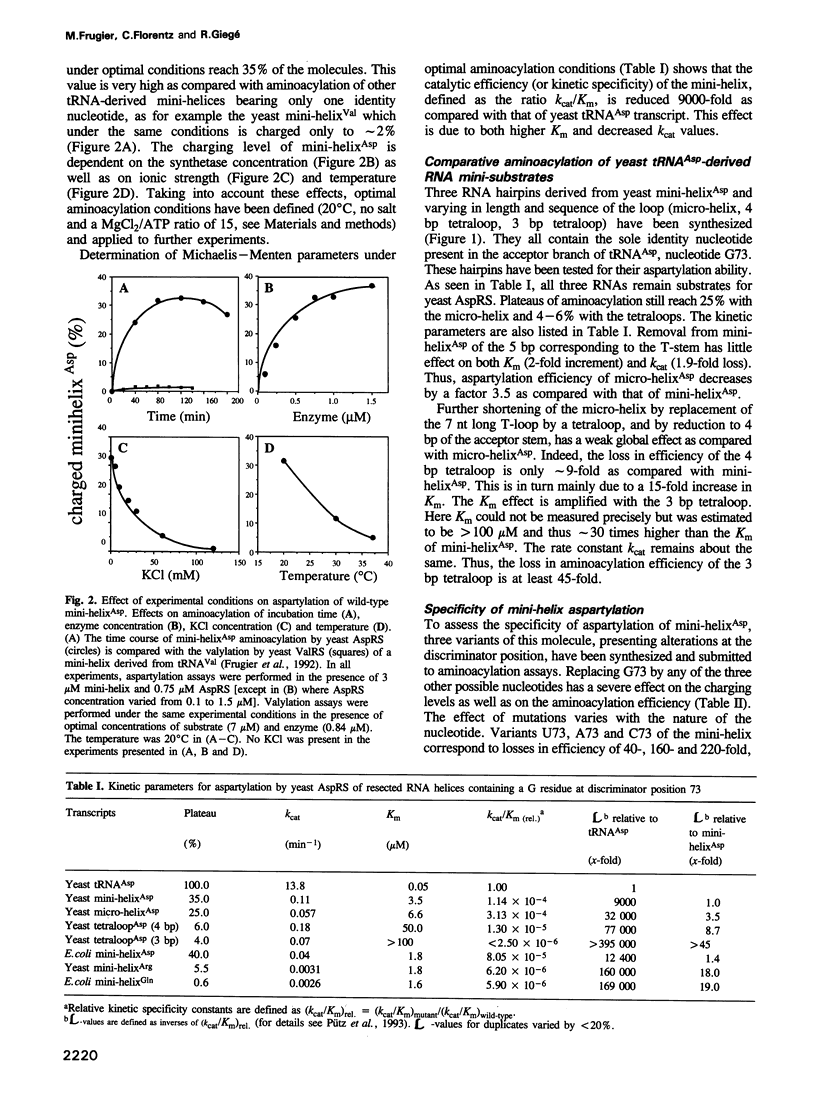
Abstract
We show here that small RNA helices which recapitulate part or all of the acceptor stem of yeast aspartate tRNA are efficiently aminoacylated by cognate class II aspartyl-tRNA synthetase. Aminoacylation is strongly dependent on the presence of the single-stranded G73 'discriminator' identity nucleotide and is essentially insensitive to the sequence of the helical region. Substrates which contain as few as 3 bp fused to G73CCAOH are aspartylated. Their charging is insensitive to the sequence of the loop closing the short helical domains. Aminoacylation of the aspartate mini-helix is not stimulated by a hairpin helix mimicking the anticodon domain and containing the three major anticodon identity nucleotides. A thermodynamic analysis demonstrates that enzyme interactions with G73 in the resected RNA substrates and in the whole tRNA are the same. Thus, if the resected RNA molecules resemble in some way the earliest substrates for aminoacylation with aspartate, then the contemporary tRNA(Asp) has quantitatively retained the influence of the major signal for aminoacylation in these substrates.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonnet J., Ebel J. P. Interpretation of incomplete reactions in tRNA aminoacylation. Aminoacylation of yeast tRNA Val II with yeast valyl-tRNA synthetase. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 4;31(2):335–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buechter D. D., Schimmel P. Aminoacylation of RNA minihelices: implications for tRNA synthetase structural design and evolution. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1993;28(4):309–322. doi: 10.3109/10409239309078438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavarelli J., Rees B., Ruff M., Thierry J. C., Moras D. Yeast tRNA(Asp) recognition by its cognate class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):181–184. doi: 10.1038/362181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheong C., Varani G., Tinoco I., Jr Solution structure of an unusually stable RNA hairpin, 5'GGAC(UUCG)GUCC. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):680–682. doi: 10.1038/346680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Seno T., Söll G. Is there a discriminator site in transfer RNA? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):3063–3067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.3063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusack S., Berthet-Colominas C., Härtlein M., Nassar N., Leberman R. A second class of synthetase structure revealed by X-ray analysis of Escherichia coli seryl-tRNA synthetase at 2.5 A. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):249–255. doi: 10.1038/347249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich A., Kern D., Bonnet J., Giegé R., Ebel J. P. Interpretation of tRNA-mischarging kinetics. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 1;70(1):147–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebel J. P., Giegé R., Bonnet J., Kern D., Befort N., Bollack C., Fasiolo F., Gangloff J., Dirheimer G. Factors determining the specificity of the tRNA aminoacylation reaction. Non-absolute specificity of tRNA-aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase recognition and particular importance of the maximal velocity. Biochimie. 1973 May;55(5):547–557. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80415-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriani G., Delarue M., Poch O., Gangloff J., Moras D. Partition of tRNA synthetases into two classes based on mutually exclusive sets of sequence motifs. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):203–206. doi: 10.1038/347203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felden B., Florentz C., Giegé R., Westhof E. Solution structure of the 3'-end of brome mosaic virus genomic RNAs. Conformational mimicry with canonical tRNAs. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 14;235(2):508–531. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francklyn C., Schimmel P. Aminoacylation of RNA minihelices with alanine. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):478–481. doi: 10.1038/337478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francklyn C., Schimmel P. Enzymatic aminoacylation of an eight-base-pair microhelix with histidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8655–8659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francklyn C., Shi J. P., Schimmel P. Overlapping nucleotide determinants for specific aminoacylation of RNA microhelices. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1121–1125. doi: 10.1126/science.1546312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frugier M., Florentz C., Giegé R. Anticodon-independent aminoacylation of an RNA minihelix with valine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3990–3994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giegé R., Puglisi J. D., Florentz C. tRNA structure and aminoacylation efficiency. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1993;45:129–206. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60869-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou Y. M., Schimmel P. A simple structural feature is a major determinant of the identity of a transfer RNA. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):140–145. doi: 10.1038/333140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khvorova A. M., Motorin YuA, Wolfson A. D., Gladilin K. L. Anticodon-dependent aminoacylation of RNA minisubstrate by lysyl-tRNA synthetase. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 21;314(3):256–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81483-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorber B., Kern D., Dietrich A., Gangloff J., Ebel J. P., Giegé R. Large scale purification and structural properties of yeast aspartyl-tRNA synthetase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 30;117(1):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91569-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinis S. A., Schimmel P. Enzymatic aminoacylation of sequence-specific RNA minihelices and hybrid duplexes with methionine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):65–69. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinis S. A., Schimmel P. Microhelix aminoacylation by a class I tRNA synthetase. Non-conserved base pairs required for specificity. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6069–6072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinnel T., Mechulam Y., Blanquet S., Fayat G. Binding of the anticodon domain of tRNA(fMet) to Escherichia coli methionyl-tRNA synthetase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jul 20;220(2):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90003-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Uhlenbeck O. C. Determination of RNA-protein contacts using thiophosphate substitutions. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2849–2855. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moras D. Structural aspects and evolutionary implications of the recognition between tRNAs and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Biochimie. 1993;75(8):651–657. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(93)90095-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musier-Forsyth K., Schimmel P. Aminoacylation of RNA oligonucleotides: minimalist structures and origin of specificity. FASEB J. 1993 Feb 1;7(2):282–289. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.2.7680012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musier-Forsyth K., Schimmel P. Functional contacts of a transfer RNA synthetase with 2'-hydroxyl groups in the RNA minor groove. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):513–515. doi: 10.1038/357513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nureki O., Niimi T., Muramatsu T., Kanno H., Kohno T., Florentz C., Giegé R., Yokoyama S. Molecular recognition of the identity-determinant set of isoleucine transfer RNA from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 25;236(3):710–724. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret V., Florentz C., Dreher T., Giege R. Structural analogies between the 3' tRNA-like structure of brome mosaic virus RNA and yeast tRNATyr revealed by protection studies with yeast tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Nov 6;185(2):331–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret V., Garcia A., Grosjean H., Ebel J. P., Florentz C., Giegé R. Relaxation of a transfer RNA specificity by removal of modified nucleotides. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):787–789. doi: 10.1038/344787a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Tinoco I., Jr Absorbance melting curves of RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:304–325. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pütz J., Puglisi J. D., Florentz C., Giegé R. Additive, cooperative and anti-cooperative effects between identity nucleotides of a tRNA. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2949–2957. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pütz J., Puglisi J. D., Florentz C., Giegé R. Identity elements for specific aminoacylation of yeast tRNA(Asp) by cognate aspartyl-tRNA synthetase. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1696–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2047878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudinger J., Florentz C., Dreher T., Giegé R. Efficient mischarging of a viral tRNA-like structure and aminoacylation of a minihelix containing a pseudoknot: histidinylation of turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 25;20(8):1865–1870. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.8.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudinger J., Puglisi J. D., Pütz J., Schatz D., Eckstein F., Florentz C., Giegé R. Determinant nucleotides of yeast tRNA(Asp) interact directly with aspartyl-tRNA synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5882–5886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. R., Saks M. E. Contributions of discrete tRNA(Ser) domains to aminoacylation by E.coli seryl-tRNA synthetase: a kinetic analysis using model RNA substrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 25;21(19):4467–4475. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.19.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel P., Giegé R., Moras D., Yokoyama S. An operational RNA code for amino acids and possible relationship to genetic code. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8763–8768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman L. H., Pelka H. Anticodon switching changes the identity of methionine and valine transfer RNAs. Science. 1988 Nov 4;242(4879):765–768. doi: 10.1126/science.3055296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg S., Misch A., Sprinzl M. Compilation of tRNA sequences and sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3011–3015. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. R., Chastain M., Puglisi J. D. Synthesis and purification of large amounts of RNA oligonucleotides. Biotechniques. 1991 Dec;11(6):764–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




