Abstract
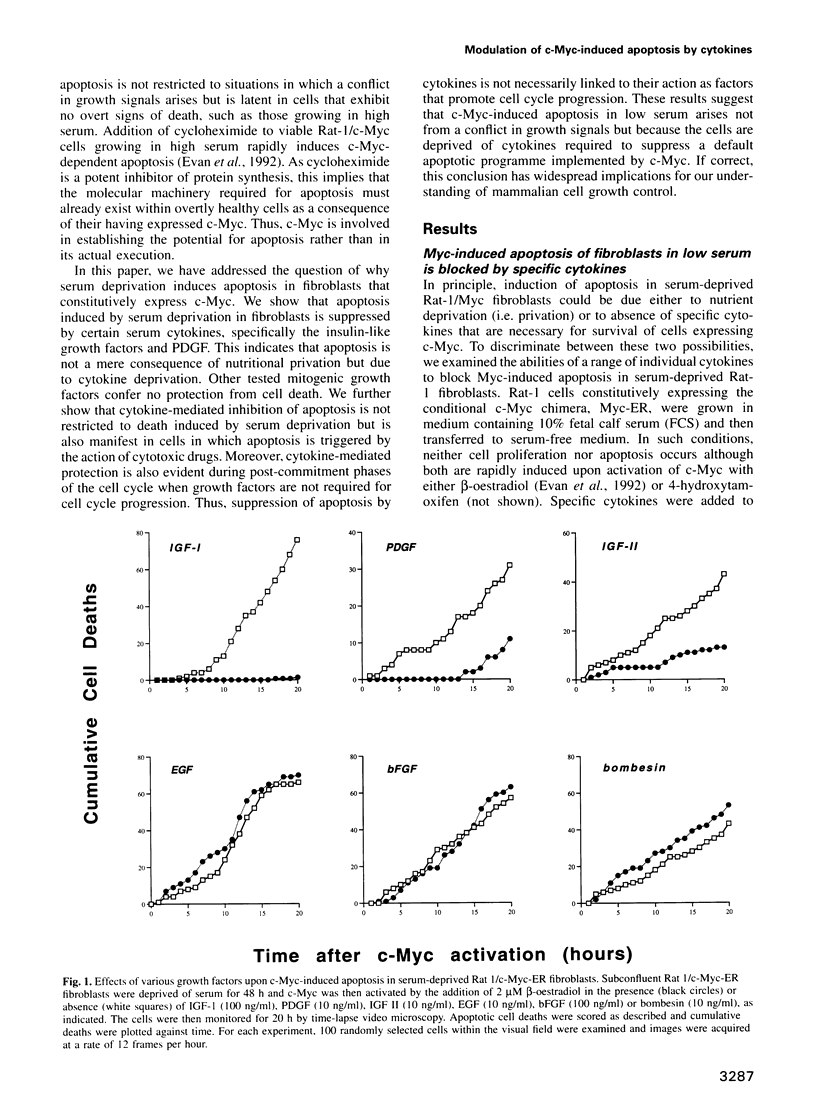
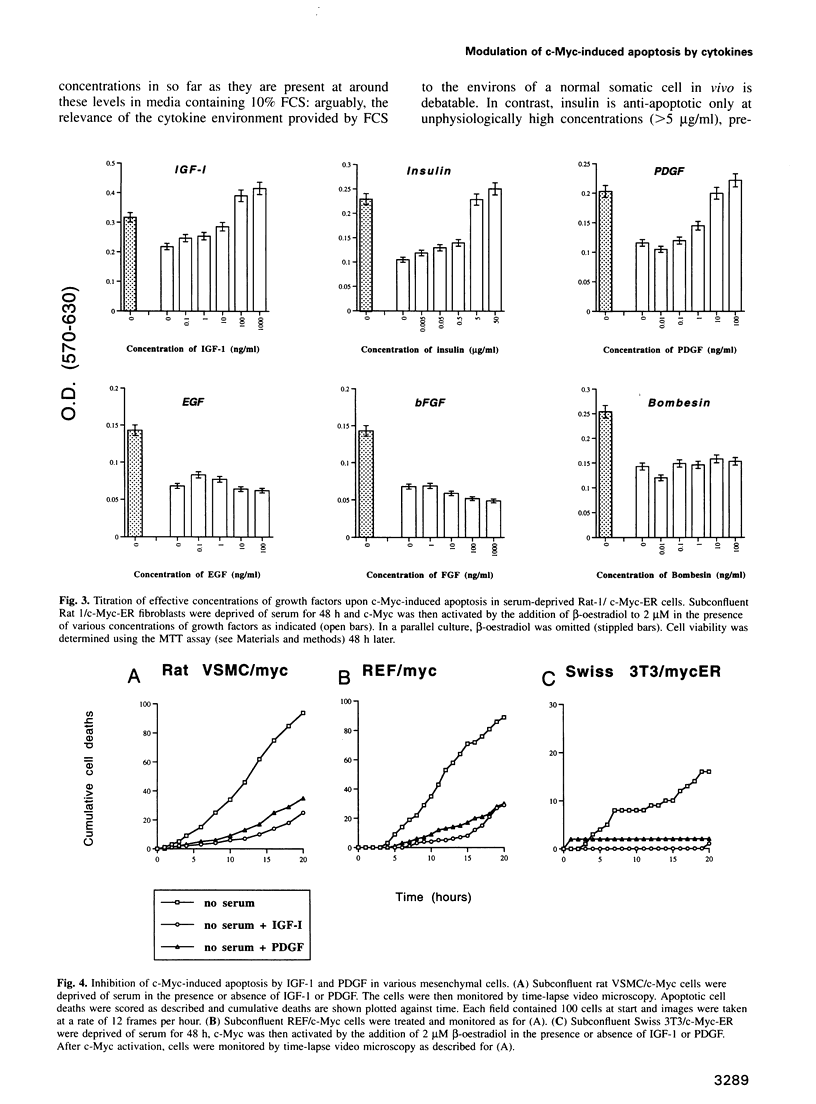
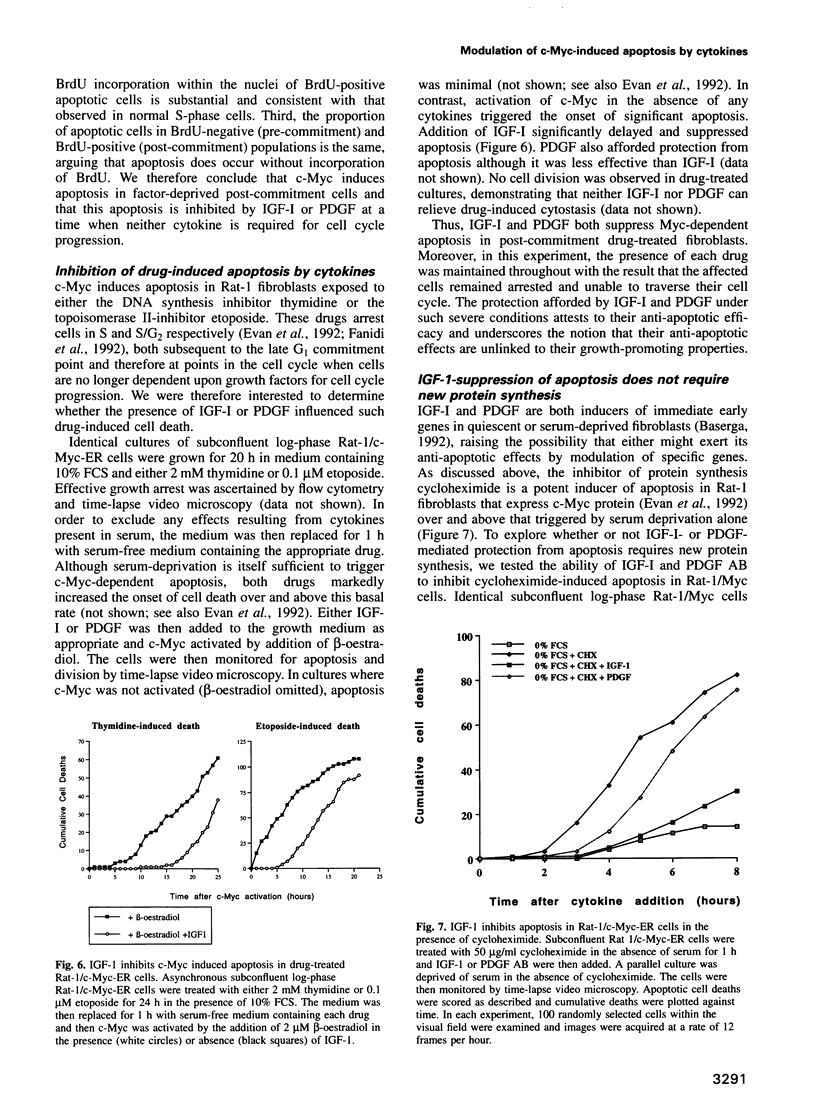
We have investigated the mechanism by which deregulated expression of c-Myc induces death by apoptosis in serum-deprived fibroblasts. We demonstrate that Myc-induced apoptosis in low serum is inhibited by a restricted group of cytokines, principally the insulin-like growth factors and PDGF. Cytokine-mediated protection from apoptosis is not linked to the cytokines' abilities to promote growth. Protection from apoptosis is evident in the post-commitment (mitogen-independent) S/G2/M phases of the cell cycle and also in cells that are profoundly blocked in cell cycle progression by drugs. Moreover, IGF-I inhibition of apoptosis occurs in the absence of protein synthesis, and so does not require immediate early gene expression. We conclude that c-Myc-induced apoptosis does not result from a conflict of growth signals but appears to be a normal physiological aspect of c-Myc function whose execution is regulated by the availability of survival factors. We discuss the possible implications of these findings for models of mammalian cell growth in vivo.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amati B., Brooks M. W., Levy N., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. Oncogenic activity of the c-Myc protein requires dimerization with Max. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90663-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati B., Dalton S., Brooks M. W., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. Transcriptional activation by the human c-Myc oncoprotein in yeast requires interaction with Max. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):423–426. doi: 10.1038/359423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati B., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. The c-Myc protein induces cell cycle progression and apoptosis through dimerization with Max. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5083–5087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06202.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askew D. S., Ashmun R. A., Simmons B. C., Cleveland J. L. Constitutive c-myc expression in an IL-3-dependent myeloid cell line suppresses cell cycle arrest and accelerates apoptosis. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1915–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga R. The double life of the IGF-1 receptor. Receptor. 