Abstract
The preS domain at the N-terminus of the large envelope protein (LHBs) of the hepatitis B virus is involved in (i) envelopment of viral nucleocapsids and (ii) binding to the host cell. While the first function suggests a cytosolic location of the preS domain during virion assembly, the function as an attachment site requires its translocation across the lipid bilayer and final exposure on the virion surface. We compared the transmembrane topology of newly synthesized LHBs in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane with its topology in the envelope of secreted virions. Protease sensitivity and the absence of glycosylation suggest that the entire preS domain of newly synthesized LHBs remains at the cytosolic side of ER vesicles. However, virions secreted from transfected cell cultures or isolated from the blood of persistent virus carriers expose antibody binding sites and proteolytic cleavage sites of the preS domain at their surface in approximately half of the LHBs molecules. Thus, preS domains appear to be transported across the viral lipid barrier by a novel post-translational translocation mechanism to fulfil a dual function in virion assembly and attachment to the host cell.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruss V., Ganem D. Mutational analysis of hepatitis B surface antigen particle assembly and secretion. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3813–3820. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3813-3820.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruss V., Ganem D. The role of envelope proteins in hepatitis B virus assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1059–1063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruss V., Thomssen R. Mapping a region of the large envelope protein required for hepatitis B virion maturation. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1643–1650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1643-1650.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budkowska A., Quan C., Groh F., Bedossa P., Dubreuil P., Bouvet J. P., Pillot J. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) binding factor in human serum: candidate for a soluble form of hepatocyte HBV receptor. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4316–4322. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4316-4322.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland C. S., Zimmer K. P., Wagner K. R., Healey G. A., Mellman I., Helenius A. Folding, trimerization, and transport are sequential events in the biogenesis of influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90381-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eble B. E., Lingappa V. R., Ganem D. The N-terminal (pre-S2) domain of a hepatitis B virus surface glycoprotein is translocated across membranes by downstream signal sequences. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1414–1419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1414-1419.