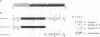Abstract
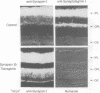
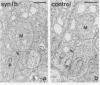
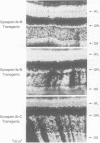
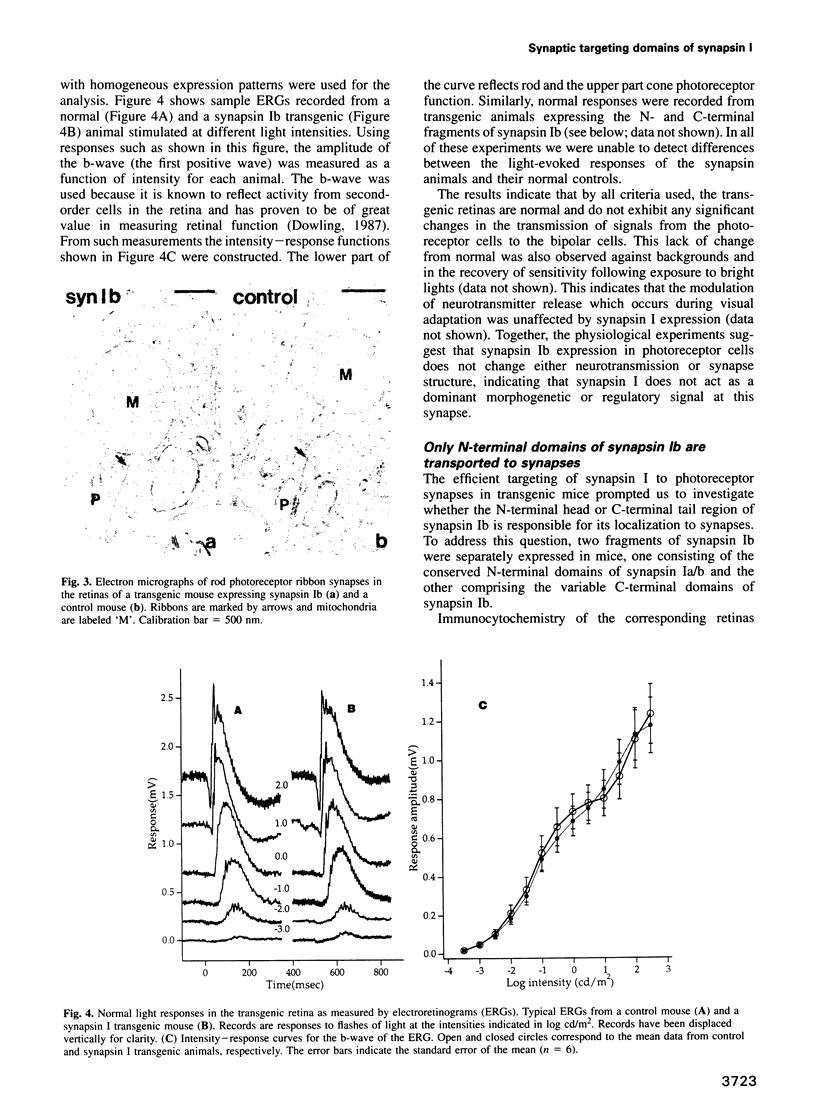
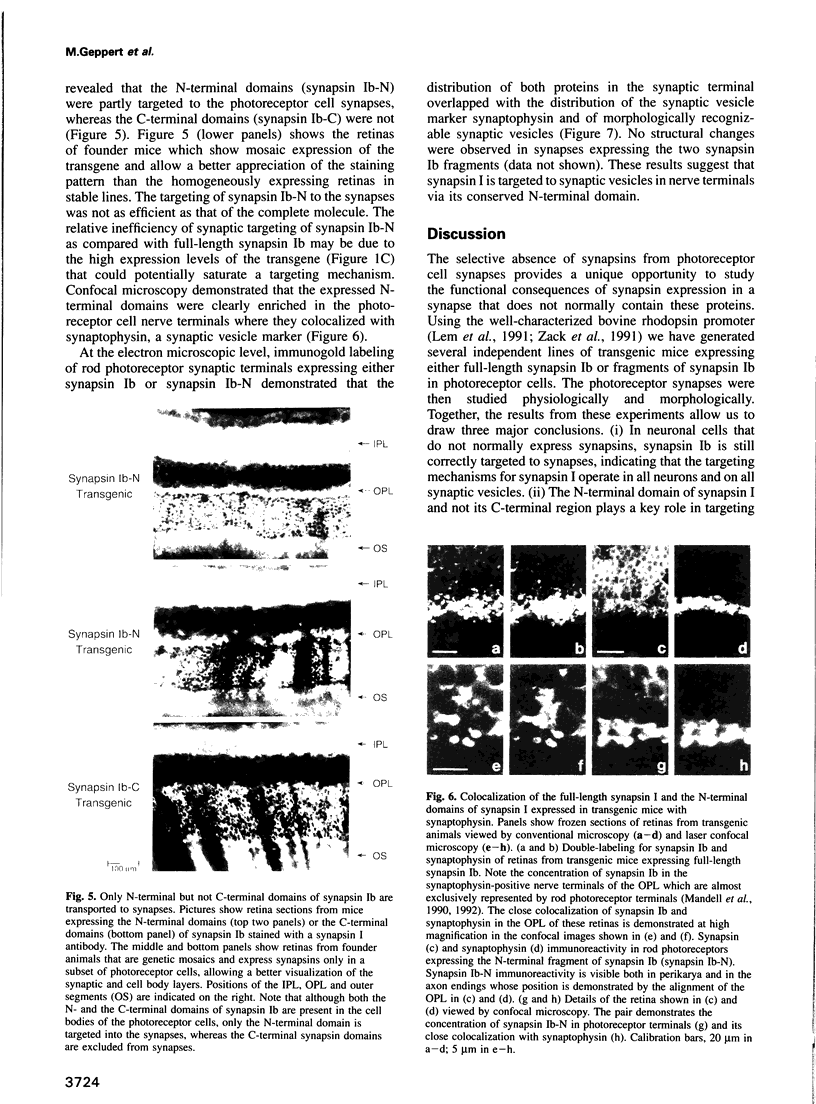
Synapsins are abundant nerve terminal proteins present at all synapses except for ribbon synapses, e.g. photoreceptor cell synapses. Multiple functions have been proposed for synapsins, including clustering of synaptic vesicles and regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. To investigate the physiological functions of synapsin and to ascertain which domains of synapsin are involved in synaptic targeting in vivo, we expressed synapsin Ib and its N- and C-terminal domains in the photoreceptor cells of transgenic mice. In these cells synapsin Ib is targeted efficiently to synaptic vesicles but has no significant effect on the development, structure or physiology of the synapses. This suggests that synapsin I does not have dominant physiological or morphoregulatory functions at these synapses. Full-length synapsin Ib and the N-terminal domains of synapsin Ib but not its C-terminal domains are transported to synapses, revealing that the molecular apparatus for synaptic targeting of synapsins is also present in cells which form ribbon synapses that normally lack synapsins. This apparatus appears to utilize the conserved N-terminal domains that are shared between all synapsins.
