Abstract
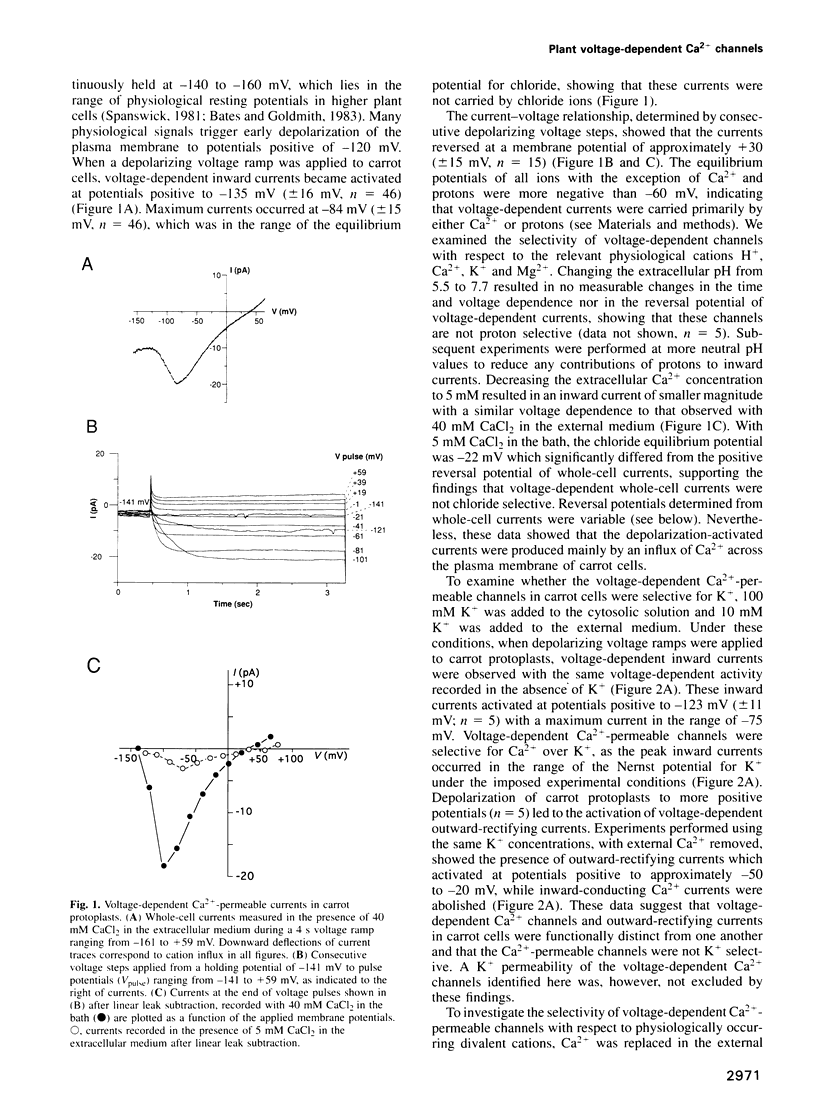
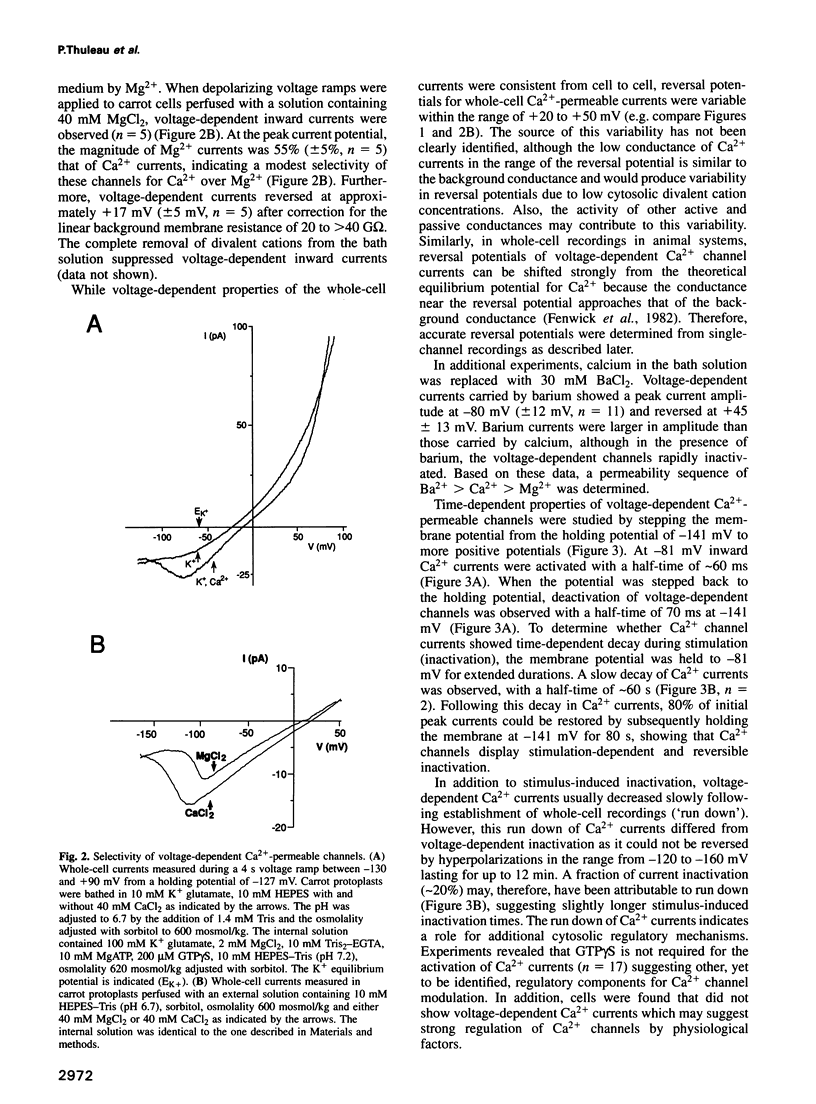
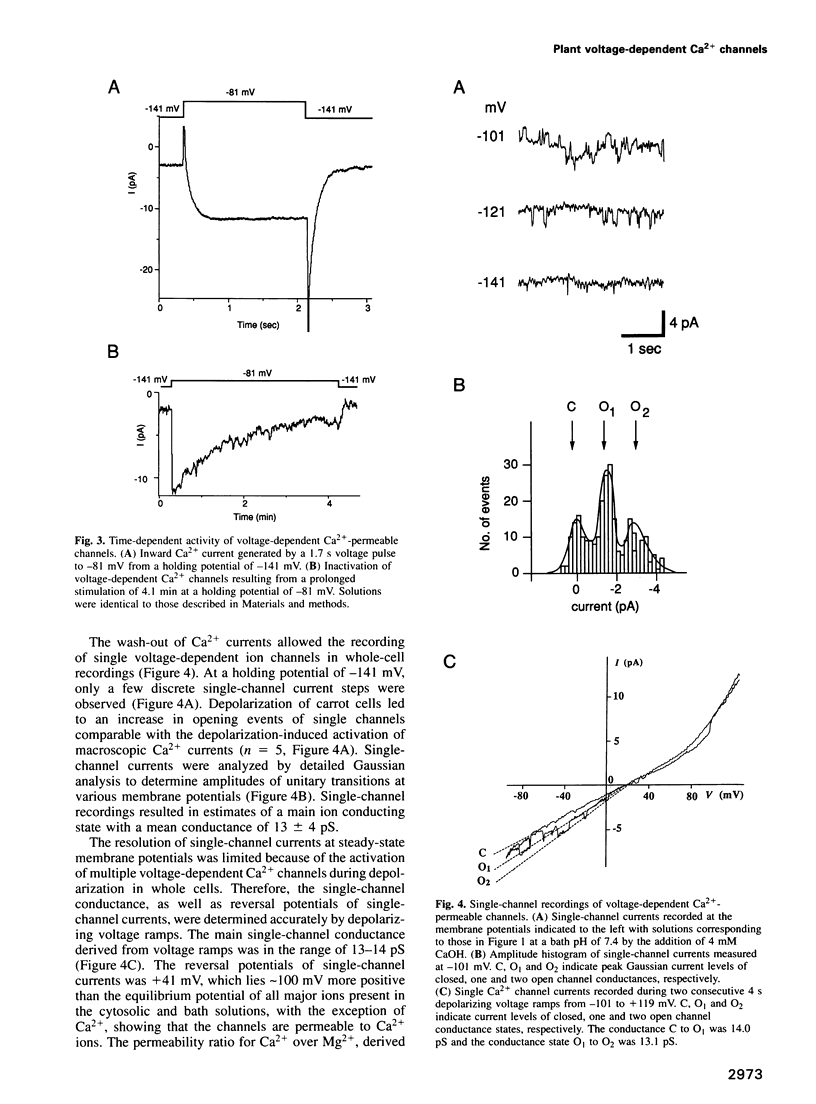
Numerous biological assays and pharmacological studies on various higher plant tissues have led to the suggestion that voltage-dependent plasma membrane Ca2+ channels play prominent roles in initiating signal transduction processes during plant growth and development. However, to date no direct evidence has been obtained for the existence of such depolarization-activated Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane of higher plant cells. Carrot suspension cells (Daucus carota L.) provide a well-suited system to determine whether voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels are present in the plasma membrane of higher plants and to characterize the properties of putative Ca2+ channels. It is known that both depolarization, caused by raising extracellular K+, and exposure to fungal toxins or oligogalacturonides induce Ca2+ influx into carrot cells. By direct application of patch-clamp techniques to isolated carrot protoplasts, we show here that depolarization of the plasma membrane positive to -135 mV activates Ca(2+)-permeable channels. These voltage-dependent ion channels were more permeable to Ca2+ than K+, while displaying large permeabilities to Ba2+ and Mg2+ ions. Ca(2+)-permeable channels showed slow and reversible inactivation. The single-channel conductance was 13 pS in 40 mM CaCl2. These data provide direct evidence for the existence of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane of a higher plant cell and point to physiological mechanisms for plant Ca2+ channel regulation. The depolarization-activated Ca(2+)-permeable channels identified here could constitute a regulated pathway for Ca2+ influx in response to physiologically occurring stimulus-induced depolarizations in higher plant cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker P. L., Singer J. J., Walsh J. V., Jr, Fay F. S. Regulation of calcium concentration in voltage-clamped smooth muscle cells. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):211–214. doi: 10.1126/science.2704996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove D. J., Hedrich R. Stretch-activated chloride, potassium, and calcium channels coexisting in plasma membranes of guard cells of Vicia faba L. Planta. 