1992 Winter;2(4):261–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M., Metzger D., Chambon P. Role of the two activating domains of the oestrogen receptor in the cell-type and promoter-context dependent agonistic activity of the anti-oestrogen 4-hydroxytamoxifen. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2811–2818. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07469.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette R. P., Echeverri F., Mahboubi A., Green D. R. Apoptotic cell death induced by c-myc is inhibited by bcl-2. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):552–554. doi: 10.1038/359552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boise L. H., González-García M., Postema C. E., Ding L., Lindsten T., Turka L. A., Mao X., Nuñez G., Thompson C. B. bcl-x, a bcl-2-related gene that functions as a dominant regulator of apoptotic cell death. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):597–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90508-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Bascom C. C., Sipes N. J., Graves-Deal R., Weissman B. E., Moses H. L. Selective inhibition of growth-related gene expression in murine keratinocytes by transforming growth factor beta. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3088–3093. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J. Apoptosis. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):126–130. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90214-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. K., Marvel J., Malde P., Lopez-Rivas A. Interleukin 3 protects murine bone marrow cells from apoptosis induced by DNA damaging agents. J Exp Med. 1992 Oct 1;176(4):1043–1051. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.4.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Levine R. A., Ran W., Kindy M. S., Sonenshein G. E., Campisi J. Regulation of c-myc transcription and mRNA abundance by serum growth factors and cell contact. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9161–9166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Picard D., Yamamoto K. R., Bishop J. M. Chimaeras of myc oncoprotein and steroid receptors cause hormone-dependent transformation of cells. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):66–68. doi: 10.1038/340066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Schirm S., Bishop J. M. The MYC protein activates transcription of the alpha-prothymosin gene. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):133–141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Littlewood T. D. The role of c-myc in cell growth. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Feb;3(1):44–49. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
