Abstract
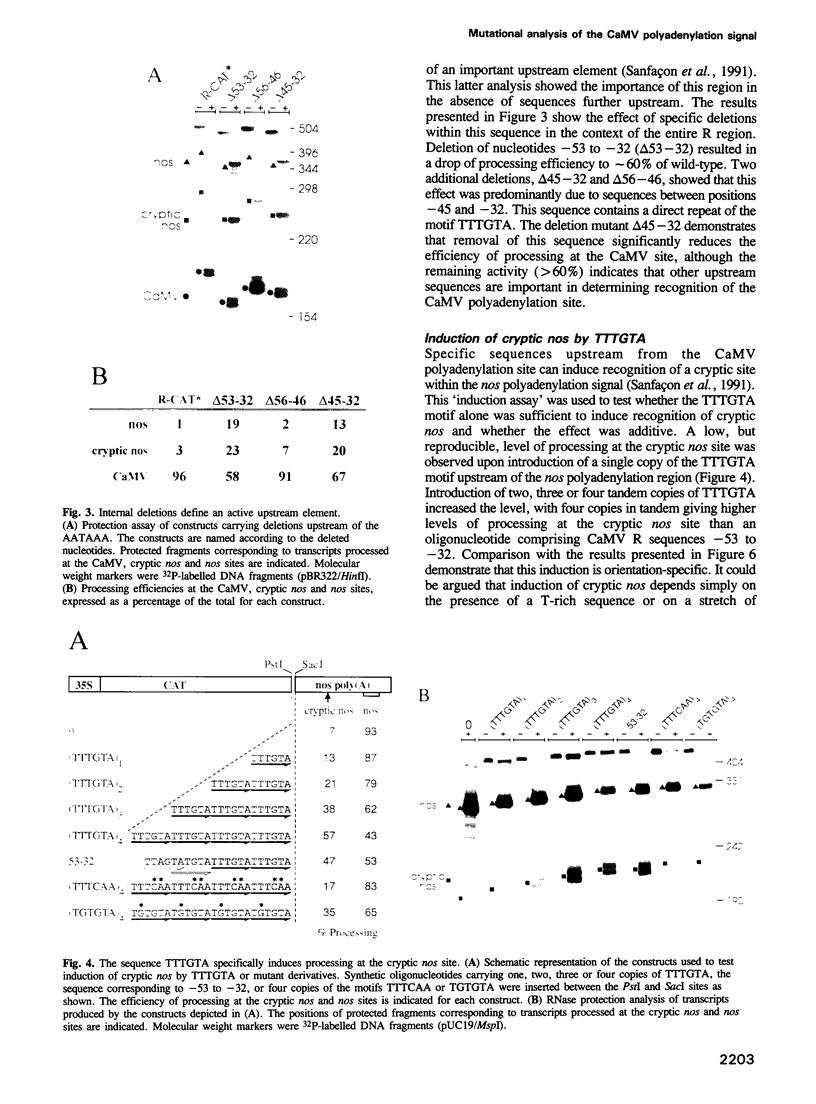
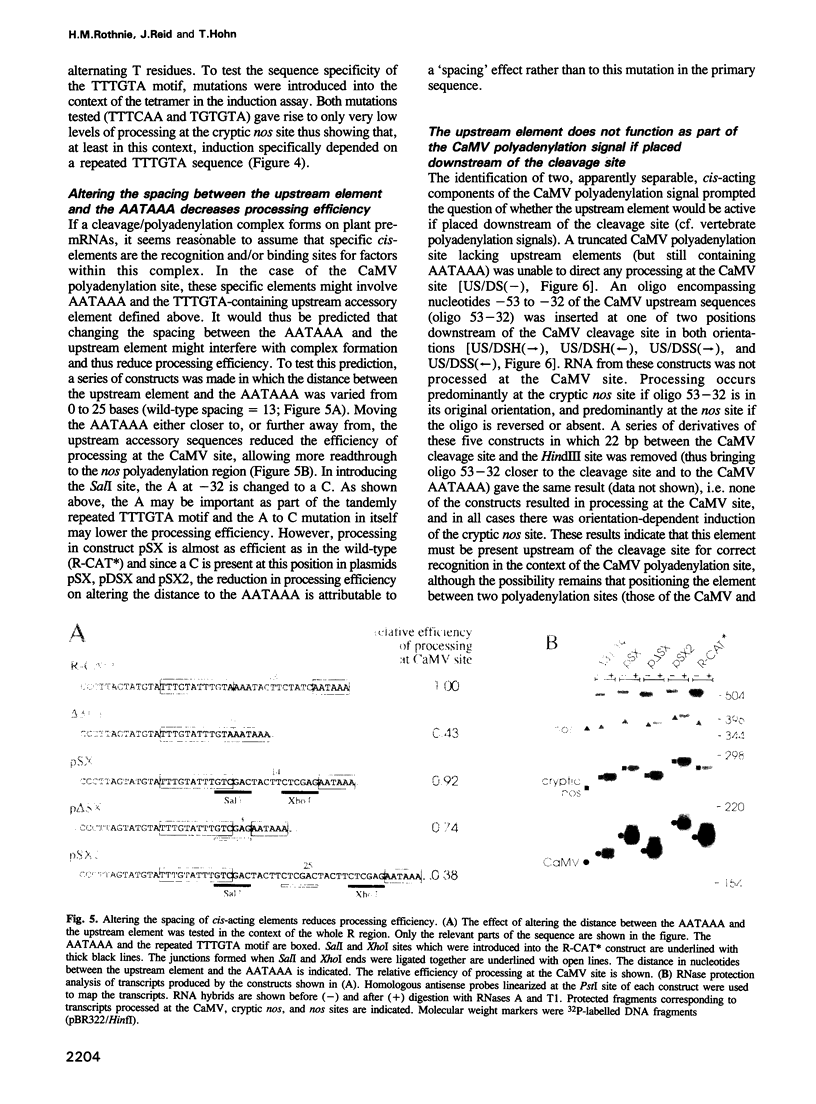
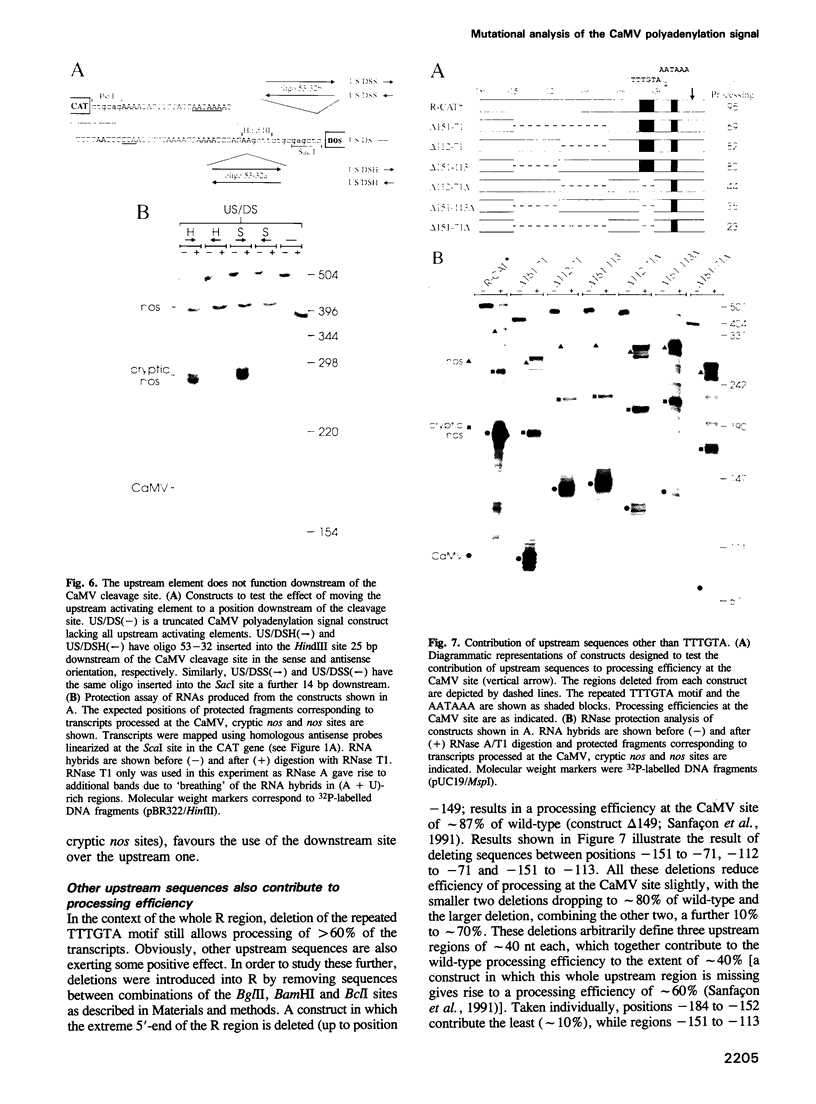
The requirement for sequence specificity in the AAUAAA motif of the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) polyadenylation signal was examined by saturation mutagenesis. While deletion of AAUAAA almost abolished processing at the CaMV polyadenylation site, none of the 18 possible single base mutations had a dramatic effect on processing efficiency. The effect of replacing all six nucleotides simultaneously varied depending on the sequence used, but some replacements were as detrimental as the deletion mutant. Taken together, these results confirm that AAUAAA is an essential component of the CaMV polyadenylation signal, but indicate that a high degree of sequence variation can be tolerated. A repeated UUUGUA motif was identified as an important upstream accessory element of the CaMV polyadenylation signal. This sequence was able to induce processing at a heterologous polyadenylation site in a sequence-specific and additive manner. The effect of altering the spacing between this upstream element and the AAUAAA was examined; moving these two elements closer together or further apart reduces the processing efficiency. The upstream element does not function to signal processing at the CaMV polyadenylation site if placed downstream of the cleavage site. Analysis of further upstream sequences revealed that almost all of the 200 nt fragment required for maximal processing contributes positively to processing efficiency. Furthermore, isolated far upstream sequences distinct from UUUGUA were also able to induce processing at a heterologous polyadenylation site.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe A., Hiraoka Y., Fukasawa T. Signal sequence for generation of mRNA 3' end in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL7 gene. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3691–3697. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07581.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell V. J., Wickens M., Bienroth S., Keller W., Sproat B. S., Lamond A. I. Site-directed ribose methylation identifies 2'-OH groups in polyadenylation substrates critical for AAUAAA recognition and poly(A) addition. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90414-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M., Barnes W. M., Chilton M. D. Structure and transcription of the nopaline synthase gene region of T-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):369–385. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienroth S., Wahle E., Suter-Crazzolara C., Keller W. Purification of the cleavage and polyadenylation factor involved in the 3'-processing of messenger RNA precursors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19768–19776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. S., Platt T. RNA processing generates the mature 3' end of yeast CYC1 messenger RNA in vitro. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1270–1274. doi: 10.1126/science.2848317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. S., Sadhale P. P., Platt T. RNA processing in vitro produces mature 3' ends of a variety of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2599–2605. