Abstract
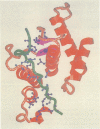
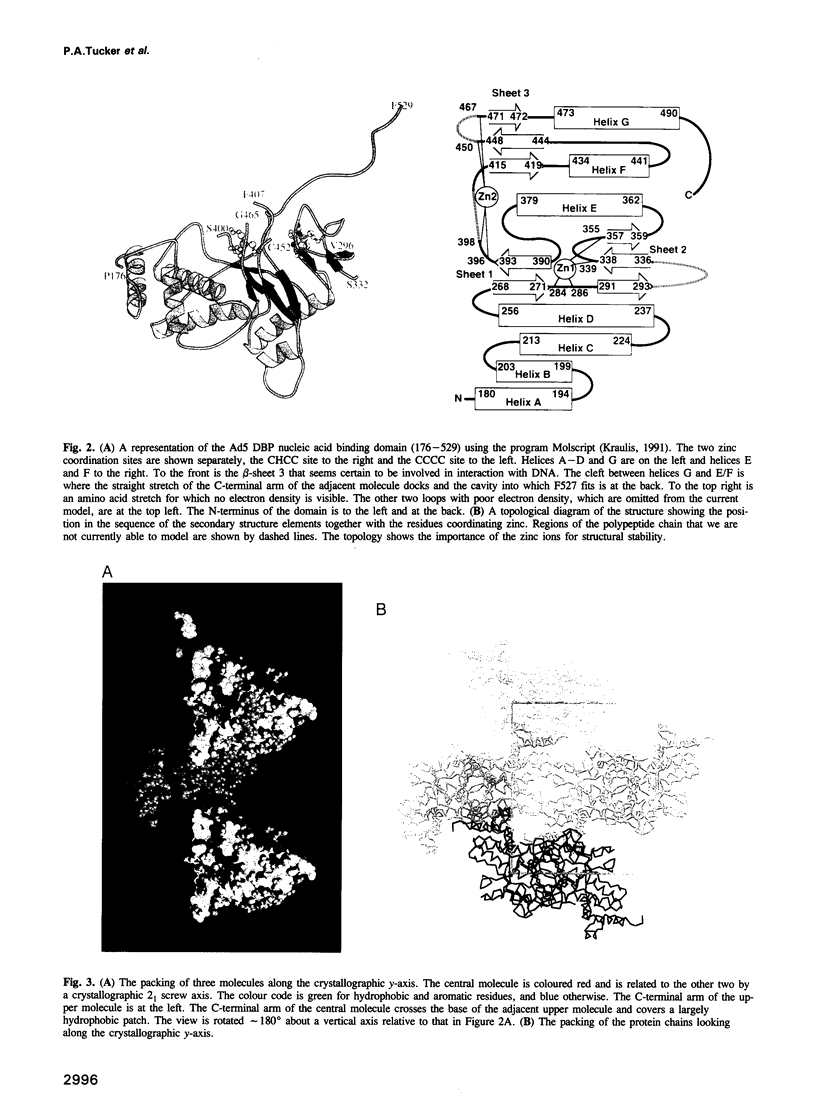
The adenovirus single-stranded DNA binding protein (Ad DBP) is a multifunctional protein required, amongst other things, for DNA replication and transcription control. It binds to single- and double-stranded DNA, as well as to RNA, in a sequence-independent manner. Like other single-stranded DNA binding proteins, it binds ssDNA, cooperatively. We report the crystal structure, at 2.6 A resolution, of the nucleic acid binding domain. This domain is active in DNA replication. The protein contains two zinc atoms in different, novel coordinations. The zinc atoms appear to be required for the stability of the protein fold rather than being involved in direct contacts with the DNA. The crystal structure shows that the protein contains a 17 amino acid C-terminal extension which hooks onto a second molecule, thereby forming a protein chain. Deletion of this C-terminal arm reduces cooperativity in DNA binding, suggesting a hook-on model for cooperativity. Based on this structural work and mutant studies, we propose that DBP forms a protein core around which the single-stranded DNA winds.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M., Frey L. T4 bacteriophage gene 32: a structural protein in the replication and recombination of DNA. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1313–1318. doi: 10.1038/2271313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Zinc fingers and other metal-binding domains. Elements for interactions between macromolecules. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6513–6516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase J. W., Williams K. R. Single-stranded DNA binding proteins required for DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:103–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleat P. H., Hay R. T. Co-operative interactions between NFI and the adenovirus DNA binding protein at the adenovirus origin of replication. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1841–1848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleghon V., Klessig D. F. Characterization of the nucleic acid binding region of adenovirus DNA binding protein by partial proteolysis and photochemical cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17872–17881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagle P. A., Klessig D. F. A zinc-binding motif located between amino acids 273 and 286 in the adenovirus DNA-binding protein is necessary for ssDNA binding. Virology. 1992 Apr;187(2):777–787. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90479-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C. W. Three-dimensional structure of complexes of single-stranded DNA-binding proteins with DNA. IKe and fd gene 5 proteins form left-handed helices with single-stranded DNA. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 5;208(1):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez C., Martín G., Sogo J. M., Salas M. Mechanism of stimulation of DNA replication by bacteriophage phi 29 single-stranded DNA-binding protein p5. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2104–2111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. K., Lee S. H., Hurwitz J. Multiple functions of human single-stranded-DNA binding protein in simian virus 40 DNA replication: single-strand stabilization and stimulation of DNA polymerases alpha and delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9757–9761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchingman G. R. Sequence of the DNA-binding protein of a human subgroup E adenovirus (type 4): comparisons with subgroup A (type 12), subgroup B (type 7), and subgroup C (type 5). Virology. 1985 Oct 15;146(1):90–101. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. Structure-function relationships of the adenovirus DNA-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11051–11060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Grodzicker T. Mutations that allow human Ad2 and Ad5 to express late genes in monkey cells map in the viral gene encoding the 72K DNA binding protein. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):957–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90335-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Van Schaik F. M., Sussenbach J. S. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding adenovirus type 2 DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4493–4500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuil M. E., van Amerongen H., van der Vliet P. C., van Grondelle R. Complex formation between the adenovirus DNA-binding protein and single-stranded poly(rA). Cooperativity and salt dependence. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 12;28(25):9795–9800. doi: 10.1021/bi00451a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenbaum J. O., Field J., Hurwitz J. The adenovirus DNA binding protein and adenovirus DNA polymerase interact to catalyze elongation of primed DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10218–10227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linné T., Philipson L. Further characterization of the phosphate moiety of the adenovirus type 2 DNA-binding protein. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(2):259–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin N., Delsert C., Klessig D. F. Nuclear localization of the adenovirus DNA-binding protein: requirement for two signals and complementation during viral infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4372–4380. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mul Y. M., van Miltenburg R. T., De Clercq E., van der Vliet P. C. Mechanism of inhibition of adenovirus DNA replication by the acyclic nucleoside triphosphate analogue (S)-HPMPApp: influence of the adenovirus DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):8917–8929. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.8917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mul Y. M., van der Vliet P. C. The adenovirus DNA binding protein effects the kinetics of DNA replication by a mechanism distinct from NFI or Oct-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):641–647. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Oubridge C., Jessen T. H., Li J., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of the RNA-binding domain of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):515–520. doi: 10.1038/348515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neale G. A., Kitchingman G. R. Biochemical analysis of adenovirus type 5 DNA-binding protein mutants. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3153–3159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neale G. A., Kitchingman G. R. Conserved region 3 of the adenovirus type 5 DNA-binding protein is important for interaction with single-stranded DNA. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):630–638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.630-638.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Stillman B. W. Functional characterization of thermolabile DNA-binding proteins that affect adenovirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):883–892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.883-892.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn C. O., Kitchingman G. R. Functional analysis of the adenovirus type 5 DNA-binding protein: site-directed mutants which are defective for adeno-associated virus helper activity. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):653–661. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.653-661.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan C., Ramachandran G. N. Stereochemical criteria for polypeptide and protein chain conformations. II. Allowed conformations for a pair of peptide units. Biophys J. 1965 Nov;5(6):909–933. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(65)86759-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin H., Marahiel M. A., Heinemann U. Universal nucleic acid-binding domain revealed by crystal structure of the B. subtilis major cold-shock protein. Nature. 1993 Jul 8;364(6433):164–168. doi: 10.1038/364164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuiver M. H., Bergsma W. G., Arnberg A. C., van Amerongen H., van Grondelle R., van der Vliet P. C. Structural alterations of double-stranded DNA in complex with the adenovirus DNA-binding protein. Implications for its function in DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 20;225(4):999–1011. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuiver M. H., van der Vliet P. C. Adenovirus DNA-binding protein forms a multimeric protein complex with double-stranded DNA and enhances binding of nuclear factor I. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):379–386. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.379-386.