Abstract
The Escherichia coli cytoplasmic membrane protein, p12, stimulates the protein translocation activity reconstituted with SecY, SecE and SecA. The gene encoding p12, which is located at 69 min on the E. coli chromosome, was deleted to examine the role of p12 in protein translocation in vivo. The deletion strain exhibited cold-sensitive growth. Pulse-chase experiments revealed that precursors of outer membrane protein A, maltose binding protein and beta-lactamase accumulated at 20 degrees C but not at 37 degrees C. The deletion strain harboring a plasmid which carries the gene encoding p12 under the control of the araBAD promoter was able to grow in the cold when p12 was expressed with the addition of arabinose. Furthermore, the accumulated precursors were rapidly processed to the mature forms upon the expression of p12. Immunoblot analysis revealed the steady-state accumulation of precursor proteins at 20 degrees C, whereas the accumulation was only marginal at 37 degrees C, indicating that the function of p12 is more critical at 20 degrees C than at 37 degrees C. Finally, proteoliposomes were reconstituted with or without p12 to demonstrate that the stimulation of the activity by p12 increases with a decrease in temperature. From these results, we concluded that p12 is directly involved in protein translocation in E. coli and plays a critical role in the cold. We propose the more systematic name, SecG, for p12.
Full text
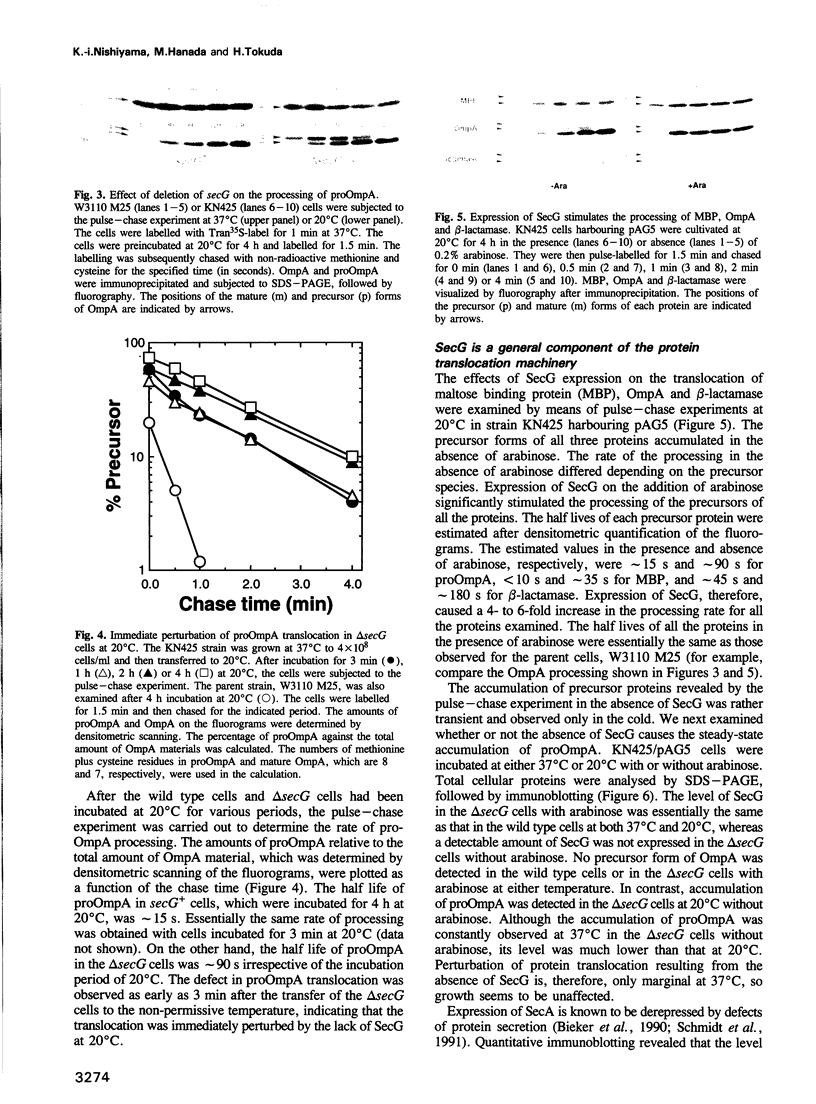
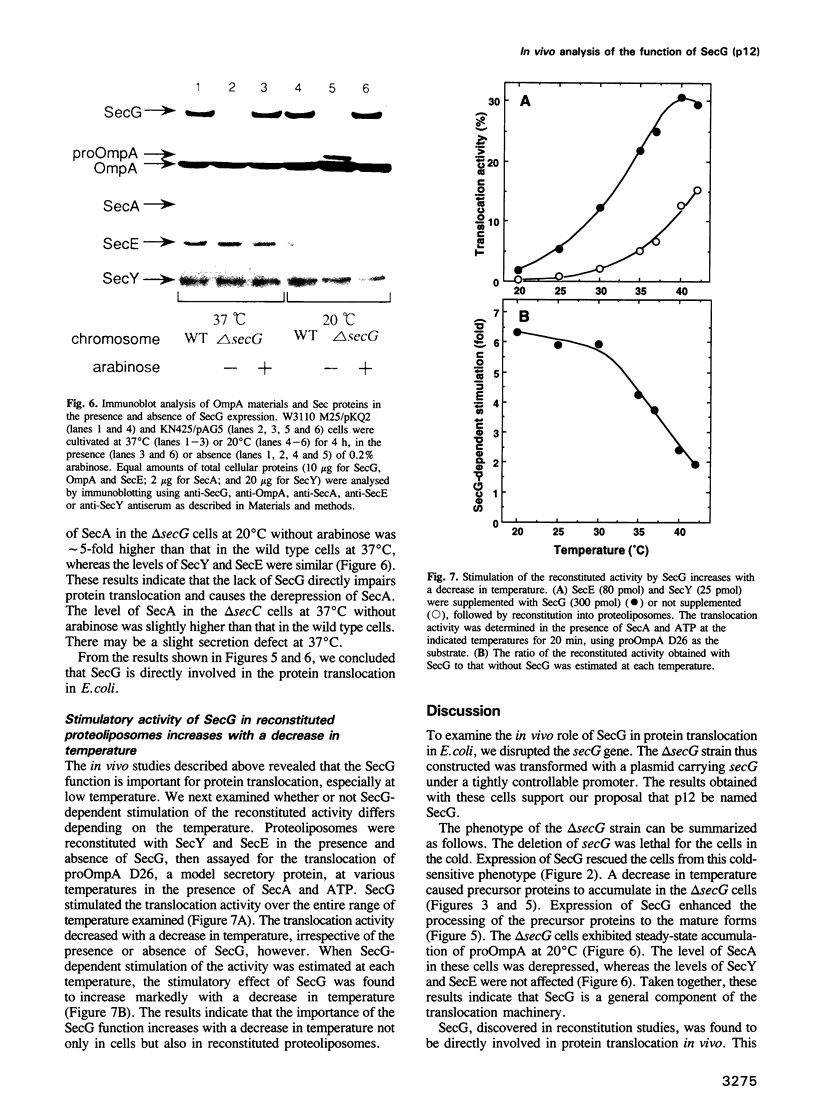
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akimaru J., Matsuyama S., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. Reconstitution of a protein translocation system containing purified SecY, SecE, and SecA from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6545–6549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akita M., Sasaki S., Matsuyama S., Mizushima S. SecA interacts with secretory proteins by recognizing the positive charge at the amino terminus of the signal peptide in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8164–8169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama Y., Ito K. The SecY membrane component of the bacterial protein export machinery: analysis by new electrophoretic methods for integral membrane proteins. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3351–3356. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkowitz R. A., Wickner W. SecD and SecF are required for the proton electrochemical gradient stimulation of preprotein translocation. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):954–963. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassilana M., Wickner W. Purified Escherichia coli preprotein translocase catalyzes multiple cycles of precursor protein translocation. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 16;32(10):2626–2630. doi: 10.1021/bi00061a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker K. L., Phillips G. J., Silhavy T. J. The sec and prl genes of Escherichia coli. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):291–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00763169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundage L., Fimmel C. J., Mizushima S., Wickner W. SecY, SecE, and band 1 form the membrane-embedded domain of Escherichia coli preprotein translocase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):4166–4170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundage L., Hendrick J. P., Schiebel E., Driessen A. J., Wickner W. The purified E. coli integral membrane protein SecY/E is sufficient for reconstitution of SecA-dependent precursor protein translocation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90111-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabelli R. J., Chen L., Tai P. C., Oliver D. B. SecA protein is required for secretory protein translocation into E. coli membrane vesicles. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90227-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabello F., Timmis K., Cohen S. N. Replication control in a composite plasmid constructed by in vitro linkage of two distinct replicons. Nature. 1976 Jan 29;259(5541):285–290. doi: 10.1038/259285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham K., Lill R., Crooke E., Rice M., Moore K., Wickner W., Oliver D. SecA protein, a peripheral protein of the Escherichia coli plasma membrane, is essential for the functional binding and translocation of proOmpA. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):955–959. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03457.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Hanley-Way S., Silhavy T. J. Suppressor mutations that restore export of a protein with a defective signal sequence. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardel C., Benson S., Hunt J., Michaelis S., Beckwith J. secD, a new gene involved in protein export in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1286–1290. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1286-1290.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardel C., Johnson K., Jacq A., Beckwith J. The secD locus of E.coli codes for two membrane proteins required for protein export. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3209–3216. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Prehn S., Hartmann E., Kalies K. U., Rapoport T. A. A mammalian homolog of SEC61p and SECYp is associated with ribosomes and nascent polypeptides during translocation. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):489–503. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90517-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Rapoport T. A. Protein translocation into proteoliposomes reconstituted from purified components of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):615–630. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann E., Sommer T., Prehn S., Görlich D., Jentsch S., Rapoport T. A. Evolutionary conservation of components of the protein translocation complex. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):654–657. doi: 10.1038/367654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain M., Ichihara S., Mizushima S. Accumulation of glyceride-containing precursor of the outer membrane lipoprotein in the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli treated with globomycin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3707–3712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Wittekind M., Nomura M., Shiba K., Yura T., Miura A., Nashimoto H. A temperature-sensitive mutant of E. coli exhibiting slow processing of exported proteins. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):789–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki H., Matsuyama S., Sasaki S., Akita M., Mizushima S. SecA protein is directly involved in protein secretion in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):431–434. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80516-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komine Y., Adachi T., Inokuchi H., Ozeki H. Genomic organization and physical mapping of the transfer RNA genes in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):579–598. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90224-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A., Beckwith J. Mutations in a new gene, secB, cause defective protein localization in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):253–260. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.253-260.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A. SecB protein: a cytosolic export factor that associates with nascent exported proteins. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):337–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00763171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Cunningham K., Brundage L. A., Ito K., Oliver D., Wickner W. SecA protein hydrolyzes ATP and is an essential component of the protein translocation ATPase of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):961–966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama S., Akimaru J., Mizushima S. SecE-dependent overproduction of SecY in Escherichia coli. Evidence for interaction between two components of the secretory machinery. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 20;269(1):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81128-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama S., Fujita Y., Mizushima S. SecD is involved in the release of translocated secretory proteins from the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):265–270. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05652.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama S., Fujita Y., Sagara K., Mizushima S. Overproduction, purification and characterization of SecD and SecF, integral membrane components of the protein translocation machinery of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 13;1122(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(92)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama K., Kabuyama Y., Akimaru J., Matsuyama S., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. SecY is an indispensable component of the protein secretory machinery of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 31;1065(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90015-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama K., Mizushima S., Tokuda H. A novel membrane protein involved in protein translocation across the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3409–3415. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama K., Mizushima S., Tokuda H. The carboxyl-terminal region of SecE interacts with SecY and is functional in the reconstitution of protein translocation activity in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7170–7176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda A., Courtright J. B., Denor P. F., Webb G., Kohara Y., Ishihama A. Rapid identification of specific genes in E. coli by hybridization to membranes containing the ordered set of phage clones. Biotechniques. 1991 Apr;10(4):474, 476-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogura T., Bouloc P., Niki H., D'Ari R., Hiraga S., Jaffé A. Penicillin-binding protein 2 is essential in wild-type Escherichia coli but not in lov or cya mutants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3025–3030. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3025-3030.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. E. coli mutant pleiotropically defective in the export of secreted proteins. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):765–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. Regulation of a membrane component required for protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogliano J. A., Beckwith J. SecD and SecF facilitate protein export in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):554–561. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogliano K. J., Beckwith J. The Cs sec mutants of Escherichia coli reflect the cold sensitivity of protein export itself. Genetics. 1993 Apr;133(4):763–773. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.4.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs P. D., Derman A. I., Beckwith J. A mutation affecting the regulation of a secA-lacZ fusion defines a new sec gene. Genetics. 1988 Apr;118(4):571–579. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.4.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell C. B., Thaler D. S., Dahlquist F. W. Chromosomal transformation of Escherichia coli recD strains with linearized plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2609–2613. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2609-2613.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Riggs P. D., Jacq A., Fath M. J., Beckwith J. The secE gene encodes an integral membrane protein required for protein export in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1035–1044. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. G., Dolan K. M., Oliver D. B. Regulation of Escherichia coli secA mRNA translation by a secretion-responsive element. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6605–6611. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6605-6611.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl F. W., Kobayashi I., Thaler D., Stahl M. M. Direction of travel of RecBC recombinase through bacteriophage lambda DNA. Genetics. 1986 Jun;113(2):215–227. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimura K. Mutant isolation and cloning of the gene encoding protease VII from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 16;153(2):753–759. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani K., Shiozuka K., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. In vitro analysis of the process of translocation of OmpA across the Escherichia coli cytoplasmic membrane. A translocation intermediate accumulates transiently in the absence of the proton motive force. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18582–18588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani K., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. Translocation of ProOmpA possessing an intramolecular disulfide bridge into membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Effect of membrane energization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17341–17347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Akimaru J., Matsuyama S., Nishiyama K., Mizushima S. Purification of SecE and reconstitution of SecE-dependent protein translocation activity. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 25;279(2):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80156-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., Ray P. H., Bassford P. J., Jr Purified secB protein of Escherichia coli retards folding and promotes membrane translocation of the maltose-binding protein in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8978–8982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane K., Ichihara S., Mizushima S. In vitro translocation of protein across Escherichia coli membrane vesicles requires both the proton motive force and ATP. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2358–2362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]