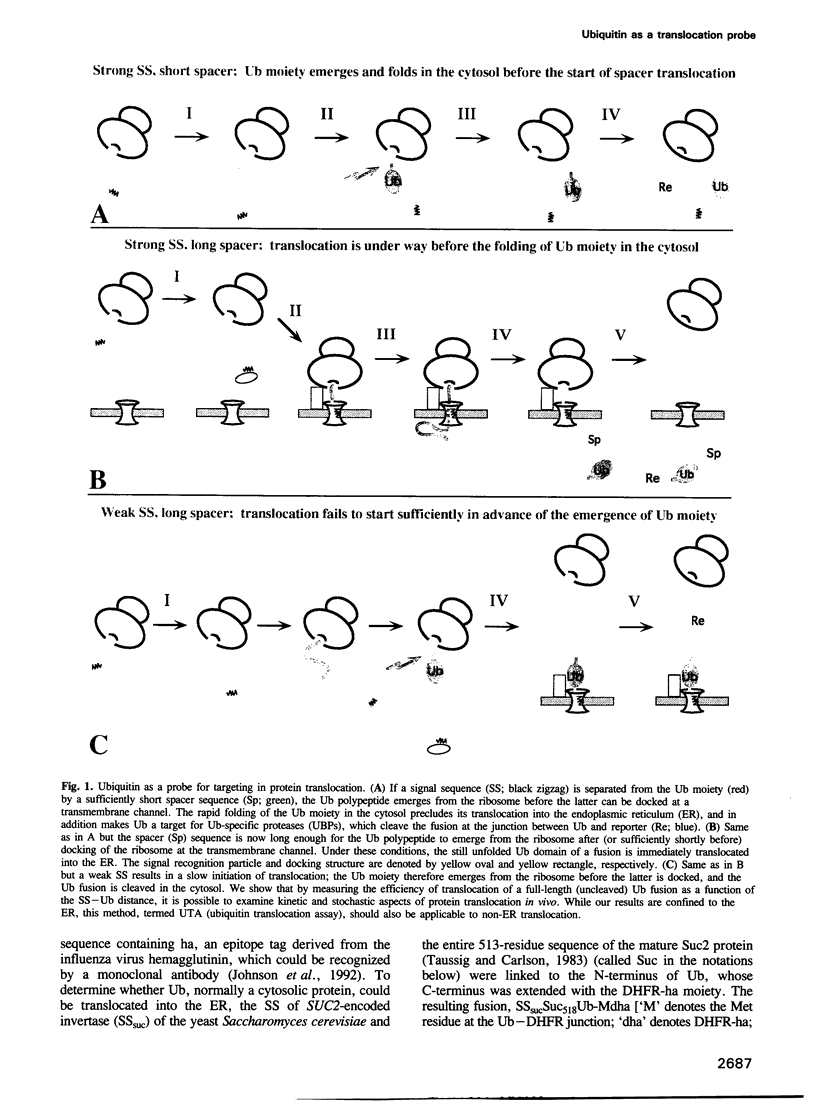
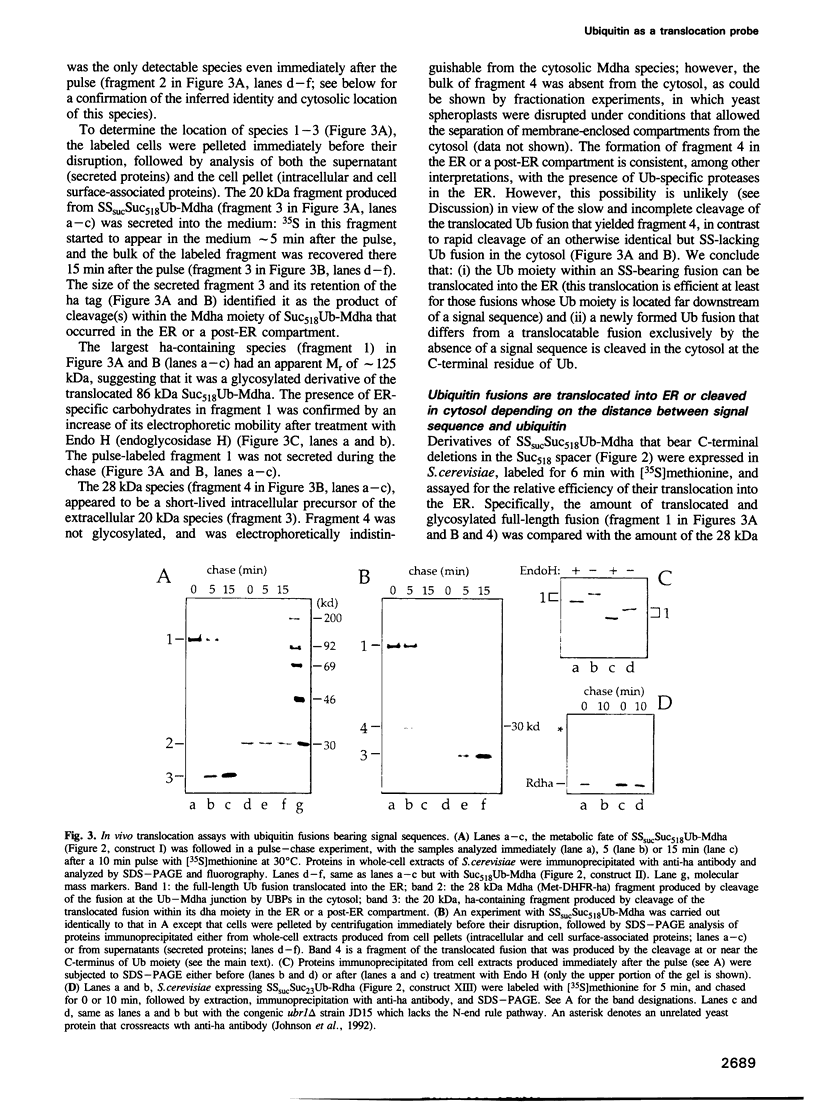
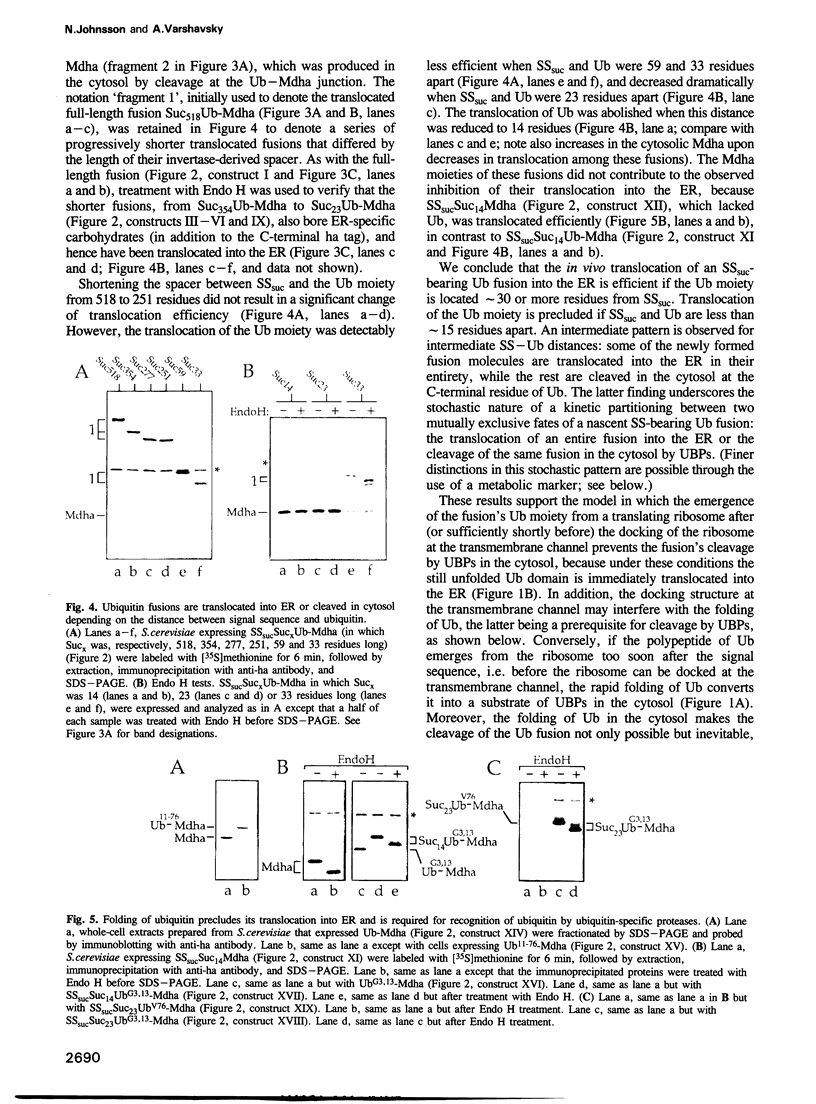
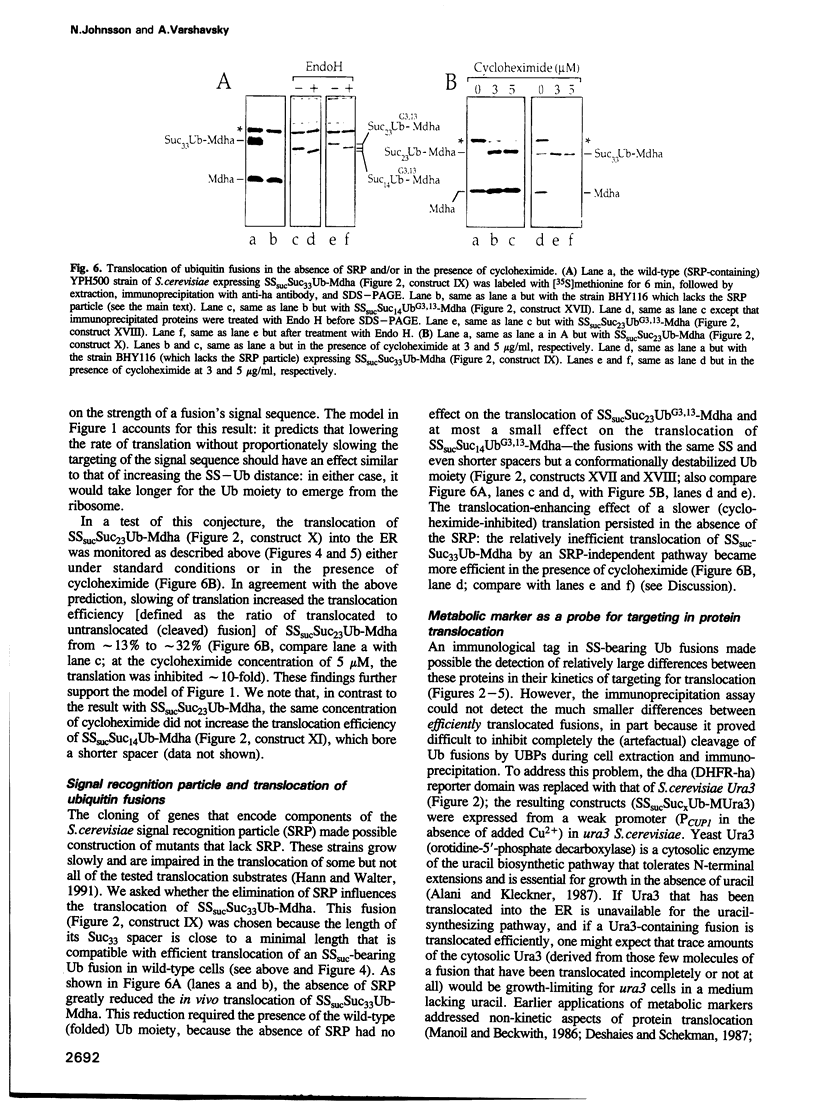
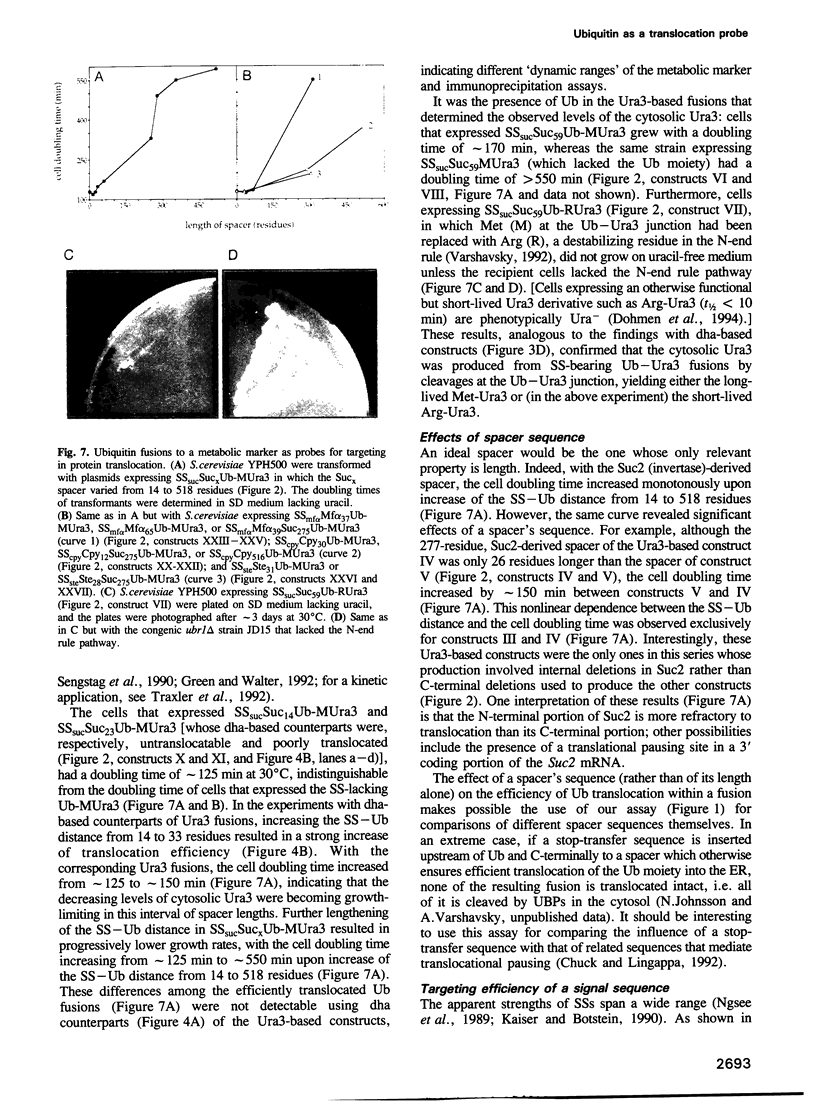
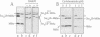Abstract
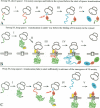
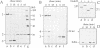
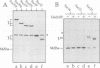
We describe a new way to analyze targeting in protein translocation. A fusion in which ubiquitin (Ub) is positioned between a signal sequence and a reporter domain is cleaved by Ub-specific proteases (UBPs) in the cytosol unless the fusion can 'escape' into a compartment such as the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The critical step involves rapid folding of the newly formed Ub moiety, which precludes its translocation and makes possible its cleavage by UBPs. However, if a sufficiently long spacer is present between the signal sequence and Ub, then by the time the Ub polypeptide emerges from the ribosome, the latter is already docked at the transmembrane channel, allowing the translocation of both the Ub and reporter domains of the fusion into the ER. We show that Ub fusions can be used as in vivo probes for kinetic and stochastic aspects of targeting in protein translocation, for distinguishing directly between cotranslational and posttranslational translocation, and for comparing the strengths of different signal sequences. This method should also be applicable to non-ER translocation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alani E., Kleckner N. A new type of fusion analysis applicable to many organisms: protein fusions to the URA3 gene of yeast. Genetics. 1987 Sep;117(1):5–12. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson H., von Heijne G. A 30-residue-long "export initiation domain" adjacent to the signal sequence is critical for protein translocation across the inner membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9751–9754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmair A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):179–186. doi: 10.1126/science.3018930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. T., Tobias J. W., Varshavsky A. Ubiquitin-specific proteases of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cloning of UBP2 and UBP3, and functional analysis of the UBP gene family. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23364–23375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel B., Wünning I., Varshavsky A. The recognition component of the N-end rule pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3179–3189. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1496–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. S., Roder H. Early hydrogen-bonding events in the folding reaction of ubiquitin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2017–2021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuck S. L., Lingappa V. R. Pause transfer: a topogenic sequence in apolipoprotein B mediates stopping and restarting of translocation. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):9–21. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90202-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Schekman R. A yeast mutant defective at an early stage in import of secretory protein precursors into the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):633–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohmen R. J., Madura K., Bartel B., Varshavsky A. The N-end rule is mediated by the UBC2(RAD6) ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7351–7355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohmen R. J., Strasser A. W., Höner C. B., Hollenberg C. P. An efficient transformation procedure enabling long-term storage of competent cells of various yeast genera. Yeast. 1991 Oct;7(7):691–692. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohmen R. J., Wu P., Varshavsky A. Heat-inducible degron: a method for constructing temperature-sensitive mutants. Science. 1994 Mar 4;263(5151):1273–1276. doi: 10.1126/science.8122109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Bartel B., Varshavsky A. The tails of ubiquitin precursors are ribosomal proteins whose fusion to ubiquitin facilitates ribosome biogenesis. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):394–401. doi: 10.1038/338394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierasch L. M. Signal sequences. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):923–930. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Lampen J. O. Beta-D-fructofuranoside fructohydrolase from yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:504–511. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Walter P. C-terminal sequences can inhibit the insertion of membrane proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):276–282. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann B. C., Poritz M. A., Walter P. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe contain a homologue to the 54-kD subunit of the signal recognition particle that in S. cerevisiae is essential for growth. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3223–3230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann B. C., Walter P. The signal recognition particle in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90577-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S. J., Randall L. L. A kinetic partitioning model of selective binding of nonnative proteins by the bacterial chaperone SecB. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):439–443. doi: 10.1126/science.1989077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Neupert W. Protein sorting to mitochondria: evolutionary conservations of folding and assembly. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):930–938. doi: 10.1126/science.2406905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S. The ubiquitin-conjugation system. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:179–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. S., Bartel B., Seufert W., Varshavsky A. Ubiquitin as a degradation signal. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):497–505. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05080.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Botstein D. Efficiency and diversity of protein localization by random signal sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3163–3173. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchler K., Sterne R. E., Thorner J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae STE6 gene product: a novel pathway for protein export in eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):3973–3984. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Herskowitz I. Structure of a yeast pheromone gene (MF alpha): a putative alpha-factor precursor contains four tandem copies of mature alpha-factor. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):933–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C., Beckwith J. Cotranslational and posttranslational protein translocation in prokaryotic systems. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:315–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. A genetic approach to analyzing membrane protein topology. Science. 1986 Sep 26;233(4771):1403–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.3529391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A. The yeast STE6 gene encodes a homologue of the mammalian multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):400–404. doi: 10.1038/340400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I. Protein translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum: a light at the end of the tunnel. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;1(6):154–159. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngsee J. K., Hansen W., Walter P., Smith M. Cassette mutagenic analysis of the yeast invertase signal peptide: effects on protein translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3400–3410. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlean P., Kuranda M. J., Albright C. F. Analysis of glycoproteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:682–697. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94050-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozkaynak E., Finley D., Solomon M. J., Varshavsky A. The yeast ubiquitin genes: a family of natural gene fusions. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1429–1439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02384.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Unity in function in the absence of consensus in sequence: role of leader peptides in export. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1156–1159. doi: 10.1126/science.2646712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport T. A. Transport of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):931–936. doi: 10.1126/science.1332192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Polypeptide chain binding proteins: catalysts of protein folding and related processes in cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):591–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz G. The protein import machinery of mitochondria. Protein Sci. 1993 Feb;2(2):141–146. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengstag C., Stirling C., Schekman R., Rine J. Genetic and biochemical evaluation of eucaryotic membrane protein topology: multiple transmembrane domains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):672–680. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrader T. E., Tobias J. W., Varshavsky A. The N-end rule in Escherichia coli: cloning and analysis of the leucyl, phenylalanyl-tRNA-protein transferase gene aat. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4364–4374. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4364-4374.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The structure and insertion of integral proteins in membranes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:247–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.001335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig R., Carlson M. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast SUC2 gene for invertase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1943–1954. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias J. W., Shrader T. E., Rocap G., Varshavsky A. The N-end rule in bacteria. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1374–1377. doi: 10.1126/science.1962196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traxler B., Lee C., Boyd D., Beckwith J. The dynamics of assembly of a cytoplasmic membrane protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5339–5345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valls L. A., Hunter C. P., Rothman J. H., Stevens T. H. Protein sorting in yeast: the localization determinant of yeast vacuolar carboxypeptidase Y resides in the propeptide. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):887–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. Naming a targeting signal. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):13–15. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90202-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. The N-end rule. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):725–735. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90285-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijay-Kumar S., Bugg C. E., Cook W. J. Structure of ubiquitin refined at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):531–544. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90679-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum III. Signal recognition protein (SRP) causes signal sequence-dependent and site-specific arrest of chain elongation that is released by microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):557–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Mechanism of protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:499–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W., Driessen A. J., Hartl F. U. The enzymology of protein translocation across the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:101–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Walter P. Discrete nascent chain lengths are required for the insertion of presecretory proteins into microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(6):1211–1219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.6.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Walter P. Signal recognition particle mediates a transient elongation arrest of preprolactin in reticulocyte lysate. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2617–2622. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Transcending the impenetrable: how proteins come to terms with membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 9;947(2):307–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]