Abstract
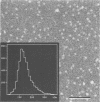
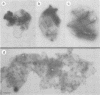
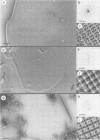
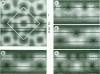
Water-permeable membranes of several plant and mammalian tissues contain specific water channel proteins, the 'aquaporins'. The best characterized aquaporin is CHIP, a 28 kDa red blood cell channel-forming integral protein. Isolated CHIP and Escherichia coli lipids may be assembled into 2-D crystals for structural analyses. Here we present (i) a structural characterization of the solubilized CHIP oligomers, (ii) projections of CHIP arrays after negative staining or metal-shadowing, and (iii) the 3-D structure at 1.6 nm resolution. Negatively stained CHIP oligomers exhibited a side length of 6.9 nm with four-fold symmetry, and a mass of 202 +/- 3 kDa determined by scanning transmission electron microscopy. Reconstituted into lipid bilayers, CHIP formed 2-D square lattices with unit cell dimensions a = b = 9.6 nm and a p422(1) symmetry. The 3-D map revealed that CHIP tetramers contain central stain-filled depressions about the fourfold axis. These cavities extend from both sides into the transbilayer domain of the molecule leaving only a thin barrier to be penetrated by the water pores. Although CHIP monomers behave as independent pores, we propose that their particular structure requires tetramerization for stable integration into the bilayer.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi U., Smith P. R., Dubochet J., Henry C., Kellenberger E. A study of the structure of the T-layer of Bacillus brevis. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(6):498–522. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agre P., Preston G. M., Smith B. L., Jung J. S., Raina S., Moon C., Guggino W. B., Nielsen S. Aquaporin CHIP: the archetypal molecular water channel. Am J Physiol. 1993 Oct;265(4 Pt 2):F463–F476. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.4.F463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berriman J., Leonard K. R. Methods for specimen thickness determination in electron microscopy. II. Changes in thickness with dose. Ultramicroscopy. 1986;19(4):349–366. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(86)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy C., Chin E., Smith B. L., Preston G. M., Agre P. Developmental gene expression and tissue distribution of the CHIP28 water-channel protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4500–4504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan S. W., Schirmer T., Rummel G., Steiert M., Ghosh R., Pauptit R. A., Jansonius J. N., Rosenbusch J. P. Crystal structures explain functional properties of two E. coli porins. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):727–733. doi: 10.1038/358727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denker B. M., Smith B. L., Kuhajda F. P., Agre P. Identification, purification, and partial characterization of a novel Mr 28,000 integral membrane protein from erythrocytes and renal tubules. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15634–15642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford R. C., Hefti A., Engel A. Ordered arrays of the photosystem I reaction centre after reconstitution: projections and surface reliefs of the complex at 2 nm resolution. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3067–3075. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07503.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin M. B., Yancey S. B., Cline J., Revel J. P., Horwitz J. The major intrinsic protein (MIP) of the bovine lens fiber membrane: characterization and structure based on cDNA cloning. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz J., Bok D. Conformational properties of the main intrinsic polypeptide (MIP26) isolated from lens plasma membranes. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8092–8098. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovmöller S., Slaughter M., Berriman J., Karlsson B., Weiss H., Leonard K. Structural studies of cytochrome reductase. Improved membrane crystals of the enzyme complex and crystallization of a subcomplex. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 5;165(2):401–406. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jap B. K., Zulauf M., Scheybani T., Hefti A., Baumeister W., Aebi U., Engel A. 2D crystallization: from art to science. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Oct;46(1-4):45–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung J. S., Preston G. M., Smith B. L., Guggino W. B., Agre P. Molecular structure of the water channel through aquaporin CHIP. The hourglass model. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14648–14654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macey R. I., Farmer R. E. Inhibition of water and solute permeability in human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 7;211(1):104–106. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannella C. A. Mitochondrial outer membrane channel (VDAC, porin) two-dimensional crystals from Neurospora. Methods Enzymol. 1986;125:595–610. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)25048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Smith B. L., Christensen E. I., Agre P. Distribution of the aquaporin CHIP in secretory and resorptive epithelia and capillary endothelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7275–7279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Smith B. L., Christensen E. I., Knepper M. A., Agre P. CHIP28 water channels are localized in constitutively water-permeable segments of the nephron. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):371–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Agre P. Isolation of the cDNA for erythrocyte integral membrane protein of 28 kilodaltons: member of an ancient channel family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11110–11114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Carroll T. P., Guggino W. B., Agre P. Appearance of water channels in Xenopus oocytes expressing red cell CHIP28 protein. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):385–387. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Jung J. S., Guggino W. B., Agre P. Membrane topology of aquaporin CHIP. Analysis of functional epitope-scanning mutants by vectorial proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1668–1673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Jung J. S., Guggino W. B., Agre P. The mercury-sensitive residue at cysteine 189 in the CHIP28 water channel. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):17–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Reizer A., Saier M. H., Jr The MIP family of integral membrane channel proteins: sequence comparisons, evolutionary relationships, reconstructed pathway of evolution, and proposed functional differentiation of the two repeated halves of the proteins. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1993;28(3):235–257. doi: 10.3109/10409239309086796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabolić I., Valenti G., Verbavatz J. M., Van Hoek A. N., Verkman A. S., Ausiello D. A., Brown D. Localization of the CHIP28 water channel in rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1992 Dec;263(6 Pt 1):C1225–C1233. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.6.C1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton W. O., Baumeister W. The correlation averaging of a regularly arranged bacterial cell envelope protein. J Microsc. 1982 Aug;127(Pt 2):127–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1982.tb00405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. L., Agre P. Erythrocyte Mr 28,000 transmembrane protein exists as a multisubunit oligomer similar to channel proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6407–6415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. L., Baumgarten R., Nielsen S., Raben D., Zeidel M. L., Agre P. Concurrent expression of erythroid and renal aquaporin CHIP and appearance of water channel activity in perinatal rats. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):2035–2041. doi: 10.1172/JCI116798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hoek A. N., Wiener M., Bicknese S., Miercke L., Biwersi J., Verkman A. S. Secondary structure analysis of purified functional CHIP28 water channels by CD and FTIR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 9;32(44):11847–11856. doi: 10.1021/bi00095a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbavatz J. M., Brown D., Sabolić I., Valenti G., Ausiello D. A., Van Hoek A. N., Ma T., Verkman A. S. Tetrameric assembly of CHIP28 water channels in liposomes and cell membranes: a freeze-fracture study. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(3):605–618. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.3.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz T., Smith B. L., Zeidel M. L., Engel A., Agre P. Biologically active two-dimensional crystals of aquaporin CHIP. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1583–1586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. S., Abele U., Weckesser J., Welte W., Schiltz E., Schulz G. E. Molecular architecture and electrostatic properties of a bacterial porin. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1627–1630. doi: 10.1126/science.1721242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigley N. G. The lattice spacing of crystalline catalase as an internal standard of length in electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1968 Sep;24(5):454–464. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(68)80048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Ambudkar S. V., Smith B. L., Agre P. Reconstitution of functional water channels in liposomes containing purified red cell CHIP28 protein. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 25;31(33):7436–7440. doi: 10.1021/bi00148a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Nielsen S., Smith B. L., Ambudkar S. V., Maunsbach A. B., Agre P. Ultrastructure, pharmacologic inhibition, and transport selectivity of aquaporin channel-forming integral protein in proteoliposomes. Biochemistry. 1994 Feb 15;33(6):1606–1615. doi: 10.1021/bi00172a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hoek A. N., Hom M. L., Luthjens L. H., de Jong M. D., Dempster J. A., van Os C. H. Functional unit of 30 kDa for proximal tubule water channels as revealed by radiation inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16633–16635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]