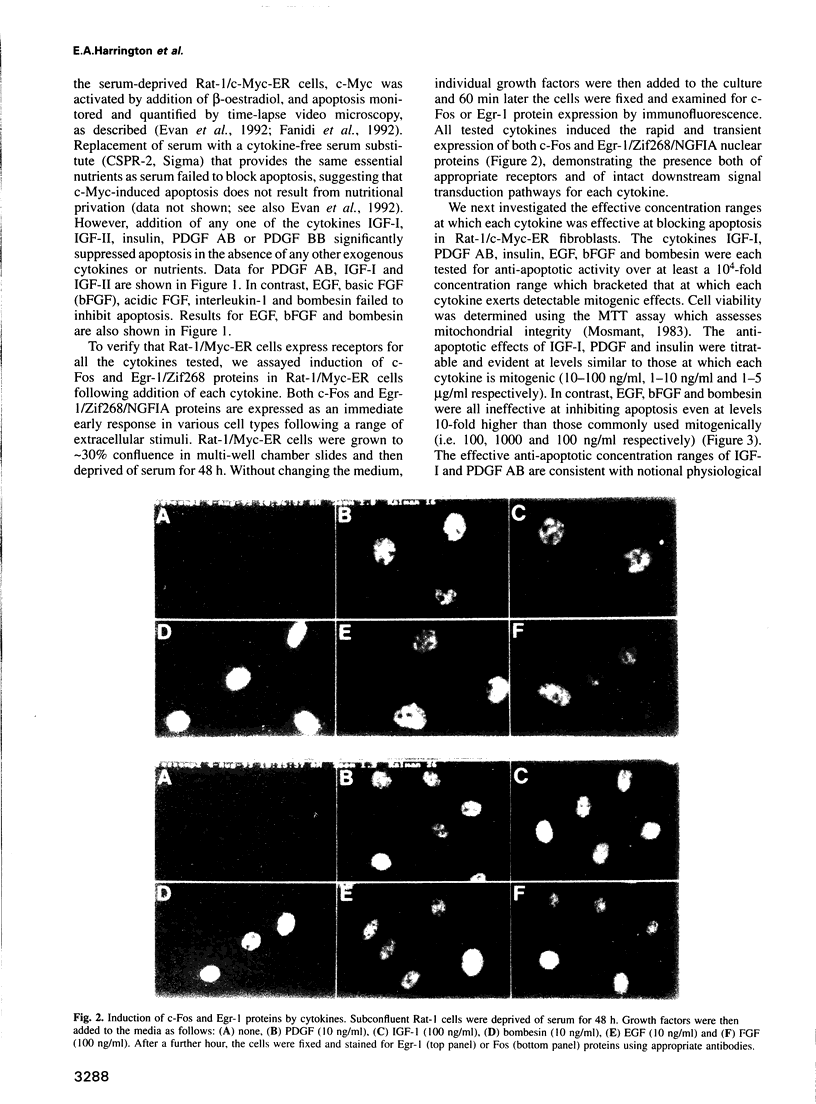
- Evan G. I., Wyllie A. H., Gilbert C. S., Littlewood T. D., Land H., Brooks M., Waters C. M., Penn L. Z., Hancock D. C. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90123-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanidi A., Harrington E. A., Evan G. I. Cooperative interaction between c-myc and bcl-2 proto-oncogenes. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):554–556. doi: 10.1038/359554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher F., Jayaraman P. S., Goding C. R. C-myc and the yeast transcription factor PHO4 share a common CACGTG-binding motif. Oncogene. 1991 Jul;6(7):1099–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R., Schwab G., Wickstrom E., Loke S. L., Pluznik D. H., Watt R., Neckers L. M. A c-myc antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits entry into S phase but not progress from G0 to G1. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):445–449. doi: 10.1038/328445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt S. P., Pini A., Evan G. Induction of c-fos-like protein in spinal cord neurons following sensory stimulation. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):632–634. doi: 10.1038/328632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Barrett J., Villa-Garcia M., Dang C. V. An amino-terminal c-myc domain required for neoplastic transformation activates transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5914–5920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Lee W. M., Chen L. L., Dang C. V. Max: functional domains and interaction with c-Myc. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):81–92. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozopas K. M., Yang T., Buchan H. L., Zhou P., Craig R. W. MCL1, a gene expressed in programmed myeloid cell differentiation, has sequence similarity to BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3516–3520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson O., Zetterberg A., Engström W. Cell-cycle-specific induction of quiescence achieved by limited inhibition of protein synthesis: counteractive effect of addition of purified growth factors. J Cell Sci. 1985 Feb;73:375–387. doi: 10.1242/jcs.73.1.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin E. Y., Orlofsky A., Berger M. S., Prystowsky M. B. Characterization of A1, a novel hemopoietic-specific early-response gene with sequence similarity to bcl-2. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 15;151(4):1979–1988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlewood T. D., Amati B., Land H., Evan G. I. Max and c-Myc/Max DNA-binding activities in cell extracts. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1783–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita T., Reed J. C. bcl-2 gene transfer increases relative resistance of S49.1 and WEHI7.2 lymphoid cells to cell death and DNA fragmentation induced by glucocorticoids and multiple chemotherapeutic drugs. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 1;52(19):5407–5411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., Hancock D. C., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I. A sensitive and quantitative enzyme-linked immunosorbence assay for the c-myc and N-myc oncoproteins. Oncogene Res. 1987;2(1):65–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oltvai Z. N., Milliman C. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):609–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90509-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn L. J., Brooks M. W., Laufer E. M., Land H. Negative autoregulation of c-myc transcription. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1113–1121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08217.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn L. J., Brooks M. W., Laufer E. M., Littlewood T. D., Morgenstern J. P., Evan G. I., Lee W. M., Land H. Domains of human c-myc protein required for autosuppression and cooperation with ras oncogenes are overlapping. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4961–4966. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Lawe D., Ziff E. B. Association of Myn, the murine homolog of max, with c-Myc stimulates methylation-sensitive DNA binding and ras cotransformation. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90457-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. Methylation-sensitive sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc basic region. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):186–189. doi: 10.1126/science.1987636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochownik E. V., Kukowska J., Rodgers C. c-myc antisense transcripts accelerate differentiation and inhibit G1 progression in murine erythroleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3683–3695. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Barres B. A., Burne J. F., Coles H. S., Ishizaki Y., Jacobson M. D. Programmed cell death and the control of cell survival: lessons from the nervous system. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):695–700. doi: 10.1126/science.8235590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L., Debbas M., Sabbatini P., Hockenbery D., Korsmeyer S., White E. The adenovirus E1A proteins induce apoptosis, which is inhibited by the E1B 19-kDa and Bcl-2 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7742–7746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Haldar S., Croce C. M., Cuddy M. P. Complementation by BCL2 and C-HA-RAS oncogenes in malignant transformation of rat embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4370–4374. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Early signals in the mitogenic response. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):161–166. doi: 10.1126/science.3018928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., de Lange T., Ramsay G., Jakobovits E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H., Lee W. Definition of regions in human c-myc that are involved in transformation and nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1697–1709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thies R. S., Ullrich A., McClain D. A. Augmented mitogenesis and impaired metabolic signaling mediated by a truncated insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12820–12825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Cory S., Adams J. M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):440–442. doi: 10.1038/335440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner A. J., Small M. B., Hay N. Myc-mediated apoptosis is blocked by ectopic expression of Bcl-2. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2432–2440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters C. M., Hancock D. C., Evan G. I. Identification and characterisation of the egr-1 gene product as an inducible, short-lived, nuclear phosphoprotein. Oncogene. 1990 May;5(5):669–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Sabbatini P., Debbas M., Wold W. S., Kusher D. I., Gooding L. R. The 19-kilodalton adenovirus E1B transforming protein inhibits programmed cell death and prevents cytolysis by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2570–2580. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickstrom E. L., Bacon T. A., Gonzalez A., Lyman G. H., Wickstrom E. Anti-c-myc DNA increases differentiation and decreases colony formation by HL-60 cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1989 Mar;25(3 Pt 1):297–302. doi: 10.1007/BF02628470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterberg A., Larsson O. Kinetic analysis of regulatory events in G1 leading to proliferation or quiescence of Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5365–5369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]