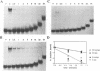
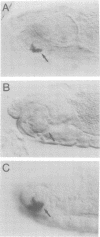
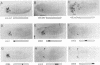
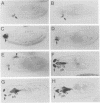
Abstract
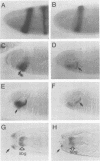
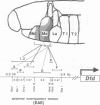
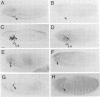
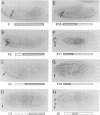
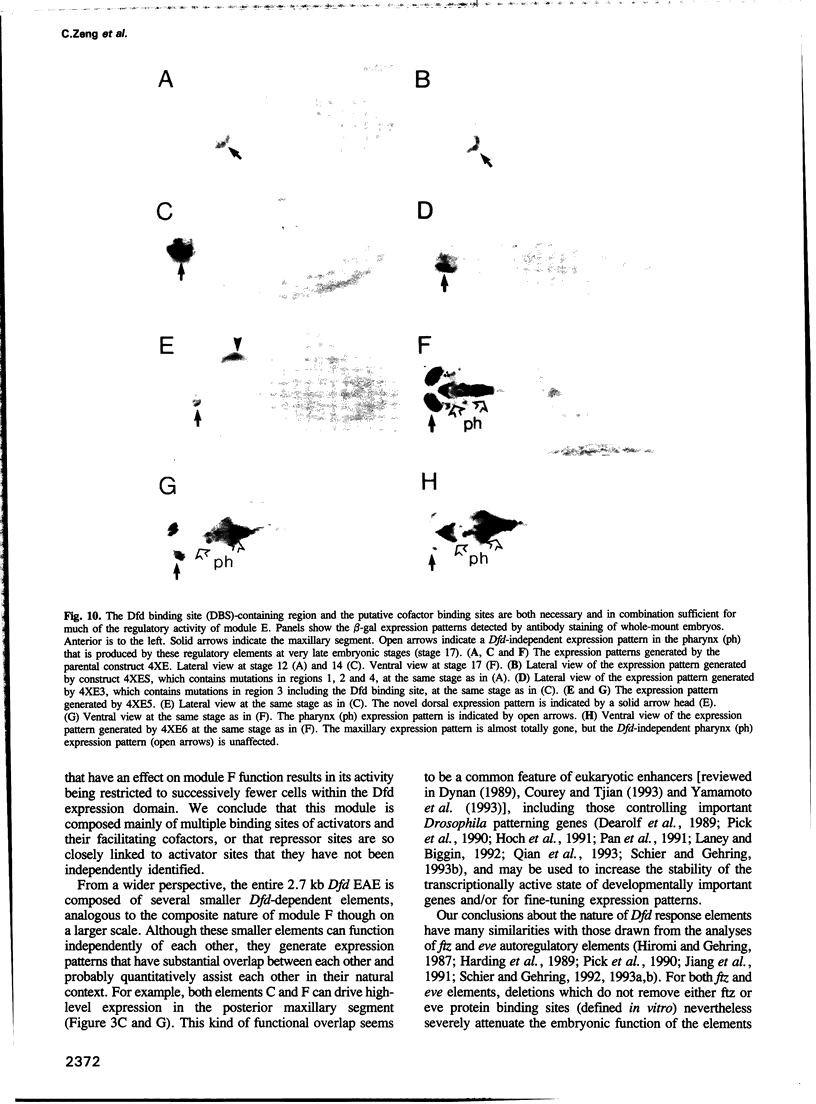
How each of the homeotic selector proteins can regulate distinct sets of DNA target elements in embryos is not understood. Here we describe a detailed functional dissection of a small element that is specifically regulated by the Deformed homeotic protein. This 120 bp element (module E) is part of a larger 2.7 kb autoregulatory enhancer that maintains Deformed (Dfd) transcription in the epidermis of the maxillary and mandibular segments of Drosophila embryos. In vitro binding assays show that module E contains only one Dfd protein binding site. Mutations in the Dfd binding site that increase or decrease its in vitro affinity for Dfd protein generate parallel changes in the regulatory activity of module E in transgenic embryos, strong evidence that the in vitro-defined binding site is a direct target of Dfd protein in embryos. However, a monomer or multimer of the Dfd binding region alone is not sufficient to supply Dfd-dependent, segment-specific reporter gene expression. An analysis of a systematic series of clustered point mutations in module E revealed that an additional region containing an imperfect inverted repeat sequence is also required for the function of this homeotic protein response element. The Dfd binding site and the putative cofactor binding site(s) in the region of the inverted repeat are both necessary and in combination sufficient for the function of module E.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter M., Schier A., Gehring W. J. Homeodomain proteins and the regulation of gene expression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;2(3):485–495. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appel B., Sakonju S. Cell-type-specific mechanisms of transcriptional repression by the homeotic gene products UBX and ABD-A in Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1099–1109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05751.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awgulewitsch A., Jacobs D. Deformed autoregulatory element from Drosophila functions in a conserved manner in transgenic mice. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):341–344. doi: 10.1038/358341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender W., Akam M., Karch F., Beachy P. A., Peifer M., Spierer P., Lewis E. B., Hogness D. S. Molecular Genetics of the Bithorax Complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1983 Jul 1;221(4605):23–29. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4605.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergson C., McGinnis W. An autoregulatory enhancer element of the Drosophila homeotic gene Deformed. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4287–4297. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07877.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Tremml G. Domain of Ultrabithorax expression in Drosophila visceral mesoderm from autoregulation and exclusion. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):576–578. doi: 10.1038/333576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Perrimon N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 1993 Jun;118(2):401–415. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.2.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breen T. R., Harte P. J. Trithorax regulates multiple homeotic genes in the bithorax and Antennapedia complexes and exerts different tissue-specific, parasegment-specific and promoter-specific effects on each. Development. 1993 Jan;117(1):119–134. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. K., Mann R. S. The segment identity functions of Ultrabithorax are contained within its homeo domain and carboxy-terminal sequences. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):796–811. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouinard S., Kaufman T. C. Control of expression of the homeotic labial (lab) locus of Drosophila melanogaster: evidence for both positive and negative autogenous regulation. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1267–1280. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christen B., Bienz M. A cis-element mediating Ultrabithorax autoregulation in the central nervous system. Mech Dev. 1992 Nov;39(1-2):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90027-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. A., Stern S., Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential positive control by Oct-1 and Oct-2: activation of a transcriptionally silent motif through Oct-1 and VP16 corecruitment. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):72–83. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dearolf C. R., Topol J., Parker C. S. Transcriptional control of Drosophila fushi tarazu zebra stripe expression. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):384–398. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The sequence specificity of homeodomain-DNA interaction. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1081–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessain S., Gross C. T., Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. Antp-type homeodomains have distinct DNA binding specificities that correlate with their different regulatory functions in embryos. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):991–1002. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05138.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driever W., Thoma G., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Determination of spatial domains of zygotic gene expression in the Drosophila embryo by the affinity of binding sites for the bicoid morphogen. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):363–367. doi: 10.1038/340363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duboule D., Dollé P. The structural and functional organization of the murine HOX gene family resembles that of Drosophila homeotic genes. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1497–1505. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S. Modularity in promoters and enhancers. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., Young K. E., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Optimal DNA sequence recognition by the Ultrabithorax homeodomain of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1179–1186. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Differential DNA sequence recognition is a determinant of specificity in homeotic gene action. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4059–4072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05499.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. A., Giniger E., Maniatis T., Ptashne M. GAL4 activates transcription in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):853–856. doi: 10.1038/332853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flegel W. A., Singson A. W., Margolis J. S., Bang A. G., Posakony J. W., Murre C. Dpbx, a new homeobox gene closely related to the human proto-oncogene pbx1 molecular structure and developmental expression. Mech Dev. 1993 May;41(2-3):155–161. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90045-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florence B., Handrow R., Laughon A. DNA-binding specificity of the fushi tarazu homeodomain. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3613–3623. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukubo-Tokunaga K., Flister S., Gehring W. J. Functional specificity of the Antennapedia homeodomain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6360–6364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. The homeobox in perspective. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Aug;17(8):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90434-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goutte C., Johnson A. D. Yeast a1 and alpha 2 homeodomain proteins form a DNA-binding activity with properties distinct from those of either protein. J Mol Biol. 1993 Oct 5;233(3):359–371. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R. The murine and Drosophila homeobox gene complexes have common features of organization and expression. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han W., Yu Y., Altan N., Pick L. Multiple proteins interact with the fushi tarazu proximal enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5549–5559. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding K., Hoey T., Warrior R., Levine M. Autoregulatory and gap gene response elements of the even-skipped promoter of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1205–1212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Scott M. P. What determines the specificity of action of Drosophila homeodomain proteins? Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):883–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90492-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., England B., Tjian R. Characterization of Drosophila transcription factors that activate the tandem promoters of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):965–977. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Gehring W. J. Regulation and function of the Drosophila segmentation gene fushi tarazu. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):963–974. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch M., Gerwin N., Taubert H., Jäckle H. Competition for overlapping sites in the regulatory region of the Drosophila gene Krüppel. Science. 