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell S., Alwine J. C. Efficiency of utilization of the simian virus 40 late polyadenylation site: effects of upstream sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4248–4258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Moore C. Separation of factors required for cleavage and polyadenylation of yeast pre-mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3470–3481. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofori G., Keller W. 3' cleavage and polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in vitro requires a poly(A) polymerase, a cleavage factor, and a snRNP. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):875–889. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeZazzo J. D., Imperiale M. J. Sequences upstream of AAUAAA influence poly(A) site selection in a complex transcription unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4951–4961. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean C., Tamaki S., Dunsmuir P., Favreau M., Katayama C., Dooner H., Bedbrook J. mRNA transcripts of several plant genes are polyadenylated at multiple sites in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2229–2240. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depicker A., Stachel S., Dhaese P., Zambryski P., Goodman H. M. Nopaline synthase: transcript mapping and DNA sequence. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):561–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. A sequence downstream of AAUAAA is required for rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3'-end formation. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):473–474. doi: 10.1038/312473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. Position-dependent sequence elements downstream of AAUAAA are required for efficient rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3' end formation. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., Nevins J. R. An ordered pathway of assembly of components required for polyadenylation site recognition and processing. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2180–2190. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall G. J., Wiebauer K., Filipowicz W. Analysis of pre-mRNA processing in transfected plant protoplasts. Methods Enzymol. 1990;181:148–161. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)81117-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerineau F., Brooks L., Mullineaux P. Effect of deletions in the cauliflower mosaic virus polyadenylation sequence on the choice of the polyadenylation sites in tobacco protoplasts. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Apr;226(1-2):141–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00273597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilley H., Dudley R. K., Jonard G., Balàzs E., Richards K. E. Transcription of Cauliflower mosaic virus DNA: detection of promoter sequences, and characterization of transcripts. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):763–773. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site cleavage in a HeLa nuclear extract is dependent on downstream sequences. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. M., Jones M. C., Blakebrough M. L., Dasgupta I., Davies J. W., Hull R. An analysis of the sequence of an infectious clone of rice tungro bacilliform virus, a plant pararetrovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2615–2621. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath C. V., Denome R. M., Cole C. N. Spatial constraints on polyadenylation signal function. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9098–9104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann S., Obermaier B., Vogel K., Domdey H. Identification of pre-mRNA polyadenylation sites in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4215–4229. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Cohen E. H. Sequences responsible for transcription termination on a gene segment in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1515–1520. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou W., Russnak R., Platt T. Poly(A) site selection in the yeast Ty retroelement requires an upstream region and sequence-specific titratable factor(s) in vitro. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 15;13(2):446–452. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R., Sadler J., Longstaff M. The sequence of carnation etched ring virus DNA: comparison with cauliflower mosaic virus and retroviruses. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3083–3090. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman L. E., Seiler S. H., Whoriskey J., Moore C. L. Point mutations upstream of the yeast ADH2 poly(A) site significantly reduce the efficiency of 3'-end formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2004–2012. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., DeZazzo J. D. Poly(A) site choice in retroelements: deja vu all over again? New Biol. 1991 Jun;3(6):531–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irniger S., Braus G. H. Saturation mutagenesis of a polyadenylation signal reveals a hexanucleotide element essential for mRNA 3' end formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):257–261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irniger S., Egli C. M., Braus G. H. Different classes of polyadenylation sites in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3060–3069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irniger S., Sanfaçon H., Egli C. M., Braus G. H. Different sequence elements are required for function of the cauliflower mosaic virus polyadenylation site in Saccharomyces cerevisiae compared with in plants. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2322–2330. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi C. P. Putative polyadenylation signals in nuclear genes of higher plants: a compilation and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9627–9640. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W., Bienroth S., Lang K. M., Christofori G. Cleavage and polyadenylation factor CPF specifically interacts with the pre-mRNA 3' processing signal AAUAAA. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4241–4249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05002.