1991 Dec;186(1):143–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00201510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies E., Schuster A. Intercellular communication in plants: Evidence for a rapidly generated, bidirectionally transmitted wound signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2422–2426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhardt D. W., Atkinson E. M., Long S. R. Depolarization of alfalfa root hair membrane potential by Rhizobium meliloti Nod factors. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):998–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.10744524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilroy S., Jones R. L. Gibberellic acid and abscisic acid coordinately regulate cytoplasmic calcium and secretory activity in barley aleurone protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3591–3595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrich R., Busch H., Raschke K. Ca2+ and nucleotide dependent regulation of voltage dependent anion channels in the plasma membrane of guard cells. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3889–3892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler P. K., Callaham D. A. Free calcium increases during anaphase in stamen hair cells of Tradescantia. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2137–2143. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P. Calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:337–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.13.030190.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. W., Shaff J. E., Grunes D. L., Kochian L. V. Aluminum effects on calcium fluxes at the root apex of aluminum-tolerant and aluminum-sensitive wheat cultivars. Plant Physiol. 1992 Jan;98(1):230–237. doi: 10.1104/pp.98.1.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. Correction for liquid junction potentials in patch clamp experiments. Methods Enzymol. 1992;207:123–131. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)07008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racusen R., Satter R. L. Rhythmic and phytochrome-regulated changes in transmembrane potential in samanea pulvini. Nature. 1975 May 29;255(5507):408–410. doi: 10.1038/255408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. I., Hagiwara S. Repetitive increases in cytosolic Ca2+ of guard cells by abscisic acid activation of nonselective Ca2+ permeable channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9305–9309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. I., Hedrich R. Involvement of ion channels and active transport in osmoregulation and signaling of higher plant cells. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 May;14(5):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. I., Raschke K., Neher E. Voltage dependence of K channels in guard-cell protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4108–4112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalding E. P., Cosgrove D. J. Large plasma-membrane depolarization precedes rapid blue-light-induced growth inhibition in cucumber. Planta. 1989;178:407–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomine S., Zimmerman S., Van Duijn B., Barbier-Brygoo H., Guern J. Calcium channel antagonists induce direct inhibition of the outward rectifying potassium channel in tobacco protoplasts. FEBS Lett. 1994 Feb 28;340(1-2):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuleau P., Graziana A., Canut H., Ranjeva R. A 75-kDa polypeptide, located primarily at the plasma membrane of carrot cell-suspension cultures, is photoaffinity labeled by the calcium channel blocker LU 49888. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec 15;87(24):10000–10004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuleau P., Graziana A., Ranjeva R., Schroeder J. I. Solubilized proteins from carrot (Daucus carota L.) membranes bind calcium channel blockers and form calcium-permeable ion channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):765–769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuleau P., Graziana A., Rossignol M., Kauss H., Auriol P., Ranjeva R. Binding of the phytotoxin zinniol stimulates the entry of calcium into plant protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5932–5935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Calcium channels, stores, and oscillations. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:715–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich C. I., Novacky A. J. Electrical Membrane Properties of Leaves, Roots, and Single Root Cap Cells of Susceptible Avena sativa: Effect of Victorin C. Plant Physiol. 1991 Mar;95(3):675–681. doi: 10.1104/pp.95.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., Schroeder J. I. Calcium-Activated K+ Channels and Calcium-Induced Calcium Release by Slow Vacuolar Ion Channels in Guard Cell Vacuoles Implicated in the Control of Stomatal Closure. Plant Cell. 1994 May;6(5):669–683. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.5.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R. E., Ashley C. C. Free Ca2+ and cytoplasmic streaming in the alga Chara. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):647–650. doi: 10.1038/296647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


