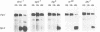Abstract
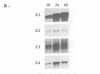
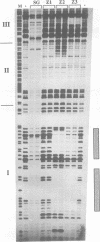
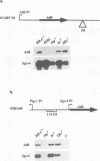
In Drosophila, all of the major metamorphic transitions are regulated by changes in the titer of the steroid hormone ecdysone. Here we examine how a key regulator of metamorphosis and primary ecdysone response gene, the Broad-Complex, transmits the hormonal signal to one of its targets, the Sgs-4 glue gene. We show that Broad-Complex RNAs accumulate in mid third instar larval salivary glands prior to Sgs-4 induction, as expected for the products of a gene that regulates the timing of Sgs-4 activation. The Broad-Complex codes for a family of zinc finger transcriptional regulators. We have identified a number of binding sites for these proteins in sequences known to regulate the timing of Sgs-4 induction, and have used these sites to derive a binding consensus for each protein. Some of these binding sites are required in vivo for Sgs-4 activity. In addition, rbp+, a genetically defined Broad-Complex function that is required for Sgs-4 induction, acts through these Broad-Complex binding sites. Thus, the Broad-Complex directly mediates a temporal and tissue-specific response to ecdysone as larvae become committed to metamorphosis.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres A. J., Fletcher J. C., Karim F. D., Thummel C. S. Molecular analysis of the initiation of insect metamorphosis: a comparative study of Drosophila ecdysteroid-regulated transcription. Dev Biol. 1993 Dec;160(2):388–404. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres A. J., Thummel C. S. Hormones, puffs and flies: the molecular control of metamorphosis by ecdysone. Trends Genet. 1992 Apr;8(4):132–138. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90371-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Chihara C., Meltzer P., Richards G. Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:655–662. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett S. W., Flynn K., Webster M. K., Beckendorf S. K. Noncoordinate expression of Drosophila glue genes: Sgs-4 is expressed at many stages and in two different tissues. Dev Biol. 1990 Aug;140(2):362–373. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckendorf S. K., Kafatos F. C. Differentiation in the salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: characterization of the glue proteins and their developmental appearance. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belyaeva E. S., Aizenzon M. G., Semeshin V. F., Kiss I. I., Koczka K., Baritcheva E. M., Gorelova T. D., Zhimulev I. F. Cytogenetic analysis of the 2B3-4--2B11 region of the X-chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Cytology of the region and mutant complementation groups. Chromosoma. 1980;81(2):281–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00285954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Spoerel N., Haymerle H., Ashburner M. The messenger RNA for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster differs in its 5' end in different developmental stages. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berreur P., Porcheron P., Moriniere M., Berreur-Bonnenfant J., Belinski-Deutsch S., Busson D., Lamour-Audit C. Ecdysteroids during the third larval instar in 1(3)ecd-1ts, a temperature-sensitive mutant of Drosophila melanogaster. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1984 Apr;54(1):76–84. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(84)90201-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollenbacher W. E., Vedeckis W. V., Gilbert L. I. Ecdysone titers and prothoracic gland activity during the larval-pupal development of Manduca sexta. Dev Biol. 1975 May;44(1):46–53. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90375-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairall L., Harrison S. D., Travers A. A., Rhodes D. Sequence-specific DNA binding by a two zinc-finger peptide from the Drosophila melanogaster Tramtrack protein. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jul 20;226(2):349–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90952-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairall L., Schwabe J. W., Chapman L., Finch J. T., Rhodes D. The crystal structure of a two zinc-finger peptide reveals an extension to the rules for zinc-finger/DNA recognition. Nature. 1993 Dec 2;366(6454):483–487. doi: 10.1038/366483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. A., Maniatis T. Regulatory elements involved in Drosophila Adh gene expression are conserved in divergent species and separate elements mediate expression in different tissues. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1275–1289. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogos J. A., Hsu T., Bolton J., Kafatos F. C. Sequence discrimination by alternatively spliced isoforms of a DNA binding zinc finger domain. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1951–1955. doi: 10.1126/science.1290524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guay P. S., Guild G. M. The ecdysone-induced puffing cascade in Drosophila salivary glands: a Broad-Complex early gene regulates intermolt and late gene transcription. Genetics. 1991 Sep;129(1):169–175. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. D., Travers A. A. The tramtrack gene encodes a Drosophila finger protein that interacts with the ftz transcriptional regulatory region and shows a novel embryonic expression pattern. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):207–216. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., England B., Tjian R. Characterization of Drosophila transcription factors that activate the tandem promoters of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):965–977. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet F., Ruiz C., Richards G. Puffs and PCR: the in vivo dynamics of early gene expression during ecdysone responses in Drosophila. Development. 1993 Jun;118(2):613–627. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.2.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongens T. A., Fowler T., Shermoen A. W., Beckendorf S. K. Functional redundancy in the tissue-specific enhancer of the Drosophila Sgs-4 gene. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2559–2567. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Guild G. M., Thummel C. S. The Drosophila Broad-Complex plays a key role in controlling ecdysone-regulated gene expression at the onset of metamorphosis. Development. 1993 Jul;118(3):977–988. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.3.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Thummel C. S. Ecdysone coordinates the timing and amounts of E74A and E74B transcription in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1067–1079. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Thummel C. S. Temporal coordination of regulatory gene expression by the steroid hormone ecdysone. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4083–4093. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05501.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss I., Beaton A. H., Tardiff J., Fristrom D., Fristrom J. W. Interactions and developmental effects of mutations in the Broad-Complex of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Feb;118(2):247–259. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Chromosome puff activity and protein synthesis in larval salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4550–4554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Larval saliva in Drosophila melanogaster: production, composition, and relationship to chromosome puffs. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 15;58(2):339–355. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick A., Brady H., Fukushima J., Karin M. The pituitary-specific regulatory gene GHF1 contains a minimal cell type-specific promoter centered around its TATA box. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1490–1503. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
