Abstract
Agrin is an extracellular matrix component which promotes the clustering of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) and other proteins at the neuromuscular junction. This aggregation process is one of the earliest steps in synapse formation. Expression of highly active isoforms of agrin, generated by alternative splicing, is restricted to neurons in the central nervous system (CNS) including motoneurons. In the experiments reported here we investigate the regions of agrin necessary for nAChR clustering activity using two different methods. First, we expressed truncated soluble forms of the agrin protein in mammalian cells and assessed their clustering activity. Second, we generated a panel of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against agrin and mapped their epitopes. Several mAbs block agrin-induced aggregation of nAChRs. One of the mAbs, Agr86, binds exclusively to the CNS-specific splicing variants and thus identifies an epitope common only to these more active isoforms. Mapping of the Agr86 epitope suggests that alternative splicing results in a distributed conformational change in the agrin protein. Taken together our data suggest that four domains in the C-terminal 55 kDa of agrin contribute to its nAChR clustering activity.
Full text
PDF

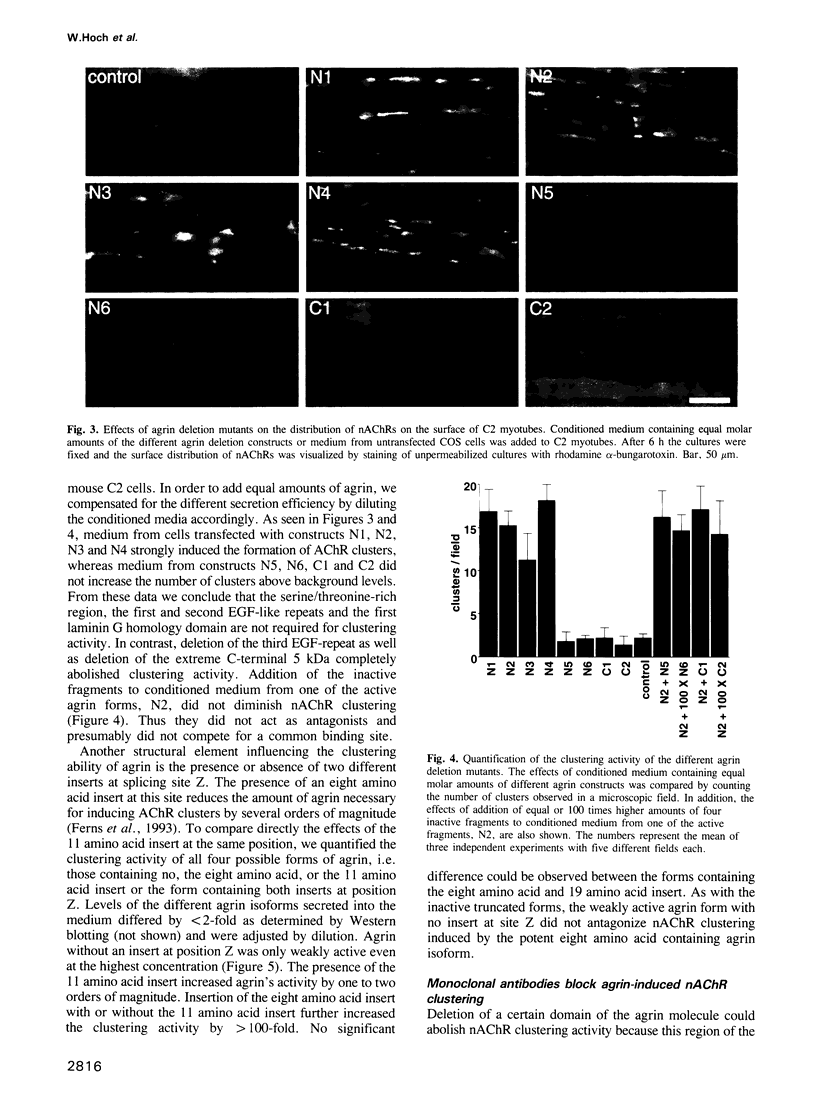
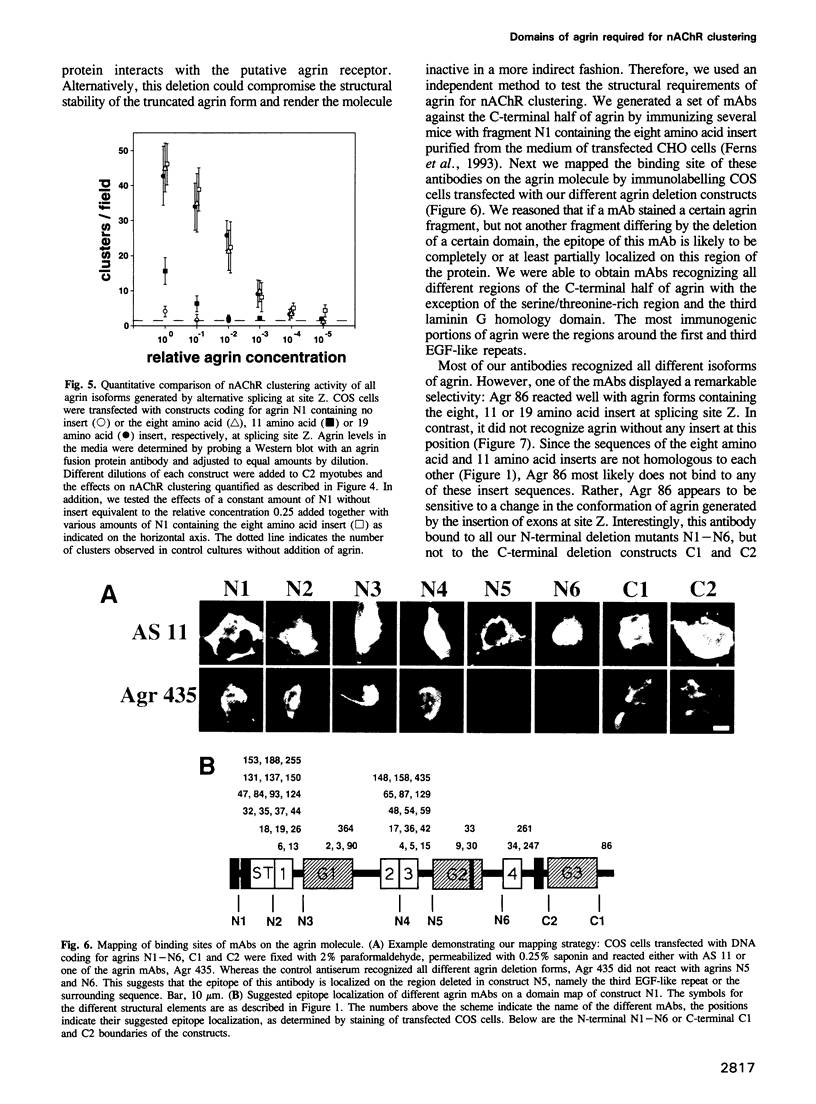



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. J., Cohen M. W., Zorychta E. Effects of innervation on the distribution of acetylcholine receptors on cultured muscle cells. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;268(3):731–756. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campanelli J. T., Hoch W., Rupp F., Kreiner T., Scheller R. H. Agrin mediates cell contact-induced acetylcholine receptor clustering. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):909–916. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90364-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns M. J., Campanelli J. T., Hoch W., Scheller R. H., Hall Z. The ability of agrin to cluster AChRs depends on alternative splicing and on cell surface proteoglycans. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90153-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns M., Hoch W., Campanelli J. T., Rupp F., Hall Z. W., Scheller R. H. RNA splicing regulates agrin-mediated acetylcholine receptor clustering activity on cultured myotubes. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1079–1086. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90129-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano Y., Kidokoro Y. Heparin and heparan sulfate partially inhibit induction of acetylcholine receptor accumulation by nerve in Xenopus culture. J Neurosci. 1989 May;9(5):1555–1561. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-05-01555.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch W., Ferns M., Campanelli J. T., Hall Z. W., Scheller R. H. Developmental regulation of highly active alternatively spliced forms of agrin. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):479–490. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90152-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtley S. M., Helenius A. Protein oligomerization in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennett R. H. Cell fusion. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:345–359. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Nastuk M. A., McKechnie B. A., Fallon J. R. The agrin receptor. Localization in the postsynaptic membrane, interaction with agrin, and relationship to the acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):25108–25117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan U. J. The agrin hypothesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:407–418. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nastuk M. A., Lieth E., Ma J. Y., Cardasis C. A., Moynihan E. B., McKechnie B. A., Fallon J. R. The putative agrin receptor binds ligand in a calcium-dependent manner and aggregates during agrin-induced acetylcholine receptor clustering. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):807–818. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitkin R. M., Smith M. A., Magill C., Fallon J. R., Yao Y. M., Wallace B. G., McMahan U. J. Identification of agrin, a synaptic organizing protein from Torpedo electric organ. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2471–2478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy L., Nikolics K. Functions of agrin and agrin-related proteins. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Feb;16(2):76–81. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90021-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reist N. E., Werle M. J., McMahan U. J. Agrin released by motor neurons induces the aggregation of acetylcholine receptors at neuromuscular junctions. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):865–868. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90200-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruegg M. A., Tsim K. W., Horton S. E., Kröger S., Escher G., Gensch E. M., McMahan U. J. The agrin gene codes for a family of basal lamina proteins that differ in function and distribution. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90090-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp F., Payan D. G., Magill-Solc C., Cowan D. M., Scheller R. H. Structure and expression of a rat agrin. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):811–823. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakashita S., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Basement membrane glycoprotein laminin binds to heparin. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 28;116(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80654-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. S., O'Dowd D. K., Smith M. A. Developmental expression and alternative splicing of chick agrin RNA. Dev Biol. 1993 Aug;158(2):523–535. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsim K. W., Ruegg M. A., Escher G., Kröger S., McMahan U. J. cDNA that encodes active agrin. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):677–689. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90089-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. G. Agrin-induced specializations contain cytoplasmic, membrane, and extracellular matrix-associated components of the postsynaptic apparatus. J Neurosci. 1989 Apr;9(4):1294–1302. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-04-01294.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. G. Inhibition of agrin-induced acetylcholine-receptor aggregation by heparin, heparan sulfate, and other polyanions. J Neurosci. 1990 Nov;10(11):3576–3582. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-11-03576.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. G., Qu Z., Huganir R. L. Agrin induces phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):869–878. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90227-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]