1992 Apr 3;256(5053):94–97. doi: 10.1126/science.1348871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch M., Seifert E., Jäckle H. Gene expression mediated by cis-acting sequences of the Krüppel gene in response to the Drosophila morphogens bicoid and hunchback. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2267–2278. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07763.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Levine M. Divergent homeo box proteins recognize similar DNA sequences in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):858–861. doi: 10.1038/332858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine K. D., Helfand S. L., Hogness D. S. The large upstream control region of the Drosophila homeotic gene Ultrabithorax. Development. 1991 Feb;111(2):407–424. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack T., McGinnis W. Establishment of the Deformed expression stripe requires the combinatorial action of coordinate, gap and pair-rule proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1187–1198. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08226.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Hoey T., Levine M. Autoregulation of a segmentation gene in Drosophila: combinatorial interaction of the even-skipped homeo box protein with a distal enhancer element. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):265–277. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Levine M. Binding affinities and cooperative interactions with bHLH activators delimit threshold responses to the dorsal gradient morphogen. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90402-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Herskowitz I. A repressor (MAT alpha 2 Product) and its operator control expression of a set of cell type specific genes in yeast. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):237–247. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis J. A. Spatial and temporal control elements of the Drosophila engrailed gene. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):433–443. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman T. C., Lewis R., Wakimoto B. Cytogenetic Analysis of Chromosome 3 in DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER: The Homoeotic Gene Complex in Polytene Chromosome Interval 84a-B. Genetics. 1980 Jan;94(1):115–133. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman T. C., Seeger M. A., Olsen G. Molecular and genetic organization of the antennapedia gene complex of Drosophila melanogaster. Adv Genet. 1990;27:309–362. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennison J. A. Transcriptional activation of Drosophila homeotic genes from distant regulatory elements. Trends Genet. 1993 Mar;9(3):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90227-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R. Mouse Hox genetic functions. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Aug;3(4):621–625. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90098-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. A homeodomain substitution changes the regulatory specificity of the deformed protein in Drosophila embryos. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):563–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. Altering the regulatory targets of the Deformed protein in Drosophila embryos by substituting the Abdominal-B homeodomain. Mech Dev. 1990 Dec;33(1):83–93. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(90)90137-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. Autoregulation of a Drosophila homeotic selector gene. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamka M. L., Boulet A. M., Sakonju S. Ectopic expression of UBX and ABD-B proteins during Drosophila embryogenesis: competition, not a functional hierarchy, explains phenotypic suppression. Development. 1992 Dec;116(4):841–854. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.4.841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laney J. D., Biggin M. D. zeste, a nonessential gene, potently activates Ultrabithorax transcription in the Drosophila embryo. Genes Dev. 1992 Aug;6(8):1531–1541. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.8.1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A. DNA binding specificity of homeodomains. Biochemistry. 1991 Dec 3;30(48):11357–11367. doi: 10.1021/bi00112a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. B. A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila. Nature. 1978 Dec 7;276(5688):565–570. doi: 10.1038/276565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin S. M., När A. M., Kalla K. A., Sack R. A., Rosenfeld M. G. Identification of a novel zinc finger protein binding a conserved element critical for Pit-1-dependent growth hormone gene expression. Genes Dev. 1993 Sep;7(9):1674–1687. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.9.1674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaffey J. W., Jones D. F., Hickel J. A., Griswold C. M. Identification and characterization of a gene activated by the deformed homeoprotein. Development. 1993 May;118(1):203–214. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier D., Preiss A., Powell J. R. Regulation of the segmentation gene fushi tarazu has been functionally conserved in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3957–3966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07616.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak A., Johnson A. D. The carboxy-terminal tail of the homeo domain protein alpha 2 is required for function with a second homeo domain protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Oct;7(10):1862–1870. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.10.1862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
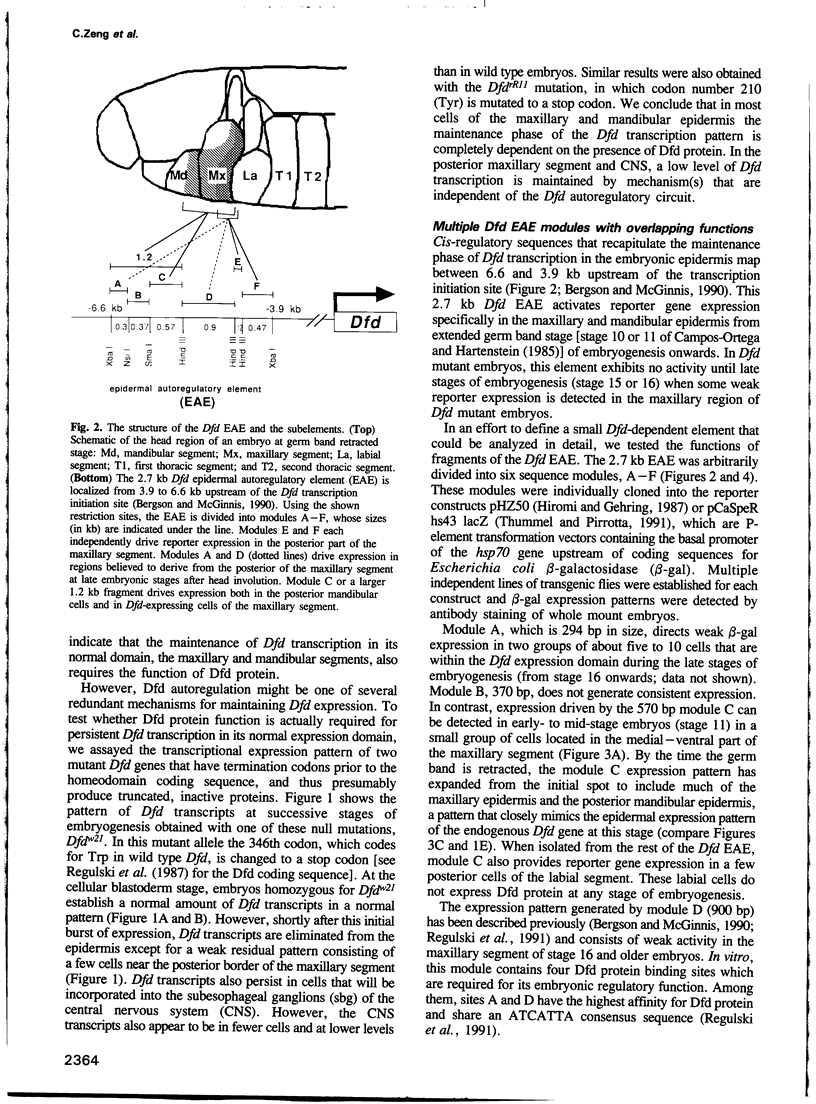
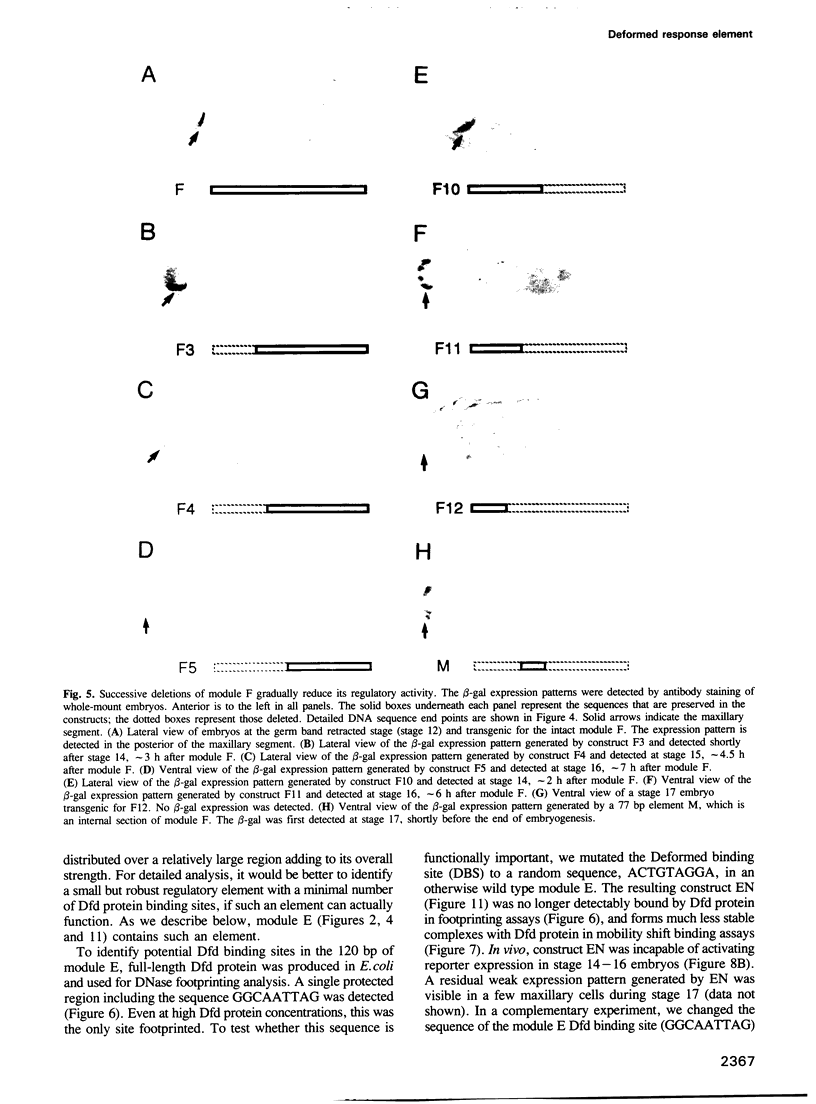
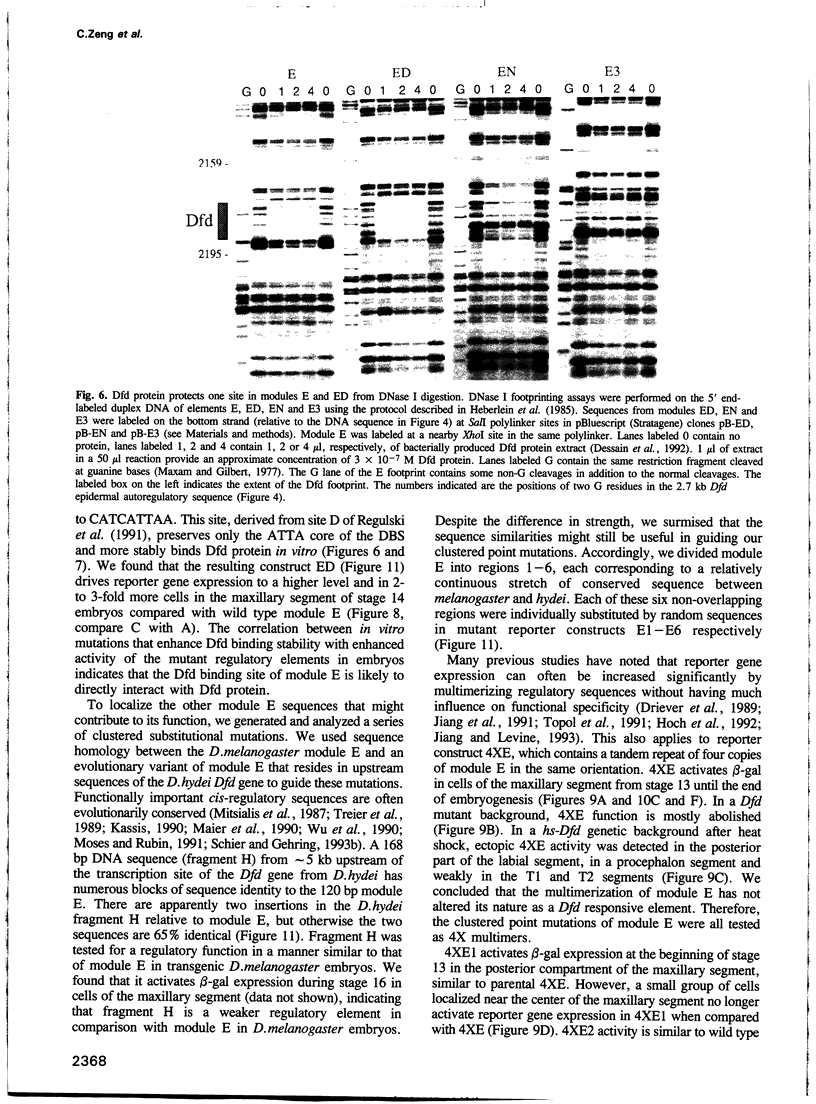
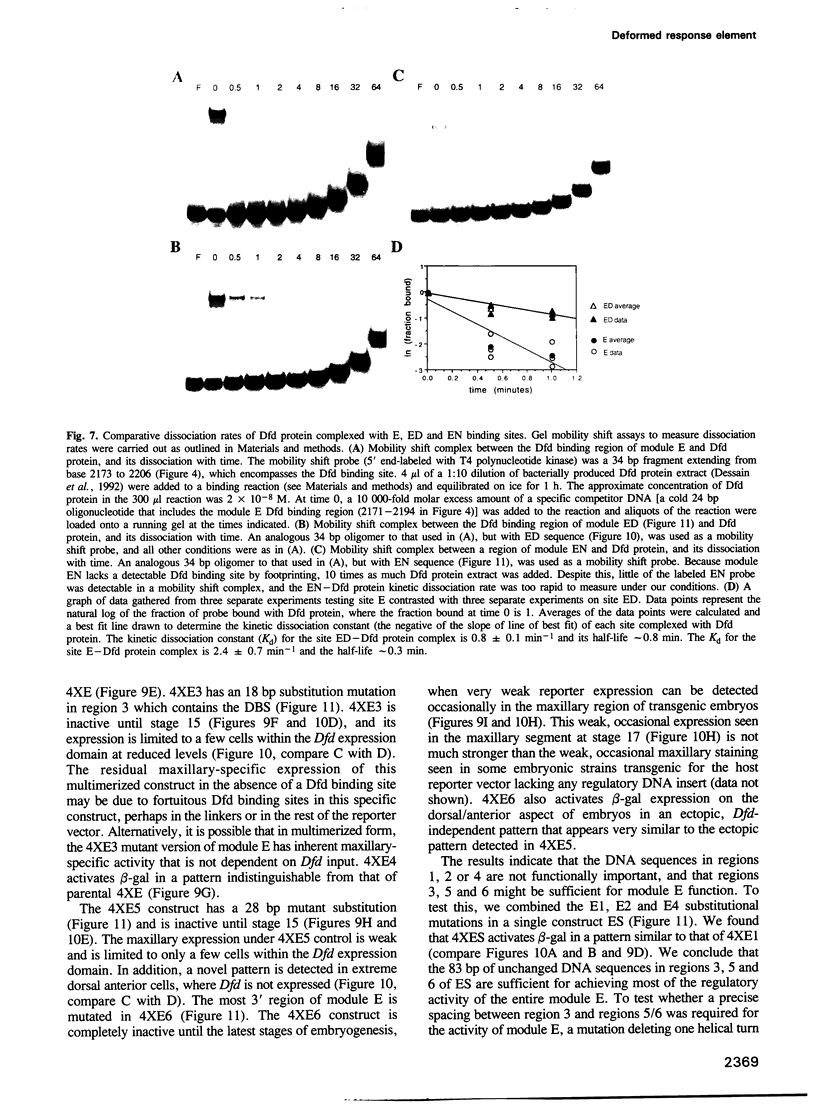
- McGinnis W., Jack T., Chadwick R., Regulski M., Bergson C., McGinnis N., Kuziora M. A. Establishment and maintenance of position-specific expression of the Drosophila homeotic selector gene Deformed. Adv Genet. 1990;27:363–402. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Krumlauf R. Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):283–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90471-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill V. K., Turner F. R., Kaufman T. C. A genetic and developmental analysis of mutations in the Deformed locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1987 Aug;122(2):379–395. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsialis S. A., Spoerel N., Leviten M., Kafatos F. C. A short 5'-flanking DNA region is sufficient for developmentally correct expression of moth chorion genes in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7987–7991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morata G. Homeotic genes of Drosophila. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Aug;3(4):606–614. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses K., Rubin G. M. Glass encodes a site-specific DNA-binding protein that is regulated in response to positional signals in the developing Drosophila eye. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):583–593. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hara E., Cohen B., Cohen S. M., McGinnis W. Distal-less is a downstream gene of Deformed required for ventral maxillary identity. Development. 1993 Mar;117(3):847–856. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.3.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan D. J., Huang J. D., Courey A. J. Functional analysis of the Drosophila twist promoter reveals a dorsal-binding ventral activator region. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1892–1901. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peifer M., Wieschaus E. Mutations in the Drosophila gene extradenticle affect the way specific homeo domain proteins regulate segmental identity. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1209–1223. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Herskowitz I. Characterization of the yeast SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 genes, which encode a global activator of transcription. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90192-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick L., Schier A., Affolter M., Schmidt-Glenewinkel T., Gehring W. J. Analysis of the ftz upstream element: germ layer-specific enhancers are independently autoregulated. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1224–1239. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz J. L., Kristie T. M., Sharp P. A. Recognition of the surface of a homeo domain protein. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2047–2057. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian S., Capovilla M., Pirrotta V. Molecular mechanisms of pattern formation by the BRE enhancer of the Ubx gene. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3865–3877. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06065.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Solis R., Zheng H., Whiting J., Krumlauf R., Bradley A. Hoxb-4 (Hox-2.6) mutant mice show homeotic transformation of a cervical vertebra and defects in the closure of the sternal rudiments. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):279–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90229-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauskolb C., Peifer M., Wieschaus E. extradenticle, a regulator of homeotic gene activity, is a homolog of the homeobox-containing human proto-oncogene pbx1. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1101–1112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90731-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regulski M., Dessain S., McGinnis N., McGinnis W. High-affinity binding sites for the Deformed protein are required for the function of an autoregulatory enhancer of the Deformed gene. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):278–286. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regulski M., McGinnis N., Chadwick R., McGinnis W. Developmental and molecular analysis of Deformed; a homeotic gene controlling Drosophila head development. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):767–777. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04819.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schier A. F., Gehring W. J. Analysis of a fushi tarazu autoregulatory element: multiple sequence elements contribute to enhancer activity. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1111–1119. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schier A. F., Gehring W. J. Direct homeodomain-DNA interaction in the autoregulation of the fushi tarazu gene. Nature. 1992 Apr 30;356(6372):804–807. doi: 10.1038/356804a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schier A. F., Gehring W. J. Functional specificity of the homeodomain protein fushi tarazu: the role of DNA-binding specificity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1450–1454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serfling E. Autoregulation--a common property of eukaryotic transcription factors? Trends Genet. 1989 May;5(5):131–133. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. L., Johnson A. D. A molecular mechanism for combinatorial control in yeast: MCM1 protein sets the spacing and orientation of the homeodomains of an alpha 2 dimer. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90212-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Herr W. The herpes simplex virus trans-activator VP16 recognizes the Oct-1 homeo domain: evidence for a homeo domain recognition subdomain. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2555–2566. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Tanaka M., Herr W. The Oct-1 homoeodomain directs formation of a multiprotein-DNA complex with the HSV transactivator VP16. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):624–630. doi: 10.1038/341624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G. Genes controlling segmental specification in the Drosophila thorax. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7380–7384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G., Struhl K., Macdonald P. M. The gradient morphogen bicoid is a concentration-dependent transcriptional activator. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1259–1273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thüringer F., Bienz M. Indirect autoregulation of a homeotic Drosophila gene mediated by extracellular signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3899–3903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topol J., Dearolf C. R., Prakash K., Parker C. S. Synthetic oligonucleotides recreate Drosophila fushi tarazu zebra-stripe expression. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):855–867. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treier M., Pfeifle C., Tautz D. Comparison of the gap segmentation gene hunchback between Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila virilis reveals novel modes of evolutionary change. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1517–1525. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremml G., Bienz M. Induction of labial expression in the Drosophila endoderm: response elements for dpp signalling and for autoregulation. Development. 1992 Oct;116(2):447–456. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.2.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vachon G., Cohen B., Pfeifle C., McGuffin M. E., Botas J., Cohen S. M. Homeotic genes of the Bithorax complex repress limb development in the abdomen of the Drosophila embryo through the target gene Distal-less. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):437–450. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90513-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijk M. A., Voorhoeve P. M., Murre C. Pbx1 is converted into a transcriptional activator upon acquiring the N-terminal region of E2A in pre-B-cell acute lymphoblastoid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6061–6065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Kassis J. A., O'Farrell P. H. A synthetic homeodomain binding site acts as a cell type specific, promoter specific enhancer in Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2573–2578. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. B., Müller-Immergluck M. M., Austin J., Robinson N. T., Chisholm A., Kenyon C. A homeotic gene cluster patterns the anteroposterior body axis of C. elegans. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):29–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90292-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedeen C., Harding K., Levine M. Spatial regulation of Antennapedia and bithorax gene expression by the Polycomb locus in Drosophila. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):739–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90840-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Y., Mote J., Jr, Brennan M. D. Tissue-specific expression phenotypes of Hawaiian Drosophila Adh genes in Drosophila melanogaster transformants. Genetics. 1990 Jul;125(3):599–610. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue D., Finney M., Ruvkun G., Chalfie M. Regulation of the mec-3 gene by the C.elegans homeoproteins UNC-86 and MEC-3. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4969–4979. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05604.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue D., Tu Y., Chalfie M. Cooperative interactions between the Caenorhabditis elegans homeoproteins UNC-86 and MEC-3. Science. 1993 Sep 3;261(5126):1324–1328. doi: 10.1126/science.8103239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng W., Andrew D. J., Mathies L. D., Horner M. A., Scott M. P. Ectopic expression and function of the Antp and Scr homeotic genes: the N terminus of the homeodomain is critical to functional specificity. Development. 1993 Jun;118(2):339–352. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.2.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink B., Engström Y., Gehring W. J., Paro R. Direct interaction of the Polycomb protein with Antennapedia regulatory sequences in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):153–162. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07931.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]