Full text
PDF

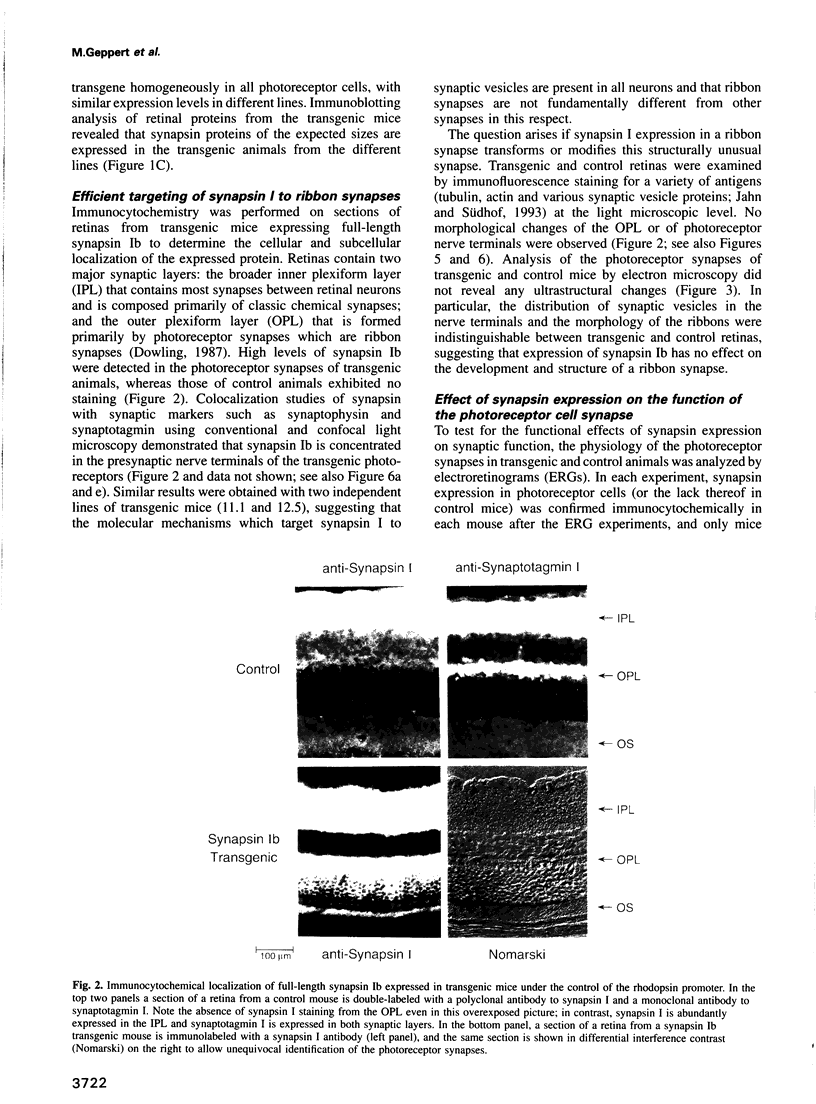



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benfenati F., Valtorta F., Rubenstein J. L., Gorelick F. S., Greengard P., Czernik A. J. Synaptic vesicle-associated Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II is a binding protein for synapsin I. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):417–420. doi: 10.1038/359417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1496–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brose N., Petrenko A. G., Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Synaptotagmin: a calcium sensor on the synaptic vesicle surface. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):1021–1025. doi: 10.1126/science.1589771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bähler M., Greengard P. Synapsin I bundles F-actin in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):704–707. doi: 10.1038/326704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Cameron R., Greengard P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. I. Its general distribution in synapses of the central and peripheral nervous system demonstrated by immunofluorescence in frozen and plastic sections. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1337–1354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Harris S. M., Jr, Huttner W. B., Greengard P. Synapsin I (Protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. II. Its specific association with synaptic vesicles demonstrated by immunocytochemistry in agarose-embedded synaptosomes. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1355–1373. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favre D., Scarfone E., Di Gioia G., De Camilli P., Dememes D. Presence of synapsin I in afferent and efferent nerve endings of vestibular sensory epithelia. Brain Res. 1986 Oct 8;384(2):379–382. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91176-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fykse E. M., Takei K., Walch-Solimena C., Geppert M., Jahn R., De Camilli P., Südhof T. C. Relative properties and localizations of synaptic vesicle protein isoforms: the case of the synaptophysins. J Neurosci. 1993 Nov;13(11):4997–5007. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-11-04997.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. G., Herreros de Tejada P., Glover M. J. Are albino rats night blind? Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1991 Jul;32(8):2366–2371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P., Valtorta F., Czernik A. J., Benfenati F. Synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins and regulation of synaptic function. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):780–785. doi: 10.1126/science.8430330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Sobue K., Kanda K., Harada A., Yorifuji H. The cytoskeletal architecture of the presynaptic terminal and molecular structure of synapsin 1. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;108(1):111–126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Schiebler W., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. III. Its association with synaptic vesicles studied in a highly purified synaptic vesicle preparation. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1374–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Synaptic vesicle traffic: rush hour in the nerve terminal. J Neurochem. 1993 Jul;61(1):12–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaseki T., Ikeuchi Y., Sugiura H., Yamauchi T. Structural features of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II revealed by electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):1049–1060. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G. A., Tokuyasu K. T., Dutton A. H., Singer S. J. An improved procedure for immunoelectron microscopy: ultrathin plastic embedding of immunolabeled ultrathin frozen sections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5744–5747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lem J., Applebury M. L., Falk J. D., Flannery J. G., Simon M. I. Tissue-specific and developmental regulation of rod opsin chimeric genes in transgenic mice. Neuron. 1991 Feb;6(2):201–210. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90356-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell J. W., Czernik A. J., De Camilli P., Greengard P., Townes-Anderson E. Differential expression of synapsins I and II among rat retinal synapses. J Neurosci. 