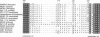Abstract
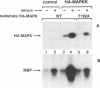
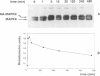
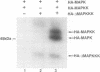
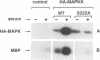
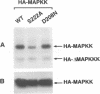
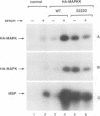
In response to various external stimuli, MAP kinases are activated by phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine by MAP kinase kinase (MAPKK), a dual specificity kinase. This kinase is in turn activated via Raf-1 and MAPKK kinase (MAPKKK). To determine regulatory phosphorylation sites of MAPKK, we isolated a Chinese hamster cDNA, that we epitope-tagged and expressed in fibroblasts. This hamster MAPKK (MEK1 isoform) can reactivate recombinant p44mapk when immunoprecipitated from growth factor-stimulated cells or when incubated with an active form of MAPKKK. Mutations at either of two residues that are conserved among kinases, D208N or S222A, abolished MAPKK activity. However, only S222A/MAPKK showed a reduction in phosphorylation in response to active MAPKKK and exerted a dominant negative effect on the serum-stimulated endogenous MAPKK. Finally, replacing Ser222 with Asp, a negatively charged residue, restored MAPKK activity independently of the upstream kinase. These results strongly suggest that Ser222 represents one key MAPKKK-dependent phosphorylation site switching on and off the activity of MAPKK, an event crucial for growth control.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Campbell J. S., Seger R., Jensen A. L., Graves L. M., Krebs E. G. Metabolic labeling of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in A431 cells demonstrates phosphorylation on serine and threonine residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5143–5147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashworth A., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. The amino acid sequence of a mammalian MAP kinase kinase. Oncogene. 1992 Dec;7(12):2555–2556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck T. W., Huleihel M., Gunnell M., Bonner T. I., Rapp U. R. The complete coding sequence of the human A-raf-1 oncogene and transforming activity of a human A-raf carrying retrovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):595–609. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambard J. C., Paris S., L'Allemain G., Pouysségur J. Two growth factor signalling pathways in fibroblasts distinguished by pertussis toxin. Nature. 1987 Apr 23;326(6115):800–803. doi: 10.1038/326800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Boulton T. G., Robbins D. J. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases: ERKs in progress. Cell Regul. 1991 Dec;2(12):965–978. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.12.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A., Erikson R. L. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):478–480. doi: 10.1126/science.1411546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Erikson R. L. Purification of a murine protein-tyrosine/threonine kinase that phosphorylates and activates the Erk-1 gene product: relationship to the fission yeast byr1 gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8205–8209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng W. P., Nickoloff J. A. Site-directed mutagenesis of virtually any plasmid by eliminating a unique site. Anal Biochem. 1992 Jan;200(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90280-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Haser W., Haystead T. A., Vincent L. A., Roberts T. M., Sturgill T. W. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase by v-Raf in NIH 3T3 cells and in vitro. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1404–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.1326789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Morgan D. O., Clauser E., Edery M., Jong S. M., Wang L. H., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Mechanisms of receptor-mediated transmembrane communication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 2):773–784. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Levin D. E. A conserved kinase cascade for MAP kinase activation in yeast. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):254–260. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Dent P., Wu J., Haystead C. M., Sturgill T. W. Ordered phosphorylation of p42mapk by MAP kinase kinase. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 13;306(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80828-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Leevers S. J., Gómez N., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. J. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90361-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan C., Seuwen K., Meloche S., Pouysségur J. Coordinate, biphasic activation of p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase and S6 kinase by growth factors in hamster fibroblasts. Evidence for thrombin-induced signals different from phosphoinositide turnover and adenylylcyclase inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13369–13375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosako H., Gotoh Y., Matsuda S., Ishikawa M., Nishida E. Xenopus MAP kinase activator is a serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activated by threonine phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2903–2908. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05359.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosako H., Nishida E., Gotoh Y. cDNA cloning of MAP kinase kinase reveals kinase cascade pathways in yeasts to vertebrates. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):787–794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Allemain G., Pouyssegur J., Weber M. J. p42/mitogen-activated protein kinase as a converging target for different growth factor signaling pathways: use of pertussis toxin as a discrimination factor. Cell Regul. 1991 Aug;2(8):675–684. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.8.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Carter C. A., Pleiman C. M., Gardner A. M., Blumer K. J., Johnson G. L. A divergence in the MAP kinase regulatory network defined by MEK kinase and Raf. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):315–319. doi: 10.1126/science.8385802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenormand P., Pagès G., Sardet C., L'Allemain G., Meloche S., Pouysségur J. MAP kinases: activation, subcellular localization and role in the control of cell proliferation. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1993;28:237–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenormand P., Sardet C., Pagès G., L'Allemain G., Brunet A., Pouysségur J. Growth factors induce nuclear translocation of MAP kinases (p42mapk and p44mapk) but not of their activator MAP kinase kinase (p45mapkk) in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):1079–1088. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda S., Kosako H., Takenaka K., Moriyama K., Sakai H., Akiyama T., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Xenopus MAP kinase activator: identification and function as a key intermediate in the phosphorylation cascade. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):973–982. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloche S., Pagès G., Pouysségur J. Functional expression and growth factor activation of an epitope-tagged p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase, p44mapk. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):63–71. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloche S., Seuwen K., Pagès G., Pouysségur J. Biphasic and synergistic activation of p44mapk (ERK1) by growth factors: correlation between late phase activation and mitogenicity. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 May;6(5):845–854. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.5.1603090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordret G. MAP kinase kinase: a node connecting multiple pathways. Biol Cell. 1993;79(3):193–207. doi: 10.1016/0248-4900(93)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebreda A. R. Inactivation of MAP kinases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jan;19(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman A. M. Conservation and reiteration of a kinase cascade. Trends Genet. 1993 Nov;9(11):390–394. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi T., Metz R., Chen L., Mattéi M. G., Carrasco D., Bravo R. Structure, mapping, and expression of erp, a growth factor-inducible gene encoding a nontransmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatase, and effect of ERP on cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5195–5205. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagès G., Lenormand P., L'Allemain G., Chambard J. C., Meloche S., Pouysségur J. Mitogen-activated protein kinases p42mapk and p44mapk are required for fibroblast proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8319–8323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. M., Rossomando A. J., Martino P., Erickson A. K., Her J. H., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Identification of the regulatory phosphorylation sites in pp42/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):885–892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. MAP kinases: charting the regulatory pathways. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1355–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.1382311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J., Sardet C., Franchi A., L'Allemain G., Paris S. A specific mutation abolishing Na+/H+ antiport activity in hamster fibroblasts precludes growth at neutral and acidic pH. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman J. V. MAP kinase and the activation of quiescent cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Molecular cloning, primary structure, and expression of the human growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ antiporter. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90901-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Ahn N. G., Posada J., Munar E. S., Jensen A. M., Cooper J. A., Cobb M. H., Krebs E. G. Purification and characterization of mitogen-activated protein kinase activator(s) from epidermal growth factor-stimulated A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14373–14381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Seger D., Lozeman F. J., Ahn N. G., Graves L. M., Campbell J. S., Ericsson L., Harrylock M., Jensen A. M., Krebs E. G. Human T-cell mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases are related to yeast signal transduction kinases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25628–25631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton V. P., Jr, Nichols D. W., Laudano A. P., Cooper G. M. Definition of the human raf amino-terminal regulatory region by deletion mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):639–647. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Wu J. Recent progress in characterization of protein kinase cascades for phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 17;1092(3):350–357. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(97)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Knighton D. R., Zheng J., Sowadski J. M., Gibbs C. S., Zoller M. J. A template for the protein kinase family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Mar;18(3):84–89. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)80001-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vouret-Craviari V., Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Scimeca J. C., Van Obberghen E., Pouysségur J. Differential activation of p44mapk (ERK1) by alpha-thrombin and thrombin-receptor peptide agonist. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):209–214. doi: 10.1042/bj2890209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Fafournoux P., Sardet C., Pouysségur J. The Na+/H+ antiporter cytoplasmic domain mediates growth factor signals and controls "H(+)-sensing". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Simonson M. S., Pouysségur J., Dunn M. J. Endothelin rapidly stimulates mitogen-activated protein kinase activity in rat mesangial cells. Biochem J. 1992 Oct 15;287(Pt 2):589–594. doi: 10.1042/bj2870589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Niman H. L., Houghten R. A., Cherenson A. R., Connolly M. L., Lerner R. A. The structure of an antigenic determinant in a protein. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yashar B. M., Kelley C., Yee K., Errede B., Zon L. I. Novel members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase activator family in Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5738–5748. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Strand A., Robbins D., Cobb M. H., Goldsmith E. J. Atomic structure of the MAP kinase ERK2 at 2.3 A resolution. Nature. 1994 Feb 24;367(6465):704–711. doi: 10.1038/367704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C. F., Guan K. L. Activation of MEK family kinases requires phosphorylation of two conserved Ser/Thr residues. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 1;13(5):1123–1131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06361.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]