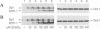Abstract
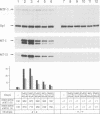
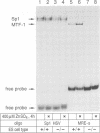
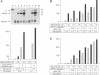
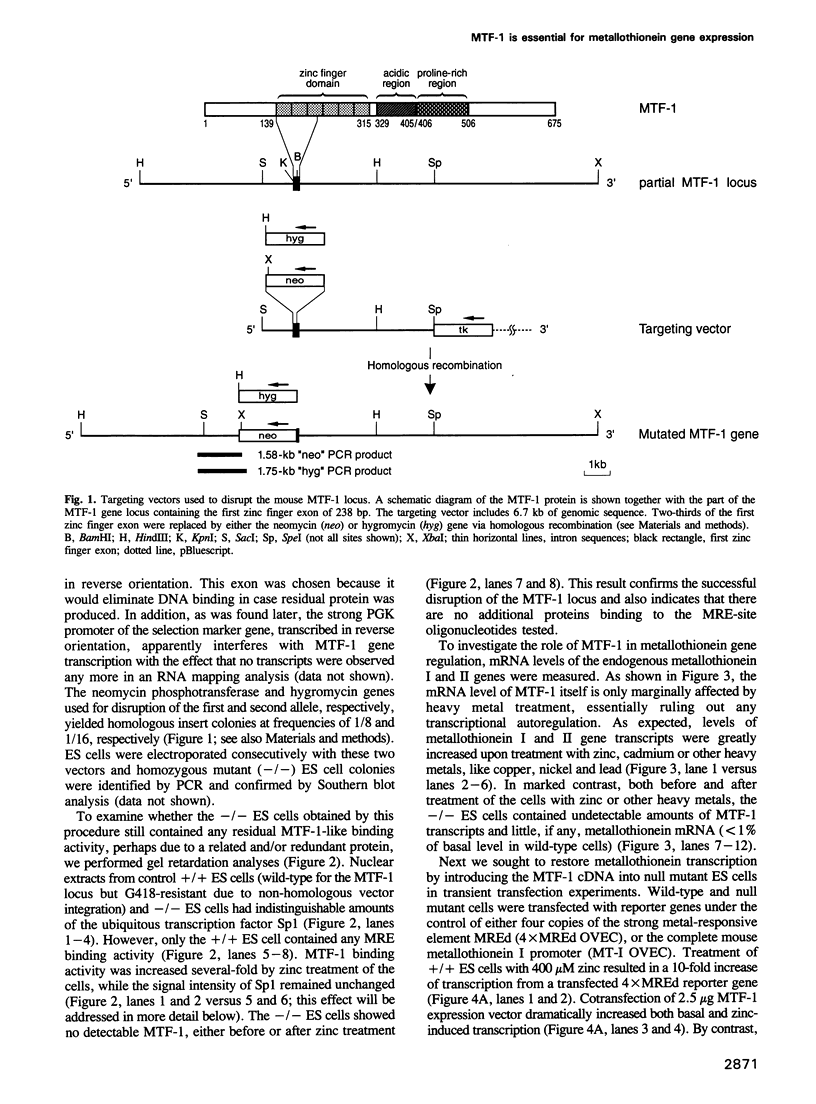
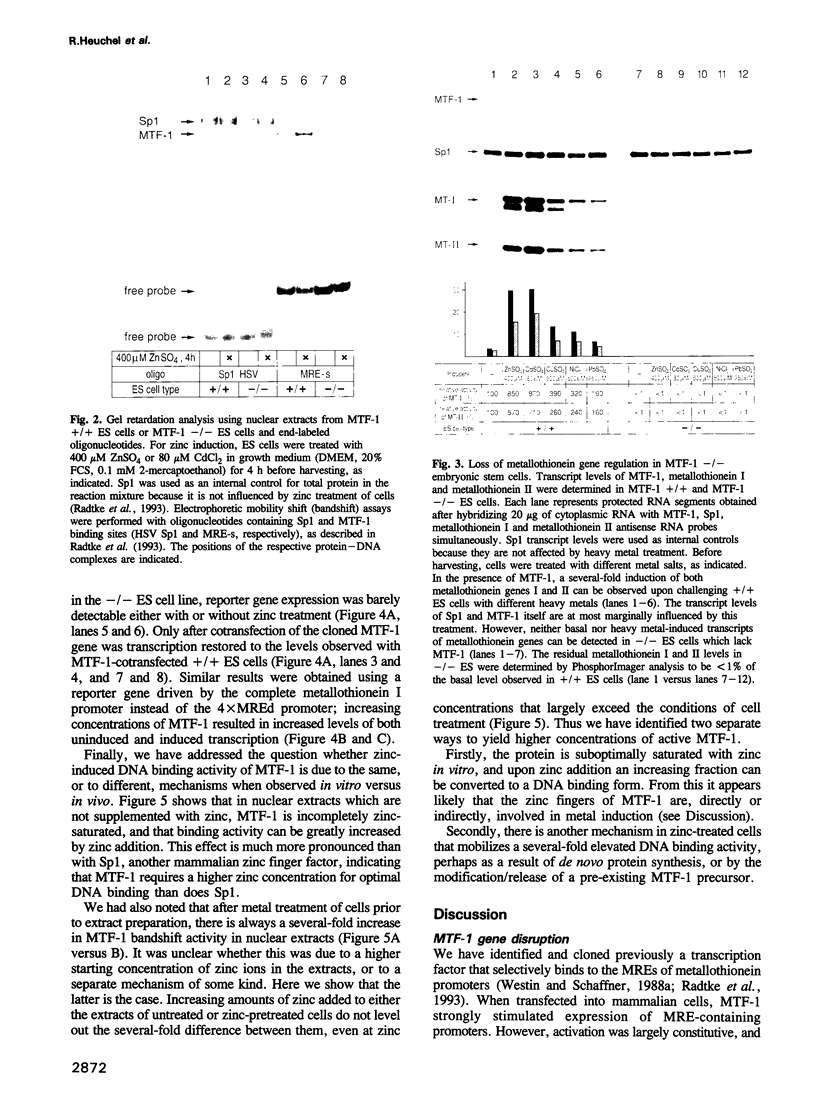
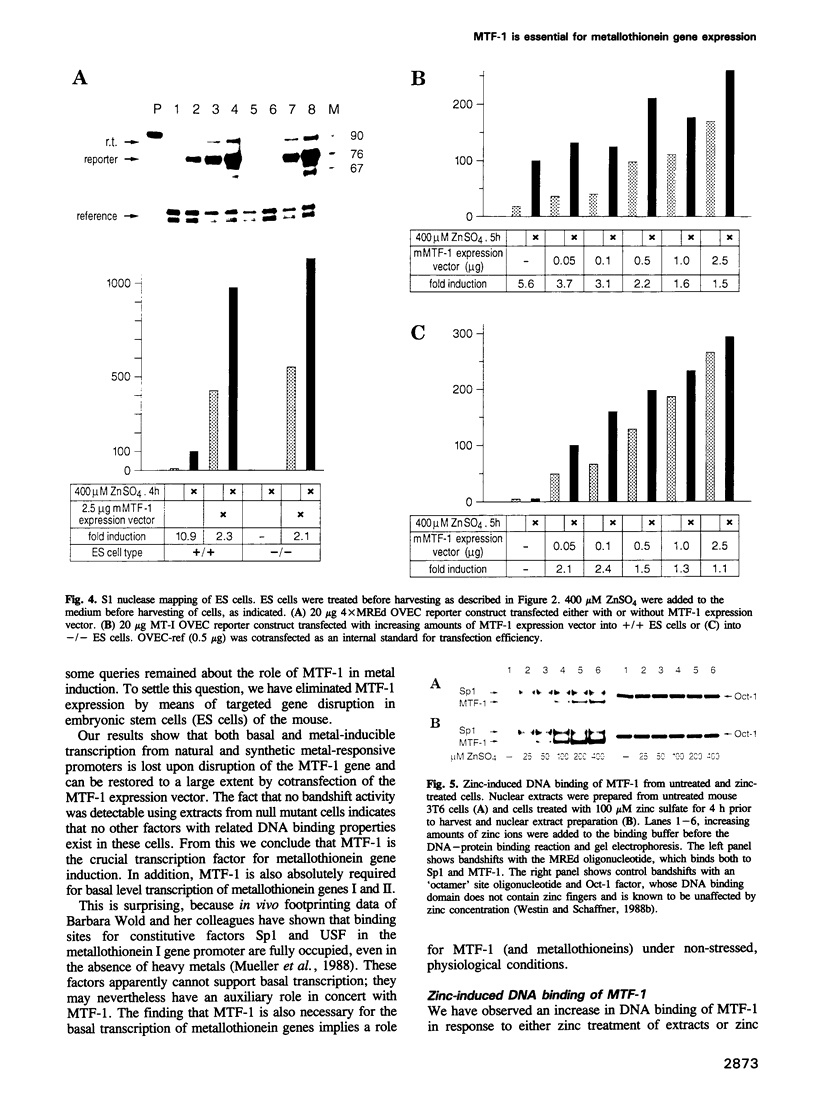
We have described and cloned previously a factor (MTF-1) that binds specifically to heavy metal-responsive DNA sequence elements in the enhancer/promoter region of metallothionein genes. MTF-1 is a protein of 72.5 kDa that contains six zinc fingers and multiple domains for transcriptional activation. Here we report the disruption of both alleles of the MTF-1 gene in mouse embryonic stem cells by homologous recombination. The resulting null mutant cell line fails to produce detectable amounts of MTF-1. Moreover, due to the loss of MTF-1, the endogenous metallothionein I and II genes are silent, indicating that MTF-1 is required for both their basal and zinc-induced transcription. In addition to zinc, other heavy metals, including cadmium, copper, nickel and lead, also fail to activate metal-responsive promoters in null mutant cells. However, cotransfection of an MTF-1 expression vector and metal-responsive reporter genes yields strong basal transcription that can be further boosted by zinc treatment of cells. These results demonstrate that MTF-1 is essential for metallothionein gene regulation. Finally, we present evidence that MTF-1 itself is a zinc sensor, which exhibits increased DNA binding activity upon zinc treatment.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen R. D., Taplitz S. J., Oberbauer A. M., Calame K. L., Herschman H. R. Metal-dependent binding of a nuclear factor to the rat metallothionein-I promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6049–6055. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews G. K. Regulation of metallothionein gene expression. Prog Food Nutr Sci. 1990;14(2-3):193–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst P., Hu S., Hackett R., Hamer D. Copper activates metallothionein gene transcription by altering the conformation of a specific DNA binding protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):705–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. Catalytic RNA: a Nobel Prize for small village science. New Biol. 1990 Jan;2(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heard J. M., Herbomel P., Ott M. O., Mottura-Rollier A., Weiss M., Yaniv M. Determinants of rat albumin promoter tissue specificity analyzed by an improved transient expression system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2425–2434. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi J. H. Overview of metallothionein. Methods Enzymol. 1991;205:613–626. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)05145-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters B. A., Kelly E. J., Quaife C. J., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Targeted disruption of metallothionein I and II genes increases sensitivity to cadmium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):584–588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Bradley A. The Wnt-1 (int-1) proto-oncogene is required for development of a large region of the mouse brain. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1073–1085. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90385-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalska A. E., Choo K. H. Targeting and germ-line transmission of a null mutation at the metallothionein I and II loci in mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8088–8092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Timmons P. M., Hébert J. M., Rigby P. W., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-2 is expressed in neural crest cell lineages during mouse embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):105–119. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Salser S. J., Wold B. Constitutive and metal-inducible protein:DNA interactions at the mouse metallothionein I promoter examined by in vivo and in vitro footprinting. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):412–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Regulation of metallothionein genes by heavy metals appears to be mediated by a zinc-sensitive inhibitor that interacts with a constitutively active transcription factor, MTF-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1219–1223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radtke F., Heuchel R., Georgiev O., Hergersberg M., Gariglio M., Dembic Z., Schaffner W. Cloned transcription factor MTF-1 activates the mouse metallothionein I promoter. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1355–1362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffner H., Reis L. F., Näf D., Weissmann C. Induction of type I interferon genes and interferon-inducible genes in embryonal stem cells devoid of interferon regulatory factor 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11503–11507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F., Davison B. L., Stuart G. W., Wilkie T. M., Norstedt G., Palmiter R. D. Regulation, linkage, and sequence of mouse metallothionein I and II genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1221–1230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F. Zinc dependent binding of a liver nuclear factor to metal response element MRE-a of the mouse metallothionein-I gene and variant sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serfling E., Lübbe A., Dorsch-Häsler K., Schaffner W. Metal-dependent SV40 viruses containing inducible enhancers from the upstream region of metallothionein genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3851–3859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Montgomery C., Geske R., Bradley A. Targeted disruption of the c-src proto-oncogene leads to osteopetrosis in mice. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):693–702. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90499-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. A 12-base-pair DNA motif that is repeated several times in metallothionein gene promoters confers metal regulation to a heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7318–7322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Palmiter R. D. Identification of multiple metal regulatory elements in mouse metallothionein-I promoter by assaying synthetic sequences. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):828–831. doi: 10.1038/317828a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguin C., Prévost J. Detection of a nuclear protein that interacts with a metal regulatory element of the mouse metallothionein 1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10547–10560. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida Y., Takio K., Titani K., Ihara Y., Tomonaga M. The growth inhibitory factor that is deficient in the Alzheimer's disease brain is a 68 amino acid metallothionein-like protein. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):337–347. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Schaffner W. A zinc-responsive factor interacts with a metal-regulated enhancer element (MRE) of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3763–3770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Schaffner W. Heavy metal ions in transcription factors from HeLa cells: Sp1, but not octamer transcription factor requires zinc for DNA binding and for activator function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5771–5781. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng J., Heuchel R., Schaffner W., Kägi J. H. Thionein (apometallothionein) can modulate DNA binding and transcription activation by zinc finger containing factor Sp1. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 25;279(2):310–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]