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt N., Briggs D., Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. Definition of an efficient synthetic poly(A) site. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1019–1025. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingner J., Kellermann J., Keller W. Cloning and expression of the essential gene for poly(A) polymerase from S. cerevisiae. Nature. 1991 Dec 12;354(6353):496–498. doi: 10.1038/354496a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingner J., Radtke I., Wahle E., Keller W. Purification and characterization of poly(A) polymerase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8741–8746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. H., Mogen B. D., Hunt A. G. Characterization of the polyadenylation signal from the T-DNA-encoded octopine synthase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5575–5581. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Yu H., Ryner L. RNA sequence containing hexanucleotide AAUAAA directs efficient mRNA polyadenylation in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):373–379. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Hart R. P., Wong W. W., Nevins J. R. Sequences capable of restoring poly(A) site function define two distinct downstream elements. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2907–2913. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medberry S. L., Lockhart B. E., Olszewski N. E. Properties of Commelina yellow mottle virus's complete DNA sequence, genomic discontinuities and transcript suggest that it is a pararetrovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5505–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogen B. D., MacDonald M. H., Graybosch R., Hunt A. G. Upstream sequences other than AAUAAA are required for efficient messenger RNA 3'-end formation in plants. Plant Cell. 1990 Dec;2(12):1261–1272. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.12.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogen B. D., MacDonald M. H., Leggewie G., Hunt A. G. Several distinct types of sequence elements are required for efficient mRNA 3' end formation in a pea rbcS gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5406–5414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russnak R. H. Regulation of polyadenylation in hepatitis B viruses: stimulation by the upstream activating signal PS1 is orientation-dependent, distance-independent, and additive. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6449–6456. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo P., Li W. Z., Hampsey D. M., Zaret K. S., Sherman F. Distinct cis-acting signals enhance 3' endpoint formation of CYC1 mRNA in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):563–571. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07983.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadhale P. P., Platt T. Unusual aspects of in vitro RNA processing in the 3' regions of the GAL1, GAL7, and GAL10 genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4262–4270. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadhale P. P., Sapolsky R., Davis R. W., Butler J. S., Platt T. Polymerase chain reaction mapping of yeast GAL7 mRNA polyadenylation sites demonstrates that 3' end processing in vitro faithfully reproduces the 3' ends observed in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3683–3688. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanfaçon H. Analysis of figwort mosaic virus (plant pararetrovirus) polyadenylation signal. Virology. 1994 Jan;198(1):39–49. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanfaçon H., Brodmann P., Hohn T. A dissection of the cauliflower mosaic virus polyadenylation signal. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):141–149. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanfaçon H., Hohn T. Proximity to the promoter inhibits recognition of cauliflower mosaic virus polyadenylation signal. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):81–84. doi: 10.1038/346081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schek N., Cooke C., Alwine J. C. Definition of the upstream efficiency element of the simian virus 40 late polyadenylation signal by using in vitro analyses. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5386–5393. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets M. D., Ogg S. C., Wickens M. P. Point mutations in AAUAAA and the poly (A) addition site: effects on the accuracy and efficiency of cleavage and polyadenylation in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5799–5805. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Four factors are required for 3'-end cleavage of pre-mRNAs. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1711–1724. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E., Keller W. The biochemistry of 3'-end cleavage and polyadenylation of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:419–440. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E. The end of the message: 3'-end processing leading to polyadenylated messenger RNA. Bioessays. 1992 Feb;14(2):113–118. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. A., Gilmartin G. M., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site efficiency reflects the stability of complex formation involving the downstream element. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):215–219. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M., Stephenson P. Role of the conserved AAUAAA sequence: four AAUAAA point mutants prevent messenger RNA 3' end formation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1045–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6208611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Pettine S. M., Shenk T. Functional analysis of point mutations in the AAUAAA motif of the SV40 late polyadenylation signal. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3899–3908. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Ueda T., Messing J. 3'-end processing of the maize 27 kDa zein mRNA. Plant J. 1993 Sep;4(3):535–544. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.04030535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkower D., Stephenson P., Sheets M., Wickens M. The AAUAAA sequence is required both for cleavage and for polyadenylation of simian virus 40 pre-mRNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2317–2323. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]