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers M. F., South T. L., Kim B., Hare D. R. High-resolution structure of an HIV zinc fingerlike domain via a new NMR-based distance geometry approach. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):329–340. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsernoglou D., Tsugita A., Tucker A. D., van der Vliet P. C. Characterization of the chymotryptic core of the adenovirus DNA-binding protein. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 2;188(2):248–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80381-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsernoglou D., Tucker A. D., Van der Vliet P. C. Crystallization of a fragment of the adenovirus DNA binding protein. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 15;172(2):237–239. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji M., Kitchingman G. R. Functional changes in temperature-sensitive mutants of the adenovirus single-stranded DNA-binding protein are accompanied by structural alterations. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):480–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.480-488.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji M., van der Vliet P. C., Kitchingman G. R. Temperature-sensitive mutants of adenovirus single-stranded DNA-binding protein. Inability to support DNA replication is associated with an altered DNA-binding activity of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16178–16187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L., Coleman J. E., Auld D. S. Zinc fingers, zinc clusters, and zinc twists in DNA-binding protein domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):999–1003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., van Oosterhout J. A., van der Vliet P. C. The Oct-1 POU domain mediates interactions between Oct-1 and other POU proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):542–551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos H. L., Brough D. E., Van der Lee F. M., Hoeben R. C., Verheijden G. F., Dooijes D., Klessig D. F., Sussenbach J. S. Characterization of adenovirus type 5 insertion and deletion mutants encoding altered DNA binding proteins. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):634–642. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos H. L., van der Lee F. M., Reemst A. M., van Loon A. E., Sussenbach J. S. The genes encoding the DNA binding protein and the 23K protease of adenovirus types 40 and 41. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90227-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos H. L., van der Lee F. M., Sussenbach J. S. The binding of in vitro synthesized adenovirus DNA binding protein to single-stranded DNA is stimulated by zinc ions. FEBS Lett. 1988 Nov 7;239(2):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80927-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. C. Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:90–112. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Kelly T. Purification and characterization of replication protein A, a cellular protein required for in vitro replication of simian virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2523–2527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijderveld D. C., Stuiver M. H., van der Vliet P. C. The adenovirus DNA binding protein enhances intermolecular DNA renaturation but inhibits intramolecular DNA renaturation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 11;21(11):2591–2598. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.11.2591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijderveld D. C., van der Vliet P. C. Helix-destabilizing properties of the adenovirus DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):1158–1164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.1158-1164.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Amerongen H., van Grondelle R., van der Vliet P. C. Interaction between adenovirus DNA-binding protein and single-stranded polynucleotides studied by circular dichroism and ultraviolet absorption. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 28;26(15):4646–4652. doi: 10.1021/bi00389a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vliet P. C., Levine A. J. DNA-binding proteins specific for cells infected by adenovirus. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 12;246(154):170–174. doi: 10.1038/newbio246170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]