situ targeting of tumor cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behr J. P., Demeneix B., Loeffler J. P., Perez-Mutul J. Efficient gene transfer into mammalian primary endocrine cells with lipopolyamine-coated DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6982–6986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bi W. L., Parysek L. M., Warnick R., Stambrook P. J. In vitro evidence that metabolic cooperation is responsible for the bystander effect observed with HSV tk retroviral gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 1993 Dec;4(6):725–731. doi: 10.1089/hum.1993.4.6-725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boussif O., Lezoualc'h F., Zanta M. A., Mergny M. D., Scherman D., Demeneix B., Behr J. P. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 1;92(16):7297–7301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.16.7297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosset F. L., Takeuchi Y., Battini J. L., Weiss R. A., Collins M. K. High-titer packaging cells producing recombinant retroviruses resistant to human serum. J Virol. 1995 Dec;69(12):7430–7436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.12.7430-7436.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G. Transfer of genes to humans: early lessons and obstacles to success. Science. 1995 Oct 20;270(5235):404–410. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5235.404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culver K. W., Ram Z., Wallbridge S., Ishii H., Oldfield E. H., Blaese R. M. In vivo gene transfer with retroviral vector-producer cells for treatment of experimental brain tumors. Science. 1992 Jun 12;256(5063):1550–1552. doi: 10.1126/science.1317968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curiel D. T., Wagner E., Cotten M., Birnstiel M. L., Agarwal S., Li C. M., Loechel S., Hu P. C. High-efficiency gene transfer mediated by adenovirus coupled to DNA-polylysine complexes. Hum Gene Ther. 1992 Apr;3(2):147–154. doi: 10.1089/hum.1992.3.2-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Mulligan R. C. Safe and efficient generation of recombinant retroviruses with amphotropic and ecotropic host ranges. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6460–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman S. M., Abboud C. N., Whartenby K. A., Packman C. H., Koeplin D. S., Moolten F. L., Abraham G. N. The "bystander effect": tumor regression when a fraction of the tumor mass is genetically modified. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 1;53(21):5274–5283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Clark M. R., Shohet S. B., Buehler J., Macher B. A. Evolutionary relationship between the natural anti-Gal antibody and the Gal alpha 1----3Gal epitope in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1369–1373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Shohet S. B., Kobrin E., Stults C. L., Macher B. A. Man, apes, and Old World monkeys differ from other mammals in the expression of alpha-galactosyl epitopes on nucleated cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17755–17762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D. Human gene therapy comes of age. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):455–460. doi: 10.1038/357455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. G., Adam M. A., Miller A. D. Gene transfer by retrovirus vectors occurs only in cells that are actively replicating at the time of infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4239–4242. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolten F. L. Tumor chemosensitivity conferred by inserted herpes thymidine kinase genes: paradigm for a prospective cancer control strategy. Cancer Res. 1986 Oct;46(10):5276–5281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguiez-Hellin P., Robert-Le Meur M., Laune S., Salzmann J. L., Klatzmann D. Génération d'un provirus recombinant défectif complémentable en trans et véhiculant un transgène. C R Acad Sci III. 1996 Jan;319(1):45–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J. Mutational analysis of the carboxyl terminus of the Moloney murine leukemia virus integration protein. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2141–2145. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2141-2145.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rother R. P., Fodor W. L., Springhorn J. P., Birks C. W., Setter E., Sandrin M. S., Squinto S. P., Rollins S. A. A novel mechanism of retrovirus inactivation in human serum mediated by anti-alpha-galactosyl natural antibody. J Exp Med. 1995 Nov 1;182(5):1345–1355. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.5.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikora K. Gene therapy for cancer. Trends Biotechnol. 1993 May;11(5):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(93)90114-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi Y., Cosset F. L., Lachmann P. J., Okada H., Weiss R. A., Collins M. K. Type C retrovirus inactivation by human complement is determined by both the viral genome and the producer cell. J Virol. 1994 Dec;68(12):8001–8007. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.12.8001-8007.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]