1992 May;12(5):1736–1749. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-05-01736.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell J. W., Townes-Anderson E., Czernik A. J., Cameron R., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsins in the vertebrate retina: absence from ribbon synapses and heterogeneous distribution among conventional synapses. Neuron. 1990 Jul;5(1):19–33. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90030-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteoli M., Takei K., Cameron R., Hurlbut P., Johnston P. A., Südhof T. C., Jahn R., De Camilli P. Association of Rab3A with synaptic vesicles at late stages of the secretory pathway. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):625–633. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navone F., Jahn R., Di Gioia G., Stukenbrok H., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Protein p38: an integral membrane protein specific for small vesicles of neurons and neuroendocrine cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2511–2527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrucci T. C., Morrow J. S. Synapsin I: an actin-bundling protein under phosphorylation control. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1355–1363. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosahl T. W., Geppert M., Spillane D., Herz J., Hammer R. E., Malenka R. C., Südhof T. C. Short-term synaptic plasticity is altered in mice lacking synapsin I. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):661–670. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90487-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer S. F., Raviola E. Membrane recycling in the cone cell endings of the turtle retina. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):802–825. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiebler W., Jahn R., Doucet J. P., Rothlein J., Greengard P. Characterization of synapsin I binding to small synaptic vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8383–8390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sihra T. S., Wang J. K., Gorelick F. S., Greengard P. Translocation of synapsin I in response to depolarization of isolated nerve terminals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8108–8112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. A new method of preparing gold probes for multiple-labeling cytochemistry. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;38(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Czernik A. J., Kao H. T., Takei K., Johnston P. A., Horiuchi A., Kanazir S. D., Wagner M. A., Perin M. S., De Camilli P. Synapsins: mosaics of shared and individual domains in a family of synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1474–1480. doi: 10.1126/science.2506642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Proteins of synaptic vesicles involved in exocytosis and membrane recycling. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):665–677. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90165-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takei K., Stukenbrok H., Metcalf A., Mignery G. A., Südhof T. C., Volpe P., De Camilli P. Ca2+ stores in Purkinje neurons: endoplasmic reticulum subcompartments demonstrated by the heterogeneous distribution of the InsP3 receptor, Ca(2+)-ATPase, and calsequestrin. J Neurosci. 1992 Feb;12(2):489–505. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-02-00489.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. Use of poly(vinylpyrrolidone) and poly(vinyl alcohol) for cryoultramicrotomy. Histochem J. 1989 Mar;21(3):163–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01007491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulliet P. R., Hall F. L., Mitchell J. P., Hardie D. G. Identification of a novel proline-directed serine/threonine protein kinase in rat pheochromocytoma. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16292–16298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack D. J., Bennett J., Wang Y., Davenport C., Klaunberg B., Gearhart J., Nathans J. Unusual topography of bovine rhodopsin promoter-lacZ fusion gene expression in transgenic mouse retinas. Neuron. 1991 Feb;6(2):187–199. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]