Abstract
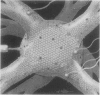
Previously, synaptic activity in the spinal cord of adult mammals was attributed exclusively to chemical neurotransmission. In this study, evidence was obtained for the existence, relative abundance, and widespread distribution of "mixed" (chemical and electrical) synapses on neurons throughout the spinal cords of adult mammals. Using combined confocal microscopy and "grid-mapped freeze fracture," 36 mixed synapses containing 88 "micro" gap junctions (median = 45 connexons) were found and mapped to 33 interneurons and motor neurons in Rexed laminae III-IX in cervical, thoracic, and lumbosacral spinal cords of adult male and female rats. Gap junctions were adjacent to presumptive active zones, where even small gap junctions would be expected to increase synaptic efficacy. Two morphological types of mixed synapse were discerned. One type contained distinctive active zones consisting of "nested" concentric toroidal deformations of pre- and postsynaptic membranes, which, because of their unusual topology, were designated as "synaptic sombreros." A second type had gap junctions adjacent to active zones consisting of broad, flat, shallow indentations of the plasma membrane. Morphometric analysis indicates that mixed synapses correspond to 3-5% of all synapses on the somata and proximal dendrites, but, because of their subcellular location and morphology, they could represent 30-100% of excitatory synapses. The relative abundance of mixed synapses on several classes of neurons in spinal cords of adult rats suggests that mixed synapses provide important but previously unrecognized pathways for bidirectional communication between neurons in the mammalian central nervous system.
Full text
PDF
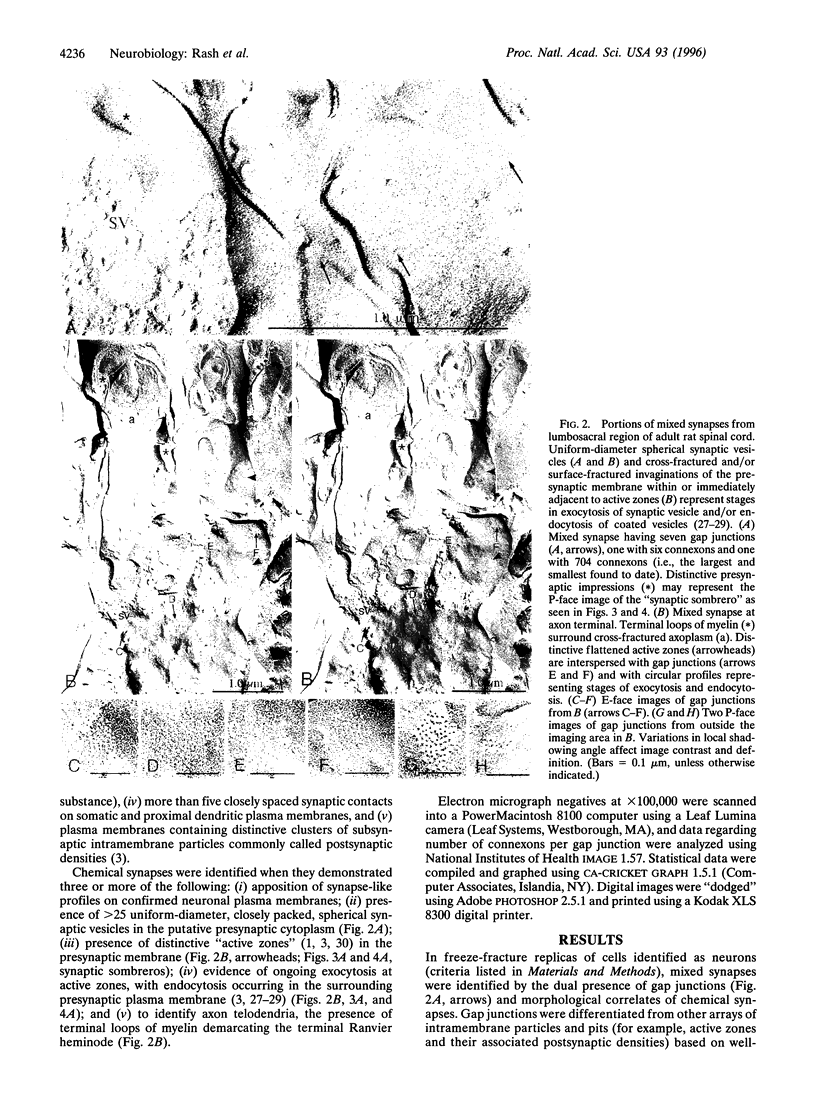

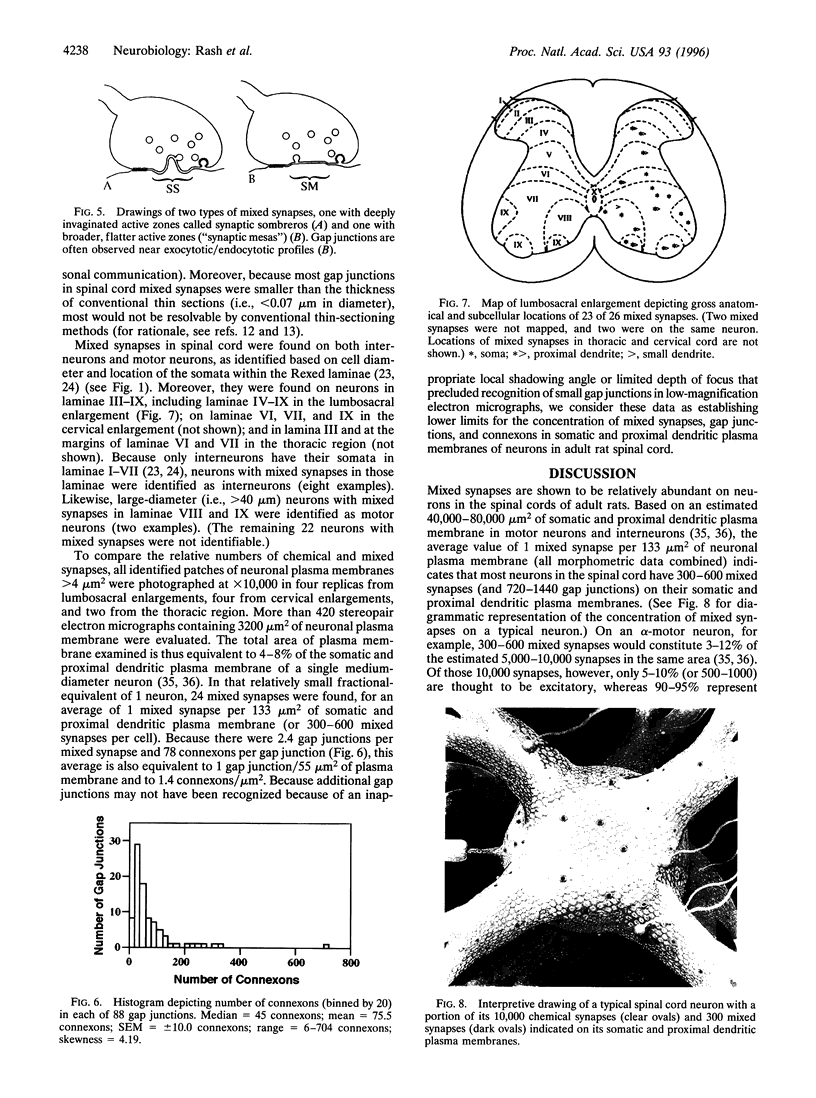

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arasaki K., Kudo N., Nakanishi T. Firing of spinal motoneurones due to electrical interaction in the rat: an in vitro study. Exp Brain Res. 1984;54(3):437–445. doi: 10.1007/BF00235469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT M. V., ALJURE E., NAKAJIMA Y., PAPPAS G. D. Electrotonic junctions between teleost spinal neurons: electrophysiology and ultrastructure. Science. 1963 Jul 19;141(3577):262–264. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3577.262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellinger D. L., Anderson W. J. Postnatal development of cell columns and their associated dendritic bundles in the lumbosacral spinal cord of the rat. II. The ventromedial cell column. Brain Res. 1987 Sep;432(1):69–82. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(87)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D., Bullivant S., Gilula N. B., Karnovsky M. J., Moor H., Mühlethaler K., Northcote D. H., Packer L., Satir B., Satir P. Freeze-etching nomenclature. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):54–56. doi: 10.1126/science.1166299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brännström T. Quantitative synaptology of functionally different types of cat medial gastrocnemius alpha-motoneurons. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Apr 15;330(3):439–454. doi: 10.1002/cne.903300311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermietzel R., Spray D. C. Gap junctions in the brain: where, what type, how many and why? Trends Neurosci. 