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eble B. E., MacRae D. R., Lingappa V. R., Ganem D. Multiple topogenic sequences determine the transmembrane orientation of the hepatitis B surface antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3591–3601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gültekin H., Heermann K. H. The use of polyvinylidenedifluoride membranes as a general blotting matrix. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;172(2):320–329. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
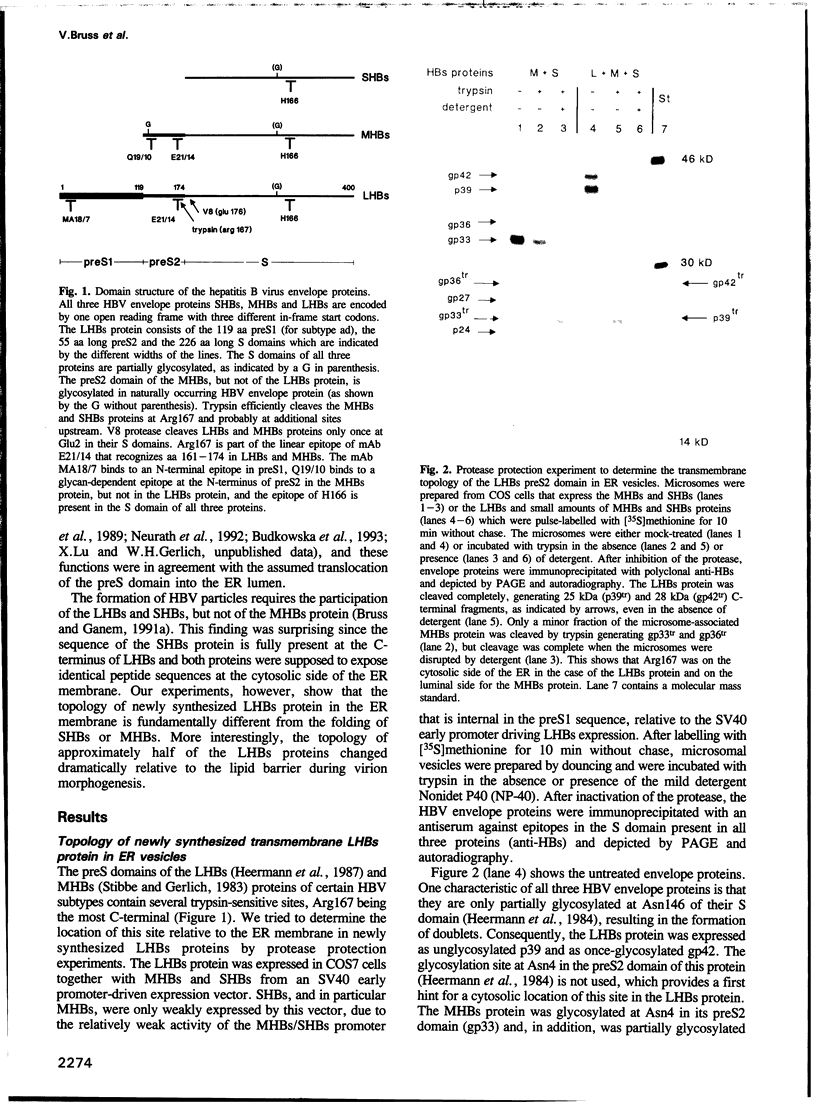
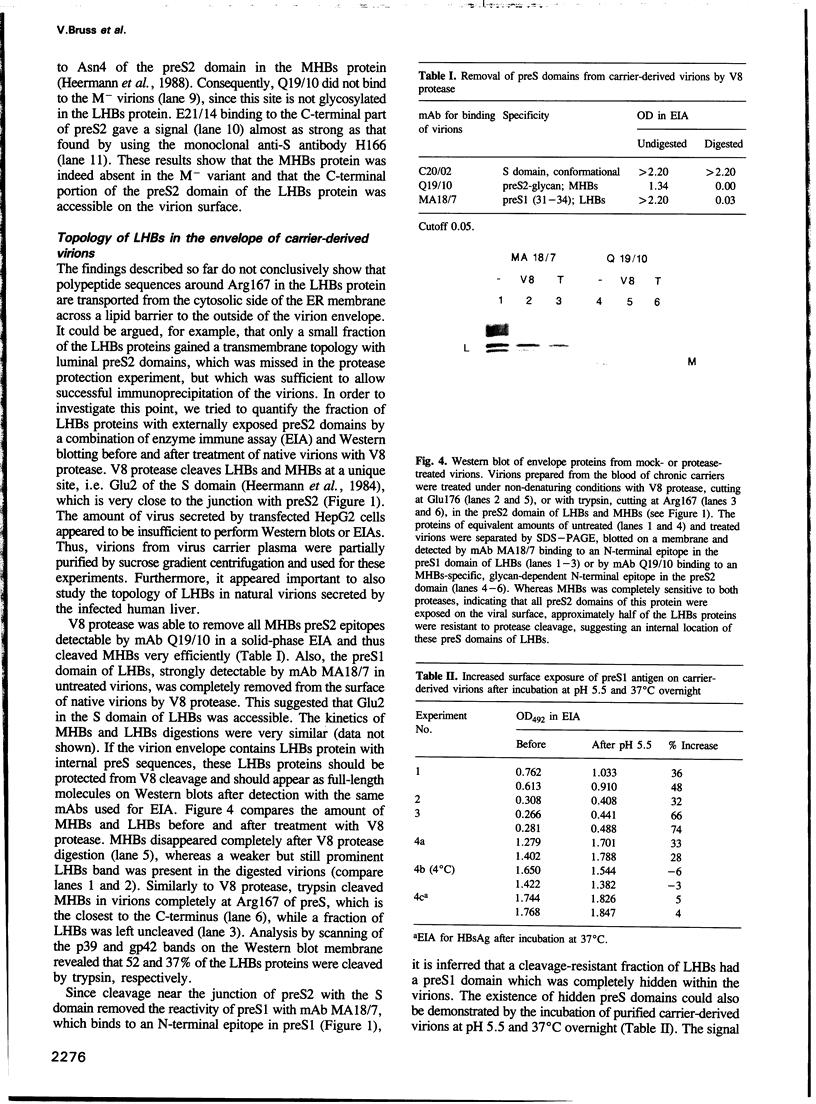
- Heermann K. H., Goldmann U., Schwartz W., Seyffarth T., Baumgarten H., Gerlich W. H. Large surface proteins of hepatitis B virus containing the pre-s sequence. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):396–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.396-402.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heermann K. H., Kruse F., Seifer M., Gerlich W. H. Immunogenicity of the gene S and Pre-S domains in hepatitis B virions and HBsAg filaments. Intervirology. 1987;28(1):14–25. doi: 10.1159/000149993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huovila A. P., Eder A. M., Fuller S. D. Hepatitis B surface antigen assembles in a post-ER, pre-Golgi compartment. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1305–1320. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N., Parker K. Identification and chemical synthesis of a host cell receptor binding site on hepatitis B virus. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Seto B., Strick N. Antibodies to synthetic peptides from the preS1 region of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) envelope (env) protein are virus-neutralizing and protective. Vaccine. 1989 Jun;7(3):234–236. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(89)90235-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N., Sproul P. Search for hepatitis B virus cell receptors reveals binding sites for interleukin 6 on the virus envelope protein. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):461–469. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson I. M., Gafvelin G., von Heijne G. Different sec-requirements for signal peptide cleavage and protein translocation in a model E. coli protein. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 22;318(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81316-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
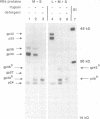
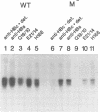
