Abstract
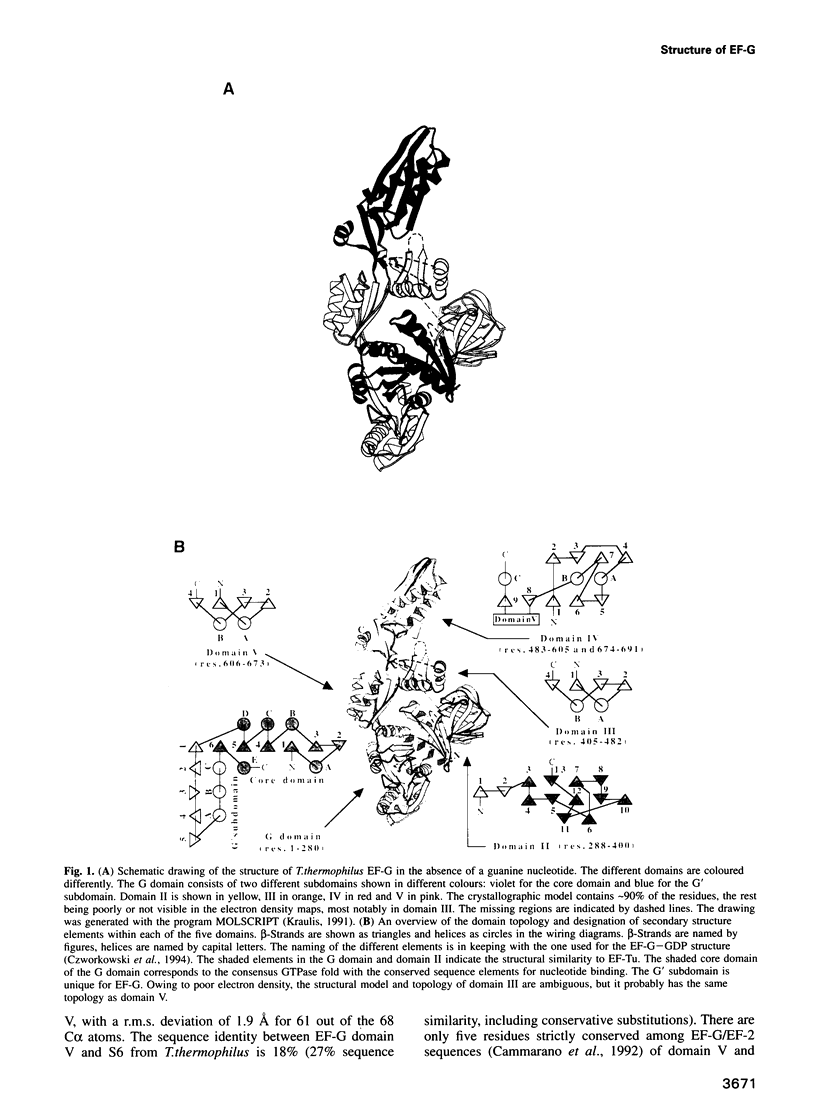
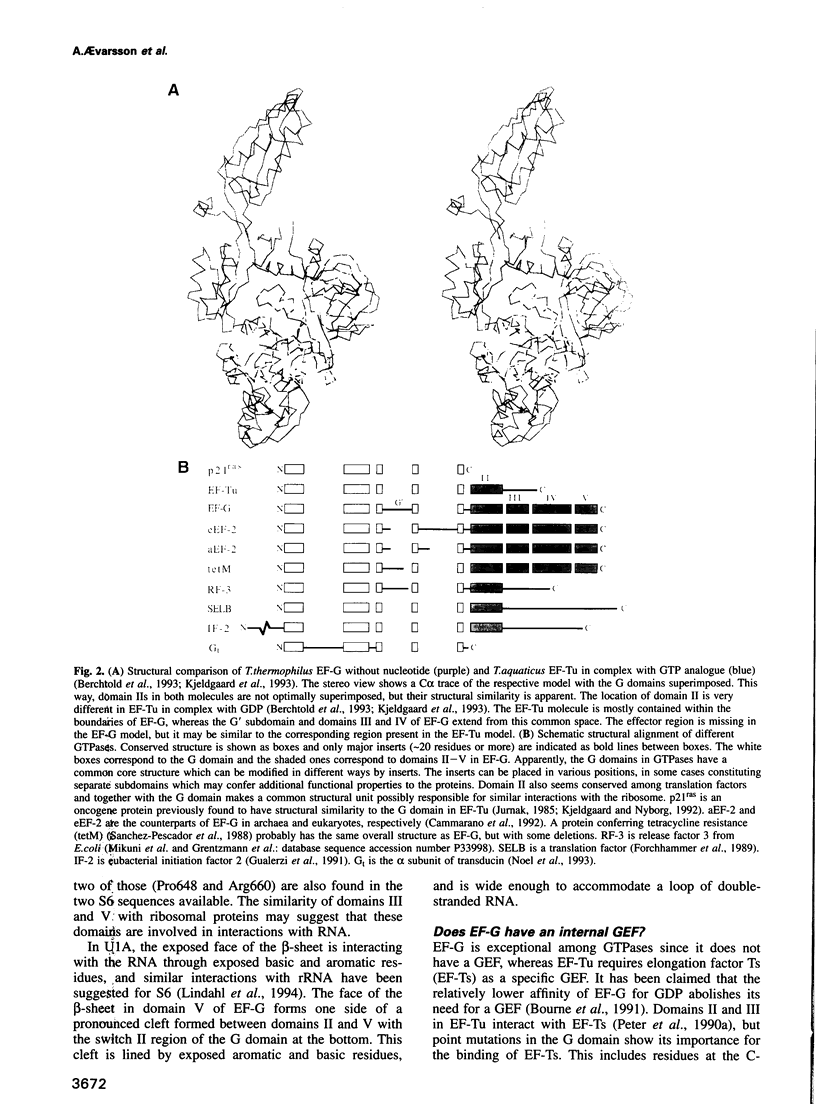
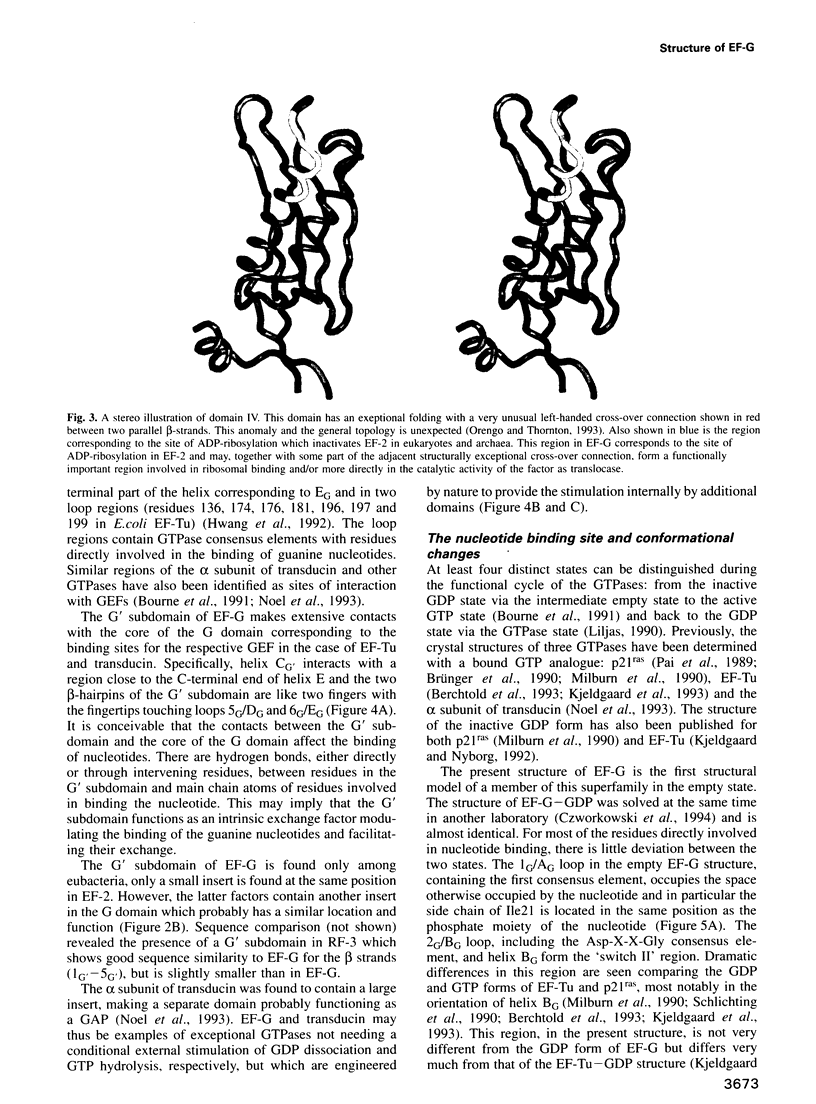
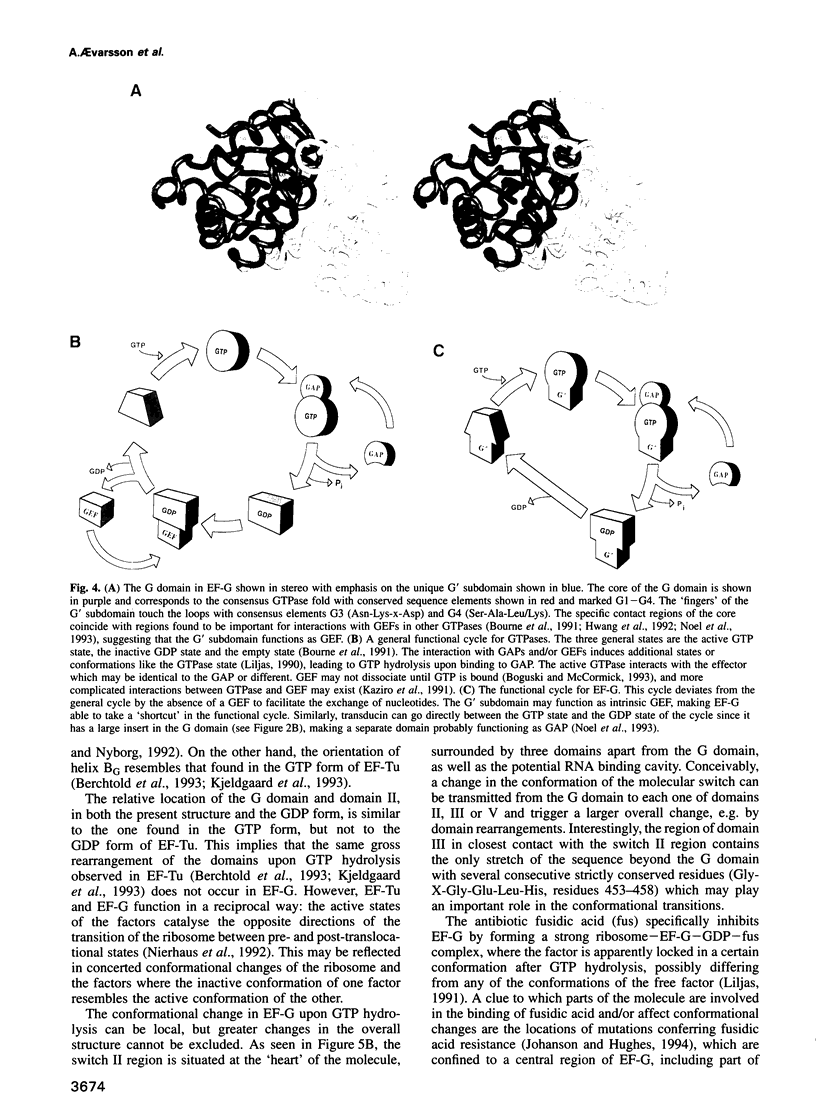
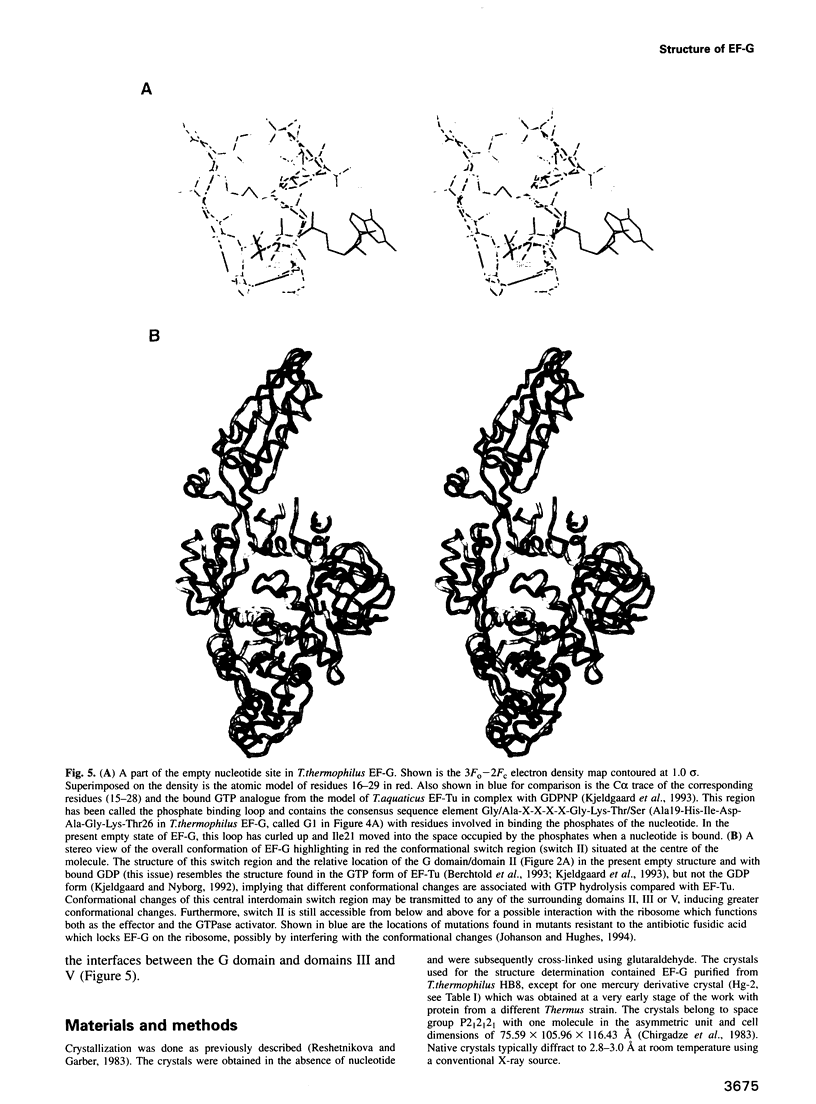
The crystal structure of Thermus thermophilus elongation factor G without guanine nucleotide was determined to 2.85 A. This GTPase has five domains with overall dimensions of 50 x 60 x 118 A. The GTP binding domain has a core common to other GTPases with a unique subdomain which probably functions as an intrinsic nucleotide exchange factor. Domains I and II are homologous to elongation factor Tu and their arrangement, both with and without GDP, is more similar to elongation factor Tu in complex with a GTP analogue than with GDP. Domains III and V show structural similarities to ribosomal proteins. Domain IV protrudes from the main body of the protein and has an extraordinary topology with a left-handed cross-over connection between two parallel beta-strands.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berchtold H., Reshetnikova L., Reiser C. O., Schirmer N. K., Sprinzl M., Hilgenfeld R. Crystal structure of active elongation factor Tu reveals major domain rearrangements. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):126–132. doi: 10.1038/365126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):506–512. doi: 10.1038/329506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., McCormick F. Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):643–654. doi: 10.1038/366643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Milburn M. V., Tong L., deVos A. M., Jancarik J., Yamaizumi Z., Nishimura S., Ohtsuka E., Kim S. H. Crystal structure of an active form of RAS protein, a complex of a GTP analog and the HRAS p21 catalytic domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4849–4853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammarano P., Palm P., Creti R., Ceccarelli E., Sanangelantoni A. M., Tiboni O. Early evolutionary relationships among known life forms inferred from elongation factor EF-2/EF-G sequences: phylogenetic coherence and structure of the archaeal domain. J Mol Evol. 1992 May;34(5):396–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00162996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgadze YuN, Nikonov S. V., Brazhnikov E. V., Garber M. B., Reshetnikova L. S. Crystallographic study of elongation factor G from Thermus thermophilus HB8. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 5;168(2):449–450. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czworkowski J., Wang J., Steitz T. A., Moore P. B. The crystal structure of elongation factor G complexed with GDP, at 2.7 A resolution. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 15;13(16):3661–3668. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06675.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Glynias M. J., Merrick W. C. GTP-binding domain: three consensus sequence elements with distinct spacing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1814–1818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fendrick J. L., Iglewski W. J., Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J. Characterization of the endogenous ADP-ribosylation of wild-type and mutant elongation factor 2 in eukaryotic cells. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Apr 1;205(1):25–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer K., Leinfelder W., Böck A. Identification of a novel translation factor necessary for the incorporation of selenocysteine into protein. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):453–456. doi: 10.1038/342453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualerzi C. O., Severini M., Spurio R., La Teana A., Pon C. L. Molecular dissection of translation initiation factor IF2. Evidence for two structural and functional domains. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16356–16362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman D. W., Query C. C., Golden B. L., White S. W., Keene J. D. RNA-binding domain of the A protein component of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein analyzed by NMR spectroscopy is structurally similar to ribosomal proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang Y. W., Carter M., Miller D. L. The identification of a domain in Escherichia coli elongation factor Tu that interacts with elongation factor Ts. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22198–22205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson U., Hughes D. Fusidic acid-resistant mutants define three regions in elongation factor G of Salmonella typhimurium. Gene. 1994 May 27;143(1):55–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurnak F. Structure of the GDP domain of EF-Tu and location of the amino acids homologous to ras oncogene proteins. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):32–36. doi: 10.1126/science.3898365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nakafuku M., Satoh T. Structure and function of signal-transducing GTP-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:349–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y. The role of guanosine 5'-triphosphate in polypeptide chain elongation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 21;505(1):95–127. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(78)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldgaard M., Nissen P., Thirup S., Nyborg J. The crystal structure of elongation factor EF-Tu from Thermus aquaticus in the GTP conformation. Structure. 1993 Sep 15;1(1):35–50. doi: 10.1016/0969-2126(93)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldgaard M., Nyborg J. Refined structure of elongation factor EF-Tu from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 5;223(3):721–742. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90986-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno K., Uchida T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S., Nakanishi T., Fukui T., Ohtsuka E., Ikehara M., Okada Y. Amino acid sequence of mammalian elongation factor 2 deduced from the cDNA sequence: homology with GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):4978–4982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.4978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljas A. Comparative biochemistry and biophysics of ribosomal proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1991;124:103–136. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61525-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl M., Svensson L. A., Liljas A., Sedelnikova S. E., Eliseikina I. A., Fomenkova N. P., Nevskaya N., Nikonov S. V., Garber M. B., Muranova T. A. Crystal structure of the ribosomal protein S6 from Thermus thermophilus. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1249–1254. doi: 10.2210/pdb1ris/pdb. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Tong L., deVos A. M., Brünger A., Yamaizumi Z., Nishimura S., Kim S. H. Molecular switch for signal transduction: structural differences between active and inactive forms of protooncogenic ras proteins. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):939–945. doi: 10.1126/science.2406906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Robertson J. M., Noller H. F. Interaction of elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu with a conserved loop in 23S RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):362–364. doi: 10.1038/334362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Oubridge C., Jessen T. H., Li J., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of the RNA-binding domain of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):515–520. doi: 10.1038/348515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H., Schilling-Bartetzko S., Twardowski T. The two main states of the elongating ribosome and the role of the alpha-sarcin stem-loop structure of 23S RNA. Biochimie. 1992 Apr;74(4):403–410. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(92)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel J. P., Hamm H. E., Sigler P. B. The 2.2 A crystal structure of transducin-alpha complexed with GTP gamma S. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):654–663. doi: 10.1038/366654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygård O., Nilsson L. Reduced ribosomal binding of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 following ADP-ribosylation. Difference in binding selectivity between polyribosomes and reconstituted monoribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 20;824(2):152–162. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omura F., Kohno K., Uchida T. The histidine residue of codon 715 is essential for function of elongation factor 2. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 1;180(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orengo C. A., Thornton J. M. Alpha plus beta folds revisited: some favoured motifs. Structure. 1993 Oct 15;1(2):105–120. doi: 10.1016/0969-2126(93)90026-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Kabsch W., Krengel U., Holmes K. C., John J., Wittinghofer A. Structure of the guanine-nucleotide-binding domain of the Ha-ras oncogene product p21 in the triphosphate conformation. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):209–214. doi: 10.1038/341209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M. E., Reiser C. O., Schirmer N. K., Kiefhaber T., Ott G., Grillenbeck N. W., Sprinzl M. Interaction of the isolated domain II/III of Thermus thermophilus elongation factor Tu with the nucleotide exchange factor EF-Ts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6889–6893. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M. E., Schirmer N. K., Reiser C. O., Sprinzl M. Mapping the effector region in Thermus thermophilus elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2876–2884. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S. Describing patterns of protein tertiary structure. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:341–358. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Pescador R., Brown J. T., Roberts M., Urdea M. S. Homology of the TetM with translational elongation factors: implications for potential modes of tetM-conferred tetracycline resistance. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1218–1218. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichting I., Almo S. C., Rapp G., Wilson K., Petratos K., Lentfer A., Wittinghofer A., Kabsch W., Pai E. F., Petsko G. A. Time-resolved X-ray crystallographic study of the conformational change in Ha-Ras p21 protein on GTP hydrolysis. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):309–315. doi: 10.1038/345309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sköld S. E. Chemical crosslinking of elongation factor G to the 23S RNA in 70S ribosomes from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4923–4932. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L., Mattioli A. Studies on diphtheria toxin. The effect of GTP on the toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of rat liver aminoacyl transferase. II. Chem Biol Interact. 1971 Apr;3(2):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(71)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirin A. S. Ribosomal translocation: facts and models. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:75–114. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubulekas I., Hughes D. A single amino acid substitution in elongation factor Tu disrupts interaction between the ternary complex and the ribosome. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(1):240–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.1.240-250.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. S., Alden R. A., Kraut J. Structure of subtilisin BPN' at 2.5 angström resolution. Nature. 1969 Jan 18;221(5177):235–242. doi: 10.1038/221235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakhnin A. V., Vorozheykina D. P., Matvienko N. I. Nucleotide sequence of the Thermus thermophilus HB8 gene coding for elongation factor G. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8863–8863. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K. Y. SQUASH - combining constraints for macromolecular phase refinement and extension. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1993 Jan 1;49(Pt 1):213–222. doi: 10.1107/S0907444992007911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]