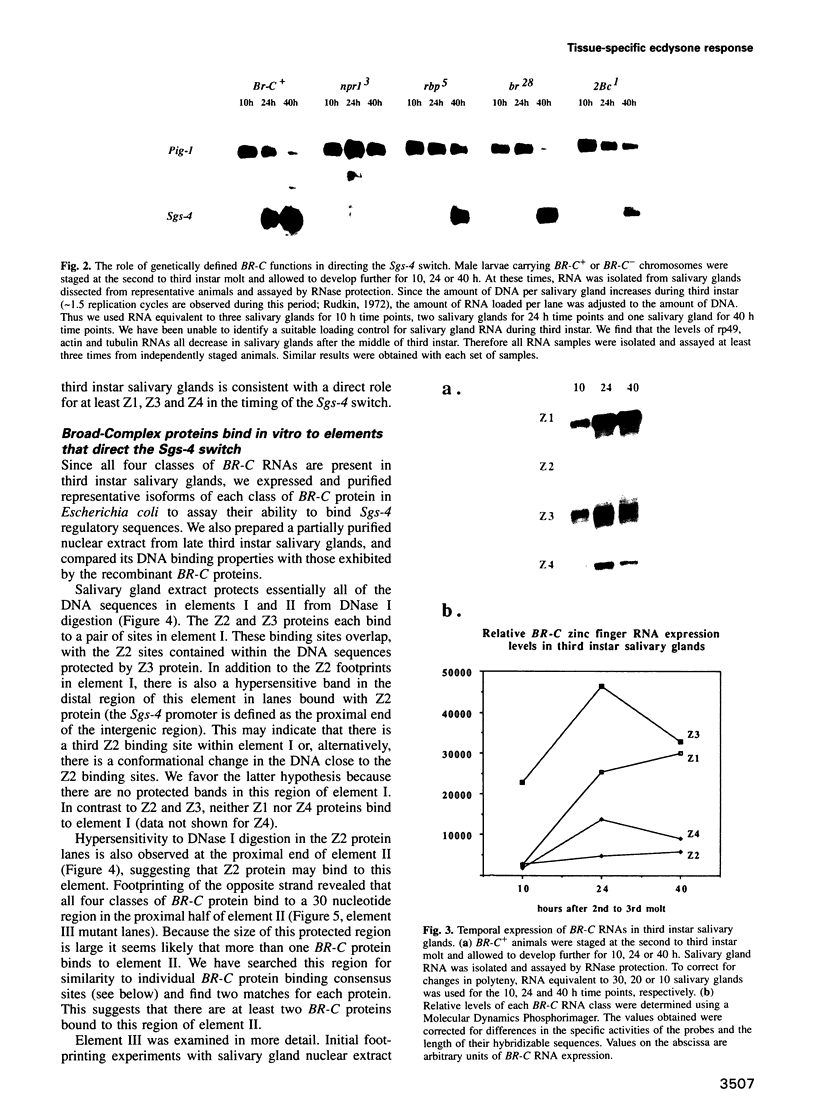
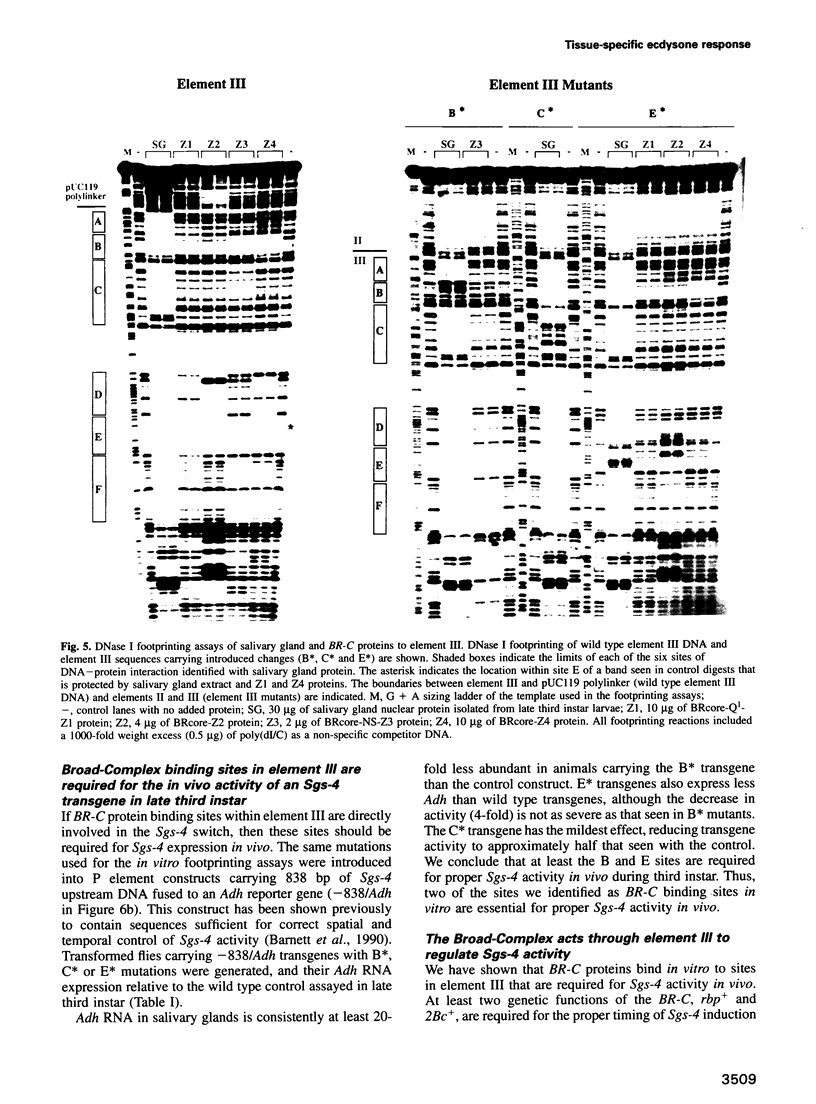
- Mougneau E., von Seggern D., Fowler T., Rosenblatt J., Jongens T., Rogers B., Gietzen D., Beckendorf S. K. A transcriptional switch between the Pig-1 and Sgs-4 genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):184–195. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Hogness D. S. An expandable gene that encodes a Drosophila glue protein is not expressed in variants lacking remote upstream sequences. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):1041–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Hogness D. S. Molecular analysis of a gene in a developmentally regulated puff of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7362–7366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poodry C. A., Hall L., Suzuki D. T. Developmental properties of Shibire: a pleiotropic mutation affecting larval and adult locomotion and development. Dev Biol. 1973 Jun;32(2):373–386. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90248-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read D., Manley J. L. Alternatively spliced transcripts of the Drosophila tramtrack gene encode zinc finger proteins with distinct DNA binding specificities. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1035–1044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudkin G. T. Replication in polytene chromosomes. Results Probl Cell Differ. 1972;4:59–85. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-37164-9_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler U., Terzaghi W., Beckmann H., Kadesch T., Cashmore A. R. DNA binding site preferences and transcriptional activation properties of the Arabidopsis transcription factor GBF1. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1275–1289. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. B., Imberski R. B., Kelly T. J. Analysis of metamorphosis in Drosophila melanogaster: characterization of giant, an ecdysteroid-deficient mutant. Dev Biol. 1984 May;103(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shermoen A. W., Jongens J., Barnett S. W., Flynn K., Beckendorf S. K. Developmental regulation by an enhancer from the Sgs-4 gene of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):207–214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04740.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeller W. C., Poole S. J., Kornberg T. In vitro transcription of the Drosophila engrailed gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):68–81. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Murphy C., Fristrom J. W. The recovery and preliminary characterization of X chromosome mutants affecting imaginal discs of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1972 Jan;27(1):71–83. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90113-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömstedt P. E., Poellinger L., Gustafsson J. A., Carlstedt-Duke J. The glucocorticoid receptor binds to a sequence overlapping the TATA box of the human osteocalcin promoter: a potential mechanism for negative regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3379–3383. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker V. K., Ashburner M. The control of ecdysterone-regulated puffs in Drosophila salivary glands. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90309-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhimulev I. F., Vlassova I. E., Belyaeva E. S. Cytogenetic analysis of the 2B3-4--2B11 region of the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. III. Puffing disturbance in salivary gland chromosomes of homozygotes for mutation l(1)pp1t10. Chromosoma. 1982;85(5):659–672. doi: 10.1007/BF00330779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweidler A., Cohen L. H. Large-scale isolation and fractionation of organs of Drosophila melanogaster larvae. J Cell Biol. 1971 Oct;51(1):240–248. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.1.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]