Abstract
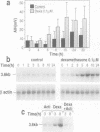
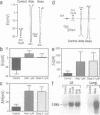
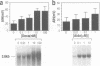
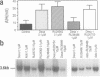
Molecular cloning of the amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel has permitted analysis of the mechanisms of its stimulation by steroids. In rat lung cells in primary culture, where its mRNA has been detected, the activity of an amiloride-sensitive channel, highly selective for Na+, is controlled by corticosteroids. Dexamethasone (0.1 microM) or aldosterone (1 microM) induced, after a minimum 10 h treatment, a large increase of the amiloride-induced hyperpolarization and of the amiloride-sensitive current. A parallel increase in the amount of the mRNA was observed. The corresponding gene is thus a target for steroid action. Using synthetic specific agonists and antagonists for mineralo- and glucocorticoid receptors, it has been shown that the steroid action on Na+ channel expression is mediated via glucocorticoid receptors. Triiodothyronine, known to modulate steroid action in several tissues, had no effect on both the amiloride-sensitive Na+ current and the level of the mRNA for the Na+ channel protein, but potentiates the stimulatory effect of dexamethasone. The increase in Na+ channel activity observed in the lung around birth can thus be explained by a direct increase in transcription of the Na+ channel gene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asher C., Garty H. Aldosterone increases the apical Na+ permeability of toad bladder by two different mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard P. L., Baxter J. D., Higgins S. J., Rousseau G. G., Tomkins G. M. General presence of glucocorticoid receptors in mammalian tissues. Endocrinology. 1974 Apr;94(4):998–1002. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-4-998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker P. M., Brown M. J., Ramsden C. A., Strang L. B., Walters D. V. The effect of thyroidectomy in the fetal sheep on lung liquid reabsorption induced by adrenaline or cyclic AMP. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;407:373–383. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker P. M., Markiewicz M., Parker K. A., Walters D. V., Strang L. B. Synergistic action of triiodothyronine and hydrocortisone on epinephrine-induced reabsorption of fetal lung liquid. Pediatr Res. 1990 Jun;27(6):588–591. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199006000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlet-Bas C., Khadouri C., Marsy S., Doucet A. Sodium-independent in vitro induction of Na+,K+-ATPase by aldosterone in renal target cells: permissive effect of triiodothyronine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1707–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basset G., Crone C., Saumon G. Fluid absorption by rat lung in situ: pathways for sodium entry in the luminal membrane of alveolar epithelium. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:325–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland R. D., Nielson D. W. Developmental changes in lung epithelial ion transport and liquid movement. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:373–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Stutts M. J., Knowles M. R., Cantley L., Gatzy J. T. Na+ transport in cystic fibrosis respiratory epithelia. Abnormal basal rate and response to adenylate cyclase activation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1245–1252. doi: 10.1172/JCI112708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRABBE J. Stimulation of active sodium transport by the isolated toad bladder with aldosterone in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:2103–2110. doi: 10.1172/JCI104436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Epithelial sodium channel related to proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):467–470. doi: 10.1038/361467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek J. M., Kim K. J., Crandall E. D. Tight monolayers of rat alveolar epithelial cells: bioelectric properties and active sodium transport. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):C688–C693. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.3.C688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clauss W., Skadhauge E. Modulation of Na and Cl transport by mineralocorticoids. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1988;90(4):583–589. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(88)90671-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen J. J., Welsh M. J. Regulation of sodium absorption by canine tracheal epithelium. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):73–79. doi: 10.1172/JCI112811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrazzini G., Maggiorini M., Kriemler S., Bärtsch P., Oelz O. Successful treatment of acute mountain sickness with dexamethasone. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 May 30;294(6584):1380–1382. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6584.1380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H., Clauss W. Regulation of Na+ channels in frog lung epithelium: a target tissue for aldosterone action. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Apr;416(1-2):62–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00370222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frings S., Purves R. D., Macknight A. D. Single-channel recordings from the apical membrane of the toad urinary bladder epithelial cell. J Membr Biol. 1988 Dec;106(2):157–172. doi: 10.1007/BF01871398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H. Mechanisms of aldosterone action in tight epithelia. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(3):193–205. doi: 10.1007/BF01870126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannopoulos G. Variations in the levels of cytoplasmic glucocorticoid receptors in lungs of various species at different developmental stages. Endocrinology. 1974 Feb;94(2):450–458. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-2-450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman B. E., Fleischer R. S., Crandall E. D. Evidence for active Na+ transport by cultured monolayers of pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C78–C83. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman B. E., Kim K. J., Crandall E. D. Evidence for active sodium transport across alveolar epithelium of isolated rat lung. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Jun;62(6):2460–2466. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.6.2460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. B., Allen J. E., Rasmussen H. Studies on the mechanism of action of aldosterone: hormone-induced changes in lipid metabolism. Biochemistry. 1971 Oct 12;10(21):3825–3831. doi: 10.1021/bi00797a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton K. L., Eaton D. C. Single-channel recordings from two types of amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channels. Membr Biochem. 1986;6(2):149–171. doi: 10.3109/09687688609065447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey B. J., Ehrenfeld J. Role of Na+/H+ exchange in the control of intracellular pH and cell membrane conductances in frog skin epithelium. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Dec;92(6):793–810. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.6.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Regulation of the (Na+ equals K+)-activated ATP hydrolyzing enzyme system in rat kidney. II. The effect of aldosterone on the activity in kidneys of adrenalectomized rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 18;192(2):326–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krozowski Z., Funder J. W. Mineralocorticoid receptors in the rat lung. Endocrinology. 1981 Dec;109(6):1811–1813. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-6-1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingueglia E., Voilley N., Waldmann R., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. Expression cloning of an epithelial amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. A new channel type with homologies to Caenorhabditis elegans degenerins. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 22;318(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Williams M. C., Widdicombe J. H., Sanders M. J., Misfeldt D. S., Berry L. C., Jr Transepithelial transport by pulmonary alveolar type II cells in primary culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6033–6037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F., Doucet A. Hormonal control of kidney functions at the cell level. Physiol Rev. 1986 Apr;66(2):377–468. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1986.66.2.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brodovich H. Epithelial ion transport in the fetal and perinatal lung. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 1):C555–C564. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.4.C555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orser B. A., Bertlik M., Fedorko L., O'Brodovich H. Cation selective channel in fetal alveolar type II epithelium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Aug 13;1094(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90021-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Frindt G. Amiloride-sensitive Na channels from the apical membrane of the rat cortical collecting tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2767–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Li J. H., Lindemann B., Edelman I. S. Aldosterone control of the density of sodium channels in the toad urinary bladder. J Membr Biol. 1982;64(1-2):91–102. doi: 10.1007/BF01870771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariban-Sohraby S., Burg M., Wiesmann W. P., Chiang P. K., Johnson J. P. Methylation increases sodium transport into A6 apical membrane vesicles: possible mode of aldosterone action. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):745–746. doi: 10.1126/science.6463652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K., Wang W., Giebisch G., Welling P. A. ATP is a coupling modulator of parallel Na,K-ATPase-K-channel activity in the renal proximal tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6418–6422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voilley N., Lingueglia E., Champigny G., Mattéi M. G., Waldmann R., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. The lung amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel: biophysical properties, pharmacology, ontogenesis, and molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):247–251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]