1993 May;16(5):186–192. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90151-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank E., Mendelson B. Specification of synaptic connections between sensory and motor neurons in the developing spinal cord. J Neurobiol. 1990 Jan;21(1):33–50. doi: 10.1002/neu.480210104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton B. P., Miledi R., Takahashi T. Electrical synapses between motoneurons in the spinal cord of the newborn rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Jun 23;208(1170):115–120. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilula N. B., Reeves O. R., Steinbach A. Metabolic coupling, ionic coupling and cell contacts. Nature. 1972 Feb 4;235(5336):262–265. doi: 10.1038/235262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogan P., Gueritaud J. P., Horcholle-Bossavit G., Tyc-Dumont S. Direct excitatory interactions between spinal motoneurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):755–767. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell A. D. Electrical interaction between antidromically stimulated frog motoneurones and dorsal root afferents: enhancement by gallamine and TEA. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(1):17–43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton J. D., Ellisman M. H. The distribution of orthogonal arrays and their relationship to intercellular junctions in neuroglia of the freeze-fractured hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;215(2):309–323. doi: 10.1007/BF00239117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S., Dennis M. J., Jan Y., Jan L., Evans L. Synaptic vesicle exocytosis captured by quick freezing and correlated with quantal transmitter release. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):275–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn H., Sotelo C., Crepel F. Electronic coupling between neurons in the rat lateral vestibular nucleus. Exp Brain Res. 1973 Jan 29;16(3):255–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landis D. M., Reese T. S. Arrays of particles in freeze-fractured astrocytic membranes. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jan;60(1):316–320. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.1.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen W. J. Biological implications of gap junction structure, distribution and composition: a review. Tissue Cell. 1983;15(5):645–671. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(83)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinas R., Baker R., Sotelo C. Electrotonic coupling between neurons in cat inferior olive. J Neurophysiol. 1974 May;37(3):560–571. doi: 10.1152/jn.1974.37.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R., PILAR G. TRANSMISSION THROUGH THE CILIARY GANGLION OF THE CHICK. J Physiol. 1963 Sep;168:464–475. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto A., Arnold A. P., Micevych P. E. Gap junctions between lateral spinal motoneurons in the rat. Brain Res. 1989 Aug 28;495(2):362–366. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto A., Arnold A. P., Zampighi G. A., Micevych P. E. Androgenic regulation of gap junctions between motoneurons in the rat spinal cord. J Neurosci. 