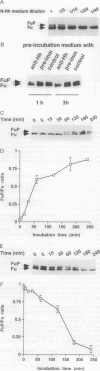
Abstract
The hedgehog gene (hh) of Drosophila melanogaster exerts both short- and long-range effects on cell patterning during development. The product of hedgehog is a secreted protein that apparently acts by triggering an intra-cellular signaling pathway, but little is known about the details of that pathway. The Drosophila gene fused (fu) encodes a serine/threonine-protein kinase that genetic experiments have implicated in signaling initiated by hedgehog. Here we report that the fused protein is phosphorylated during the course of Drosophila embryogenesis, as a result of hedgehog activity. In cell culture, phosphorylation of fused protein occurs in response to the biologically active form of hedgehog and cannot be blocked by activation of protein kinase A, which is thought to be an antagonist of signaling from hedgehog. These results suggest that fused and protein kinase A function downstream of hedgehog but in parallel pathways that eventually converge distal to fused. The reconstruction of signaling from hedgehog in cell culture should provide further access to the mechanisms by which hedgehog acts.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooker G., Harper J. F., Terasaki W. L., Moylan R. D. Radioimmunoassay of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:1–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capdevila J., Guerrero I. Targeted expression of the signaling molecule decapentaplegic induces pattern duplications and growth alterations in Drosophila wings. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 3;13(19):4459–4468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06768.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasan R., Anderson K. V. The role of easter, an apparent serine protease, in organizing the dorsal-ventral pattern of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Benjumea F. J., Cohen B., Cohen S. M. Cell interaction between compartments establishes the proximal-distal axis of Drosophila legs. Nature. 1994 Nov 10;372(6502):175–179. doi: 10.1038/372175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Porter J. A., Chiang C., Chang D. T., Beachy P. A., Tessier-Lavigne M. Long-range sclerotome induction by sonic hedgehog: direct role of the amino-terminal cleavage product and modulation by the cyclic AMP signaling pathway. Cell. 1995 May 5;81(3):457–465. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fietz M. J., Jacinto A., Taylor A. M., Alexandre C., Ingham P. W. Secretion of the amino-terminal fragment of the hedgehog protein is necessary and sufficient for hedgehog signalling in Drosophila. Curr Biol. 1995 Jun 1;5(6):643–650. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00129-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes A. J., Nakano Y., Taylor A. M., Ingham P. W. Genetic analysis of hedgehog signalling in the Drosophila embryo. Dev Suppl. 1993:115–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bellido A., Ripoll P., Morata G. Developmental compartmentalisation of the wing disk of Drosophila. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 24;245(147):251–253. doi: 10.1038/newbio245251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heemskerk J., DiNardo S. Drosophila hedgehog acts as a morphogen in cellular patterning. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):449–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M., Porter J. A., Chiang C., Chang D., Tessier-Lavigne M., Beachy P. A., Rosenthal A. Induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons by Sonic hedgehog. Neuron. 1995 Jul;15(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W., Fietz M. J. Quantitative effects of hedgehog and decapentaplegic activity on the patterning of the Drosophila wing. Curr Biol. 1995 Apr 1;5(4):432–440. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. Localized hedgehog activity controls spatial limits of wingless transcription in the Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):560–562. doi: 10.1038/366560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. Pattern formation. Hedgehog points the way. Curr Biol. 1994 Apr 1;4(4):347–350. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. Signalling by hedgehog family proteins in Drosophila and vertebrate development. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Aug;5(4):492–498. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(95)90054-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W., Taylor A. M., Nakano Y. Role of the Drosophila patched gene in positional signalling. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):184–187. doi: 10.1038/353184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. L., Tabin C. The long and short of hedgehog signaling. Cell. 1995 May 5;81(3):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90381-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasnow M. A., Saffman E. E., Kornfeld K., Hogness D. S. Transcriptional activation and repression by Ultrabithorax proteins in cultured Drosophila cells. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):1031–1043. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., Ekker S. C., von Kessler D. P., Porter J. A., Sun B. I., Beachy P. A. Autoproteolysis in hedgehog protein biogenesis. Science. 1994 Dec 2;266(5190):1528–1537. doi: 10.1126/science.7985023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohler J. Requirements for hedgehog, a segmental polarity gene, in patterning larval and adult cuticle of Drosophila. Genetics. 1988 Dec;120(4):1061–1072. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.4.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrimon N. Hedgehog and beyond. Cell. 1995 Feb 24;80(4):517–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90503-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter J. A., von Kessler D. P., Ekker S. C., Young K. E., Lee J. J., Moses K., Beachy P. A. The product of hedgehog autoproteolytic cleavage active in local and long-range signalling. Nature. 1995 Mar 23;374(6520):363–366. doi: 10.1038/374363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Préat T., Thérond P., Lamour-Isnard C., Limbourg-Bouchon B., Tricoire H., Erk I., Mariol M. C., Busson D. A putative serine/threonine protein kinase encoded by the segment-polarity fused gene of Drosophila. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):87–89. doi: 10.1038/347087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Préat T., Thérond P., Limbourg-Bouchon B., Pham A., Tricoire H., Busson D., Lamour-Isnard C. Segmental polarity in Drosophila melanogaster: genetic dissection of fused in a Suppressor of fused background reveals interaction with costal-2. Genetics. 1993 Dec;135(4):1047–1062. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.4.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G., Basler K. Organizing activity of wingless protein in Drosophila. Cell. 1993 Feb 26;72(4):527–540. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata T., Eaton S., Kornberg T. B. The Drosophila hedgehog gene is expressed specifically in posterior compartment cells and is a target of engrailed regulation. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2635–2645. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata T., Kornberg T. B. Hedgehog is a signaling protein with a key role in patterning Drosophila imaginal discs. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therond P., Busson D., Guillemet E., Limbourg-Bouchon B., Preat T., Terracol R., Tricoire H., Lamour-Isnard C. Molecular organisation and expression pattern of the segment polarity gene fused of Drosophila melanogaster. Mech Dev. 1993 Nov;44(1):65–80. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90017-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Boulet A. M., Lipshitz H. D. Vectors for Drosophila P-element-mediated transformation and tissue culture transfection. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder E. L., Perrimon N. Dual functions of wingless in the Drosophila leg imaginal disc. Development. 1995 Feb;121(2):477–488. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.2.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]