- Ostapchuk P., Hearing P., Ganem D. A dramatic shift in the transmembrane topology of a viral envelope glycoprotein accompanies hepatitis B viral morphogenesis. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 1;13(5):1048–1057. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Inhibition of secretion of hepatitis B surface antigen by a related presurface polypeptide. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1388–1391. doi: 10.1126/science.3787251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. The preS1 protein of hepatitis B virus is acylated at its amino terminus with myristic acid. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1672–1677. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1672-1677.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. L., Paul D. A., Lam J., Tribby I. I., Achord D. T. Antigenic structure of hepatitis B surface antigen: identification of the "d" subtype determinant by chemical modification and use of monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):920–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontisso P., Ruvoletto M. G., Gerlich W. H., Heermann K. H., Bardini R., Alberti A. Identification of an attachment site for human liver plasma membranes on hepatitis B virus particles. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):522–530. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90564-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheu S. Y., Lo S. J. Preferential ribosomal scanning is involved in the differential synthesis of the hepatitis B viral surface antigens from subgenomic transcripts. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):353–357. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90764-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon K., Lingappa V. R., Ganem D. Secreted hepatitis B surface antigen polypeptides are derived from a transmembrane precursor. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2163–2168. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sominskaya I., Pushko P., Dreilina D., Kozlovskaya T., Pumpen P. Determination of the minimal length of preS1 epitope recognized by a monoclonal antibody which inhibits attachment of hepatitis B virus to hepatocytes. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1992;181(4):215–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00215767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens E. B., Compans R. W. Assembly of animal viruses at cellular membranes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:489–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibbe W., Gerlich W. H. Structural relationships between minor and major proteins of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):626–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.626-628.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirk H. J., Thornton J. M., Howard C. R. A topological model for hepatitis B surface antigen. Intervirology. 1992;33(3):148–158. doi: 10.1159/000150244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau C., Guerra B., Lanford R. E. Role of the large hepatitis B virus envelope protein in infectivity of the hepatitis delta virion. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):366–372. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.366-372.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]