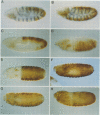
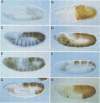
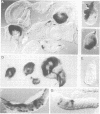
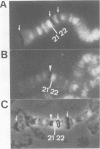
Abstract
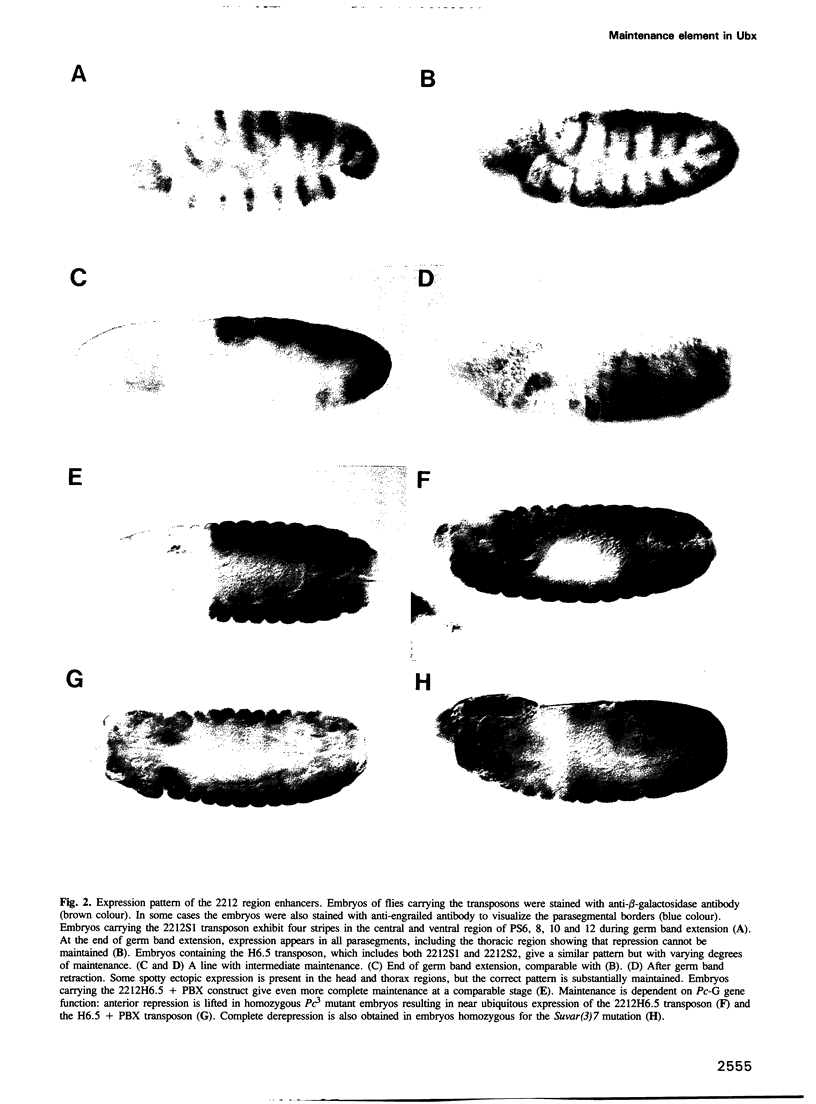
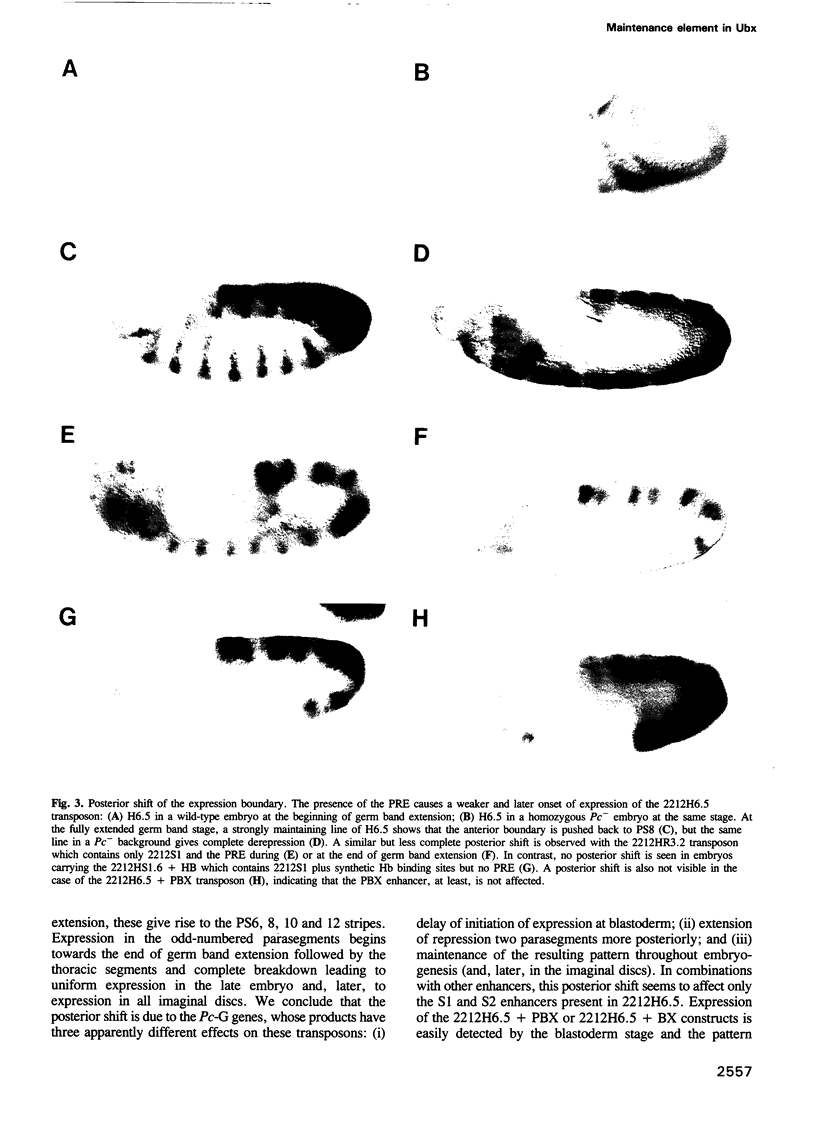
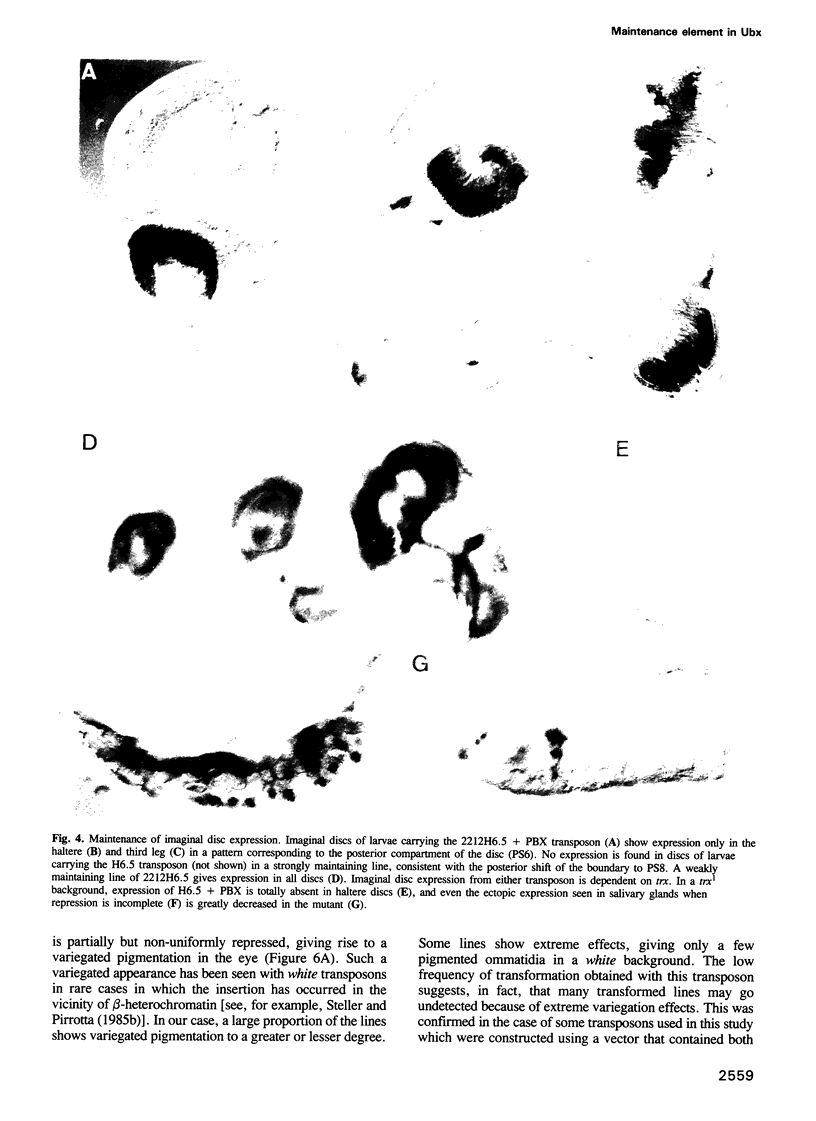
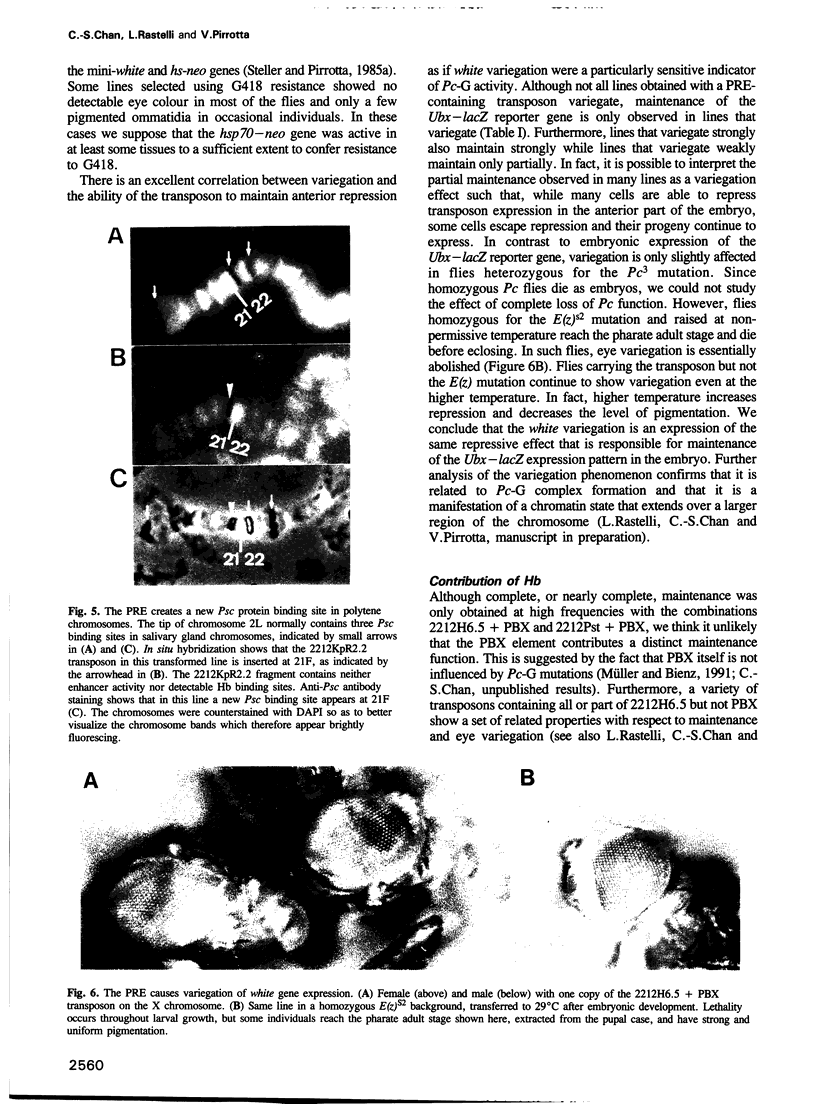
Segmentation genes provide the signals for the activation and regulation of homeotic genes in Drosophila but cannot maintain the resulting pattern of expression because their activity ceases halfway through embryogenesis. Maintenance of the pattern is due to the Polycomb group of genes (Pc-G) and the trithorax group of genes (trx-G), responsible for the persistence of the active or repressed state of homeotic genes. We have identified a regulatory element in the Ubx gene that responds to Pc-G and trx-G genes. Transposons carrying this element create new binding sites for Pc-G products in the polytene chromosomes. This Pc-G maintenance element (PRE), establishes a repressive complex that keeps enhancers repressed in cells in which they were originally repressed and maintains this state through many cell divisions. The trx-G products stimulate the expression of enhancers in cells in which they were originally active. This mechanism is responsible for the correct regulation of imaginal disc enhancers, which lack themselves antero-posterior positional information. The PRE also causes severe variegation of the mini-white gene present in the transposon, a phenomenon very similar to heterochromatic position-effect variegation. The significance of this mechanism for homeotic gene regulation is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B., Sternglanz R. Gene expression. Chromatin contract to silence. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):193–194. doi: 10.1038/344193a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellen H. J., O'Kane C. J., Wilson C., Grossniklaus U., Pearson R. K., Gehring W. J. P-element-mediated enhancer detection: a versatile method to study development in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1288–1300. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender W., Akam M., Karch F., Beachy P. A., Peifer M., Spierer P., Lewis E. B., Hogness D. S. Molecular Genetics of the Bithorax Complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1983 Jul 1;221(4605):23–29. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4605.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M. Molecular mechanisms of determination in Drosophila. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;4(6):955–961. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90124-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCamillis M., Cheng N. S., Pierre D., Brock H. W. The polyhomeotic gene of Drosophila encodes a chromatin protein that shares polytene chromosome-binding sites with Polycomb. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):223–232. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan I. The bithorax complex. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:285–319. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dura J. M., Ingham P. Tissue- and stage-specific control of homeotic and segmentation gene expression in Drosophila embryos by the polyhomeotic gene. Development. 1988 Aug;103(4):733–741. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.4.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg J. C., James T. C., Foster-Hartnett D. M., Hartnett T., Ngan V., Elgin S. C. Mutation in a heterochromatin-specific chromosomal protein is associated with suppression of position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9923–9927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauvarque M. O., Dura J. M. polyhomeotic regulatory sequences induce developmental regulator-dependent variegation and targeted P-element insertions in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1508–1520. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke A., DeCamillis M., Zink D., Cheng N., Brock H. W., Paro R. Polycomb and polyhomeotic are constituents of a multimeric protein complex in chromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2941–2950. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hama C., Ali Z., Kornberg T. B. Region-specific recombination and expression are directed by portions of the Drosophila engrailed promoter. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1079–1093. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heemskerk J., DiNardo S., Kostriken R., O'Farrell P. H. Multiple modes of engrailed regulation in the progression towards cell fate determination. Nature. 1991 Aug 1;352(6334):404–410. doi: 10.1038/352404a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine K. D., Helfand S. L., Hogness D. S. The large upstream control region of the Drosophila homeotic gene Ultrabithorax. Development. 1991 Feb;111(2):407–424. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. S., Gelbart W. M. Genetic analysis of the enhancer of zeste locus and its role in gene regulation in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1990 Sep;126(1):185–199. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis J. A., VanSickle E. P., Sensabaugh S. M. A fragment of engrailed regulatory DNA can mediate transvection of the white gene in Drosophila. Genetics. 1991 Aug;128(4):751–761. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.4.