Abstract
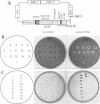
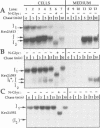
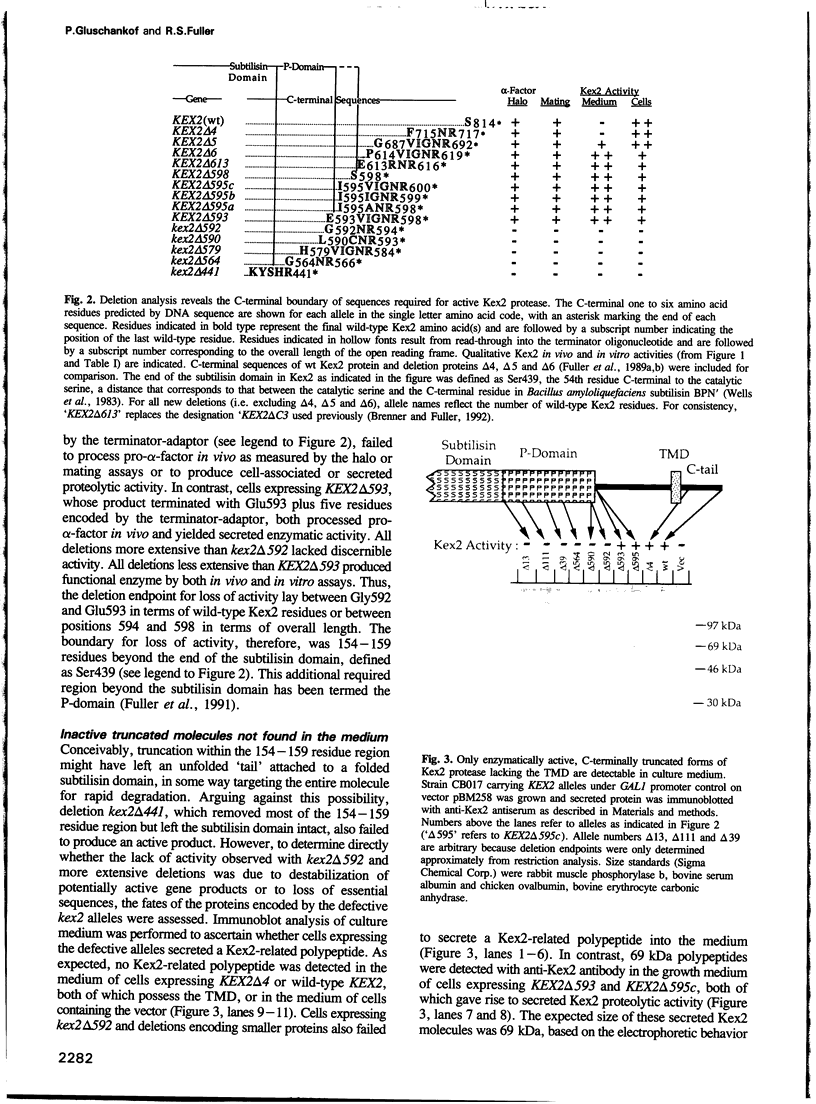
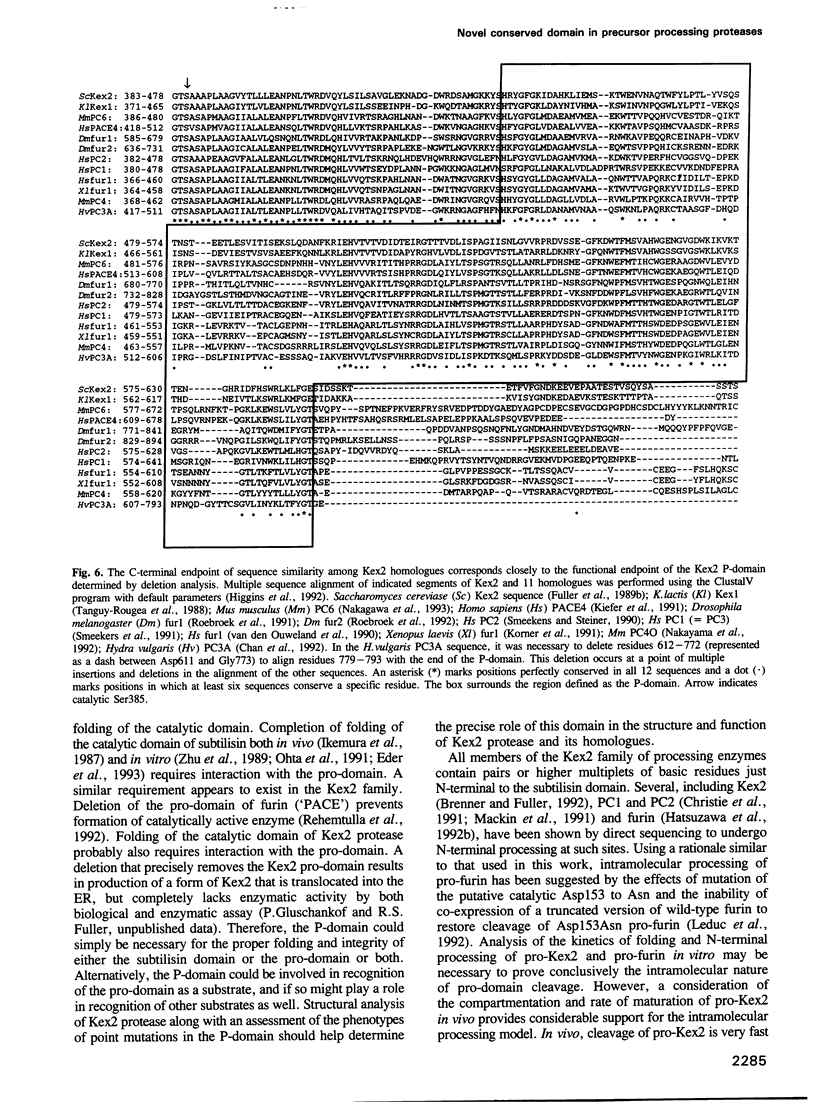
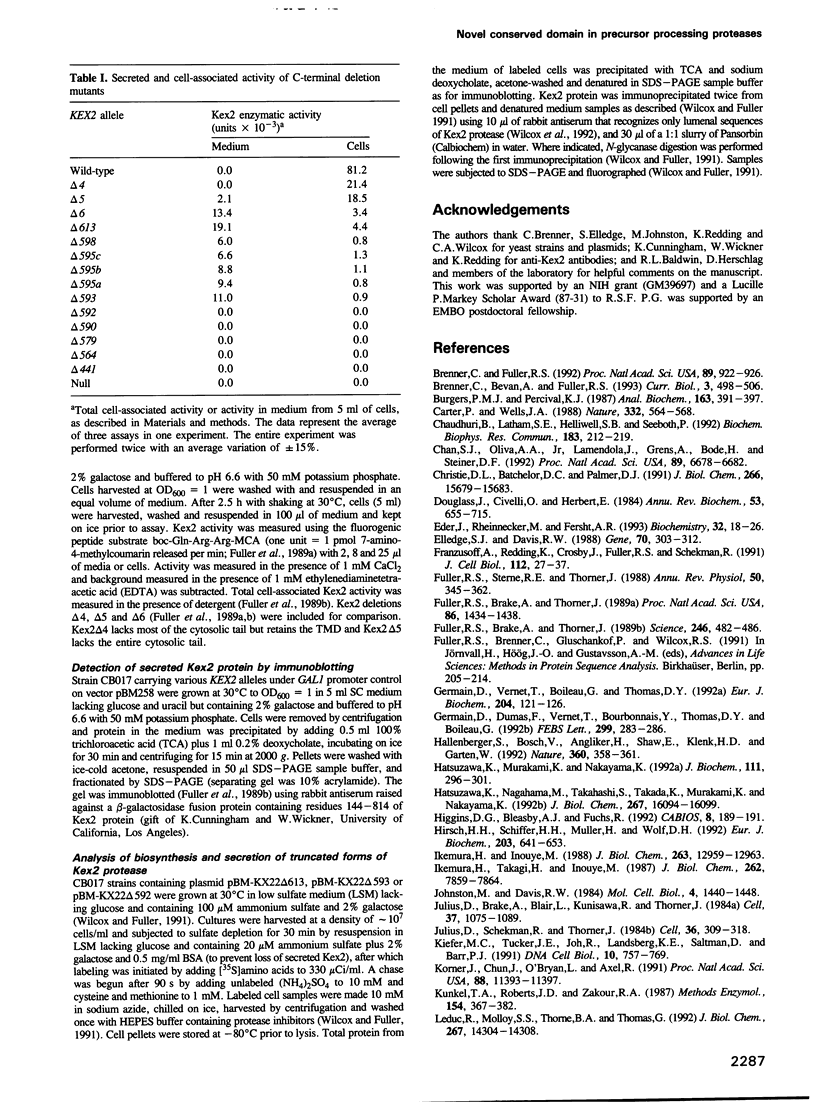
The Kex2 protease of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is the prototype of a family of eukaryotic subtilisin homologs thought to process prohormones and other precursors in the secretory pathway. Deletion analysis of Kex2 protease shows that a sequence of 154-159 residues carboxyl to the subtilisin domain is essential for the formation of active enzyme. Disruption of this region, termed the 'P-domain', blocks the normally rapid intra-molecular cleavage of the N-terminal pro-segment of pro-Kex2 protease in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The C-terminal boundary of the P-domain coincides closely with the endpoint of similarity between Kex2 protease and its mammalian homologues. The conservation of and functional requirement for the P-domain sharpens the distinction between a 'Kex2 family' of processing enzymes and degradative 'subtilases', and implies that the Kex2-related enzymes have in common entirely novel structural features that are important in the maturation of precursor polypeptide substrates. Failure to cleave the N-terminal pro-domain, due either to truncation of the P-domain or to mutation of the active site histidine or serine, results in stable, intracellular retention of pro-enzyme, apparently in the ER. Thus pro-Kex2 protease appears to contain an ER retention signal which is removed or destroyed by cleavage of the pro-domain.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner C., Bevan A., Fuller R. S. One-step site-directed mutagenesis of the Kex2 protease oxyanion hole. Curr Biol. 1993 Aug 1;3(8):498–506. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90040-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner C., Fuller R. S. Structural and enzymatic characterization of a purified prohormone-processing enzyme: secreted, soluble Kex2 protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):922–926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgers P. M., Percival K. J. Transformation of yeast spheroplasts without cell fusion. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jun;163(2):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P., Wells J. A. Dissecting the catalytic triad of a serine protease. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):564–568. doi: 10.1038/332564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Oliva A. A., Jr, LaMendola J., Grens A., Bode H., Steiner D. F. Conservation of the prohormone convertase gene family in metazoa: analysis of cDNAs encoding a PC3-like protein from hydra. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6678–6682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri B., Latham S. E., Helliwell S. B., Seeboth P. A novel Kex2 enzyme can process the proregion of the yeast alpha-factor leader in the endoplasmic reticulum instead of in the Golgi. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 28;183(1):212–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91630-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie D. L., Batchelor D. C., Palmer D. J. Identification of kex2-related proteases in chromaffin granules by partial amino acid sequence analysis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15679–15683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass J., Civelli O., Herbert E. Polyprotein gene expression: generation of diversity of neuroendocrine peptides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:665–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eder J., Rheinnecker M., Fersht A. R. Folding of subtilisin BPN': characterization of a folding intermediate. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 12;32(1):18–26. doi: 10.1021/bi00052a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Davis R. W. A family of versatile centromeric vectors designed for use in the sectoring-shuffle mutagenesis assay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzusoff A., Redding K., Crosby J., Fuller R. S., Schekman R. Localization of components involved in protein transport and processing through the yeast Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(1):27–37. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Brake A. J., Thorner J. Intracellular targeting and structural conservation of a prohormone-processing endoprotease. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):482–486. doi: 10.1126/science.2683070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Brake A., Thorner J. Yeast prohormone processing enzyme (KEX2 gene product) is a Ca2+-dependent serine protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1434–1438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Sterne R. E., Thorner J. Enzymes required for yeast prohormone processing. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:345–362. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain D., Dumas F., Vernet T., Bourbonnais Y., Thomas D. Y., Boileau G. The pro-region of the Kex2 endoprotease of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is removed by self-processing. FEBS Lett. 1992 Mar 16;299(3):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80132-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain D., Vernet T., Boileau G., Thomas D. Y. Expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Kex2p endoprotease in inset cells. Evidence for a carboxy-terminal autoprocessing event. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 15;204(1):121–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16613.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallenberger S., Bosch V., Angliker H., Shaw E., Klenk H. D., Garten W. Inhibition of furin-mediated cleavage activation of HIV-1 glycoprotein gp160. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):358–361. doi: 10.1038/360358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatsuzawa K., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Molecular and enzymatic properties of furin, a Kex2-like endoprotease involved in precursor cleavage at Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg sites. J Biochem. 1992 Mar;111(3):296–301. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatsuzawa K., Nagahama M., Takahashi S., Takada K., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Purification and characterization of furin, a Kex2-like processing endoprotease, produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16094–16099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Bleasby A. J., Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Apr;8(2):189–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch H. H., Schiffer H. H., Müller H., Wolf D. H. Biogenesis of the yeast vacuole (lysosome). Mutation in the active site of the vacuolar serine proteinase yscB abolishes proteolytic maturation of its 73-kDa precursor to the 41.5-kDa pro-enzyme and a newly detected 41-kDa peptide. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 1;203(3):641–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura H., Inouye M. In vitro processing of pro-subtilisin produced in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12959–12963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura H., Takagi H., Inouye M. Requirement of pro-sequence for the production of active subtilisin E in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7859–7864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Brake A., Blair L., Kunisawa R., Thorner J. Isolation of the putative structural gene for the lysine-arginine-cleaving endopeptidase required for processing of yeast prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1075–1089. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Schekman R., Thorner J. Glycosylation and processing of prepro-alpha-factor through the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer M. C., Tucker J. E., Joh R., Landsberg K. E., Saltman D., Barr P. J. Identification of a second human subtilisin-like protease gene in the fes/fps region of chromosome 15. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;10(10):757–769. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner J., Chun J., O'Bryan L., Axel R. Prohormone processing in Xenopus oocytes: characterization of cleavage signals and cleavage enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11393–11397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduc R., Molloy S. S., Thorne B. A., Thomas G. Activation of human furin precursor processing endoprotease occurs by an intramolecular autoproteolytic cleavage. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14304–14308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackin R. B., Noe B. D., Spiess J. Identification of a somatostatin-14-generating propeptide converting enzyme as a member of the kex2/furin/PC family. Endocrinology. 1991 Oct;129(4):2263–2265. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-4-2263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno K., Nakamura T., Ohshima T., Tanaka S., Matsuo H. Characterization of KEX2-encoded endopeptidase from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 28;159(1):305–311. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92438-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno K., Nakamura T., Ohshima T., Tanaka S., Matsuo H. Yeast KEX2 genes encodes an endopeptidase homologous to subtilisin-like serine proteases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):246–254. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80832-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa T., Hosaka M., Torii S., Watanabe T., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Identification and functional expression of a new member of the mammalian Kex2-like processing endoprotease family: its striking structural similarity to PACE4. J Biochem. 