1988 Nov;8(11):4177–4183. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-11-04177.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. M., Heuser J. E. Endocytosis of synaptic vesicle membrane at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):685–698. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G. Interaction between spinal motoneurons of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1966 Mar;29(2):275–287. doi: 10.1152/jn.1966.29.2.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereda A. E., Nairn A. C., Wolszon L. R., Faber D. S. Postsynaptic modulation of synaptic efficacy at mixed synapses on the Mauthner cell. J Neurosci. 1994 Jun;14(6):3704–3712. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-06-03704.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REXED B. A cytoarchitectonic atlas of the spinal cord in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1954 Apr;100(2):297–379. doi: 10.1002/cne.901000205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rash J. E., Walrond J. P., Morita M. Structural and functional correlates of synaptic transmission in the vertebrate neuromuscular junction. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1988 Oct;10(2):153–185. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060100204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rash J. E., Yasumura T. Improved structural detail in freeze-fracture replicas: high-angle shadowing of gap junctions cooled below -170 degrees C and protected by liquid nitrogen-cooled shrouds. Microsc Res Tech. 1992 Jan 15;20(2):187–204. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1070200207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel J. P., Karnovsky M. J. Hexagonal array of subunits in intercellular junctions of the mouse heart and liver. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jun;33(3):C7–C12. doi: 10.1083/jcb.33.3.c7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapovalov A. I., Shiriaev B. I. Two types of electronic EPSP evoked in amphibian motoneurons by ventral root stimulation. Exp Brain Res. 1978 Nov 15;33(3-4):313–323. doi: 10.1007/BF00235556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloper J. J. Gap junctions between dendrites in the primate neocortex. Brain Res. 1972 Sep 29;44(2):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90327-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo C., Korn H. Morphological correlates of electrical and other interactions through low-resistance pathways between neurons of the vertebrate central nervous system. Int Rev Cytol. 1978;55:67–107. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61887-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. D., Navarrete R. Postnatal changes in motoneurone electrotonic coupling studied in the in vitro rat lumbar spinal cord. J Physiol. 1991 Feb;433:283–305. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werman R., Carlen P. L. Unusual behavior of the La EPSP in cat spinal motoneurons. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 13;112(2):395–401. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90294-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]