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennison J. A., Russell M. A. Dosage-Dependent Modifiers of Homoeotic Mutations in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1987 May;116(1):75–86. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence P. A., Johnston P. Pattern formation in the Drosophila embryo: allocation of cells to parasegments by even-skipped and fushi tarazu. Development. 1989 Apr;105(4):761–767. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.4.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locke J., Kotarski M. A., Tartof K. D. Dosage-dependent modifiers of position effect variegation in Drosophila and a mass action model that explains their effect. Genetics. 1988 Sep;120(1):181–198. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E. C., Adler P. N. The Polycomb group gene Posterior Sex Combs encodes a chromosomal protein. Development. 1993 Feb;117(2):641–655. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.2.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Krumlauf R. Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):283–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90471-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller J., Bienz M. Long range repression conferring boundaries of Ultrabithorax expression in the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3147–3155. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04876.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlando V., Paro R. Mapping Polycomb-repressed domains in the bithorax complex using in vivo formaldehyde cross-linked chromatin. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1187–1198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90328-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paro R., Hogness D. S. The Polycomb protein shares a homologous domain with a heterochromatin-associated protein of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):263–267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paro R. Imprinting a determined state into the chromatin of Drosophila. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):416–421. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90303-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelegri F., Lehmann R. A role of polycomb group genes in the regulation of gap gene expression in Drosophila. Genetics. 1994 Apr;136(4):1341–1353. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.4.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian S., Capovilla M., Pirrotta V. Molecular mechanisms of pattern formation by the BRE enhancer of the Ubx gene. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3865–3877. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06065.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian S., Capovilla M., Pirrotta V. The bx region enhancer, a distant cis-control element of the Drosophila Ubx gene and its regulation by hunchback and other segmentation genes. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1415–1425. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07662.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastelli L., Chan C. S., Pirrotta V. Related chromosome binding sites for zeste, suppressors of zeste and Polycomb group proteins in Drosophila and their dependence on Enhancer of zeste function. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1513–1522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05795.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinitz J., Levine M. Control of the initiation of homeotic gene expression by the gap genes giant and tailless in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1990 Jul;140(1):57–72. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90053-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J., Chiang A., Bender W., Shimell M. J., O'Connor M. Elements of the Drosophila bithorax complex that mediate repression by Polycomb group products. Dev Biol. 1993 Jul;158(1):131–144. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J., Peifer M., Bender W., O'Connor M. Regulatory elements of the bithorax complex that control expression along the anterior-posterior axis. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3945–3956. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. A transposable P vector that confers selectable G418 resistance to Drosophila larvae. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):167–171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. Expression of the Drosophila white gene under the control of the hsp70 heat shock promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3765–3772. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. A., Lehmann R. A gap gene, hunchback, regulates the spatial expression of Ultrabithorax. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):311–321. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90453-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. T. Transvection, nuclear structure, and chromatin proteins. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):587–590. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang C. C., Bienz M. Segmental determination in Drosophila conferred by hunchback (hb), a repressor of the homeotic gene Ultrabithorax (Ubx). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7511–7515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]