1993 Feb;113(2):132–135. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Kim W. S., Torii S., Hosaka M., Nakagawa T., Ikemizu J., Baba T., Murakami K. Identification of the fourth member of the mammalian endoprotease family homologous to the yeast Kex2 protease. Its testis-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5897–5900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebes V. L., Jones E. W. Activation of the proteinase B precursor of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by autocatalysis and by an internal sequence. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):22851–22857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Ferro S., Schekman R. Order of events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta Y., Hojo H., Aimoto S., Kobayashi T., Zhu X., Jordan F., Inouye M. Pro-peptide as an intramolecular chaperone: renaturation of denatured subtilisin E with a synthetic pro-peptide [corrected]. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1507–1510. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power S. D., Adams R. M., Wells J. A. Secretion and autoproteolytic maturation of subtilisin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3096–3100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redding K., Holcomb C., Fuller R. S. Immunolocalization of Kex2 protease identifies a putative late Golgi compartment in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):527–538. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehemtulla A., Dorner A. J., Kaufman R. J. Regulation of PACE propeptide-processing activity: requirement for a post-endoplasmic reticulum compartment and autoproteolytic activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8235–8239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Creemers J. W., Pauli I. G., Kurzik-Dumke U., Rentrop M., Gateff E. A., Leunissen J. A., Van de Ven W. J. Cloning and functional expression of Dfurin2, a subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme of Drosophila melanogaster with multiple repeats of a cysteine motif. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17208–17215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Pauli I. G., Zhang Y., van de Ven W. J. cDNA sequence of a Drosophila melanogaster gene, Dfur1, encoding a protein structurally related to the subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme furin. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 9;289(2):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81052-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeboth P. G., Heim J. In-vitro processing of yeast alpha-factor leader fusion proteins using a soluble yscF (Kex2) variant. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1991 Sep;35(6):771–776. doi: 10.1007/BF00169893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Marcinkiewicz M., Benjannet S., Gaspar L., Beaubien G., Mattei M. G., Lazure C., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. Cloning and primary sequence of a mouse candidate prohormone convertase PC1 homologous to PC2, Furin, and Kex2: distinct chromosomal localization and messenger RNA distribution in brain and pituitary compared to PC2. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):111–122. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siezen R. J., de Vos W. M., Leunissen J. A., Dijkstra B. W. Homology modelling and protein engineering strategy of subtilases, the family of subtilisin-like serine proteinases. Protein Eng. 1991 Oct;4(7):719–737. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.7.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Avruch A. S., LaMendola J., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F. Identification of a cDNA encoding a second putative prohormone convertase related to PC2 in AtT20 cells and islets of Langerhans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):340–344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F. Identification of a human insulinoma cDNA encoding a novel mammalian protein structurally related to the yeast dibasic processing protease Kex2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):2997–3000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Smeekens S. P., Ohagi S., Chan S. J. The new enzymology of precursor processing endoproteases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23435–23438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanguy-Rougeau C., Wésolowski-Louvel M., Fukuhara H. The Kluyveromyces lactis KEX1 gene encodes a subtilisin-type serine proteinase. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 18;234(2):464–470. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80139-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Ferrari E., Henner D. J., Estell D. A., Chen E. Y. Cloning, sequencing, and secretion of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subtilisin in Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7911–7925. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. A., Fuller R. S. Posttranslational processing of the prohormone-cleaving Kex2 protease in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae secretory pathway. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(2):297–307. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. A., Redding K., Wright R., Fuller R. S. Mutation of a tyrosine localization signal in the cytosolic tail of yeast Kex2 protease disrupts Golgi retention and results in default transport to the vacuole. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Dec;3(12):1353–1371. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.12.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X. L., Ohta Y., Jordan F., Inouye M. Pro-sequence of subtilisin can guide the refolding of denatured subtilisin in an intermolecular process. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):483–484. doi: 10.1038/339483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y. S., Zhang X. Y., Cartwright C. P., Tipper D. J. Kex2-dependent processing of yeast K1 killer preprotoxin includes cleavage at ProArg-44. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):511–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ouweland A. M., van Duijnhoven H. L., Keizer G. D., Dorssers L. C., Van de Ven W. J. Structural homology between the human fur gene product and the subtilisin-like protease encoded by yeast KEX2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):664–664. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]