Abstract
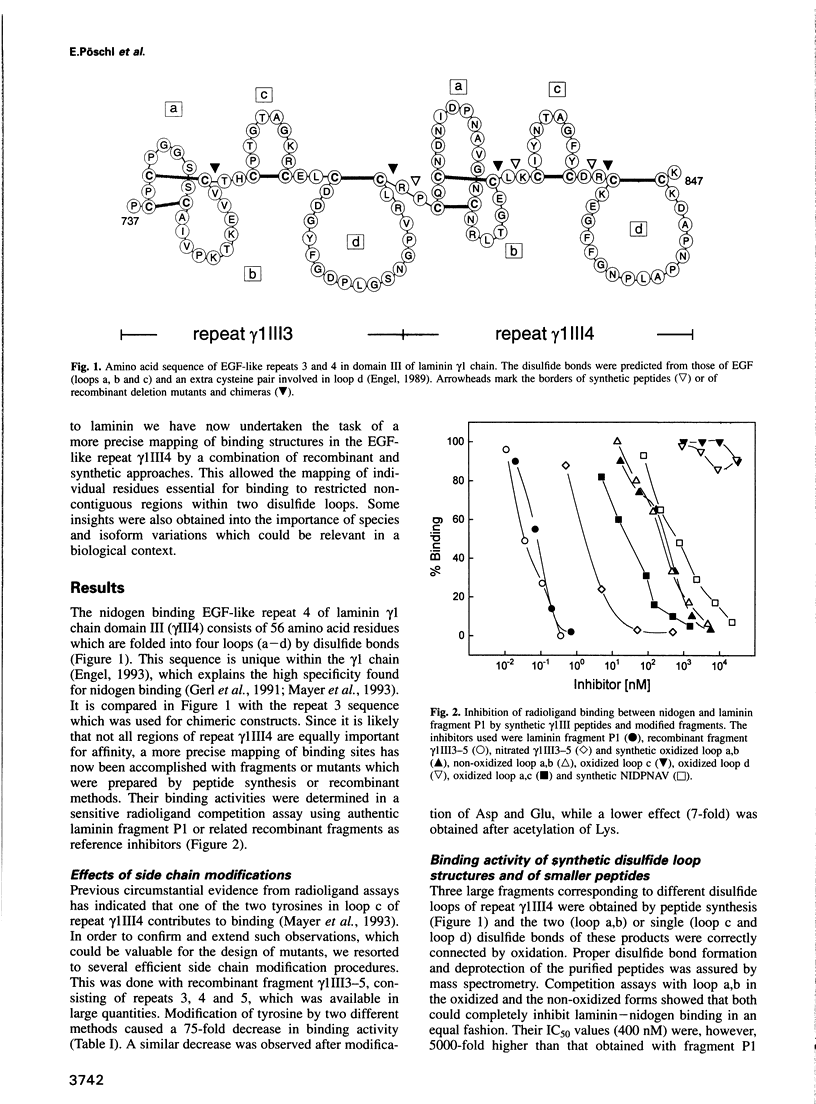
High affinity binding of nidogen to laminin is mediated by an EGF-like repeat gamma 1III4 of the mouse laminin gamma 1 chain and has now been restricted to two short noncontiguous regions of its 56 residue sequence by use of synthetic peptides and recombinant mutants. Disulfide loop a,b of the repeat and a modified loop a,c could completely inhibit binding, with a 5000-fold or 300-fold reduced affinity respectively. Synthetic loops c and d lacked inhibitory activity. Some binding contribution of Tyr819 in loop c was, however, shown by mutation and side chain modification. Together with studies of loop chimeras, this indicated a distinct cooperativity between the two binding sites. The major binding site of loop a was localized to the heptapeptide NIDPNAV (position 798-804). A change of Asp800 to Asn or Ala803 to Val caused a strong reduction in binding activity, while only small effects were observed for the changes Pro801 to Gln and Ile799 to Val. The latter replacement corresponds to the single substitution found in the same region of the Drosophila laminin gamma 1 chain. However, the changes Asn802 to Ser or Val804 to Ser, both known to exist in the laminin gamma 2 chain, were deleterious mutations. This demonstrated conservation of binding structures in laminins of distantly related species, but not between homologous chains of laminin isoforms.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. C., Wiedemann H., Timpl R. Protein binding and cell adhesion properties of two laminin isoforms (AmB1eB2e, AmB1sB2e) from human placenta. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jan;107(Pt 1):329–338. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.1.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgeson R. E., Chiquet M., Deutzmann R., Ekblom P., Engel J., Kleinman H., Martin G. R., Meneguzzi G., Paulsson M., Sanes J. A new nomenclature for the laminins. Matrix Biol. 1994 Apr;14(3):209–211. doi: 10.1016/0945-053x(94)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campion S. R., Biamonti C., Montelione G. T., Niyogi S. K. The role of asparagine-32 in forming the receptor-binding epitope of human epidermal growth factor. Protein Eng. 1993 Aug;6(6):651–659. doi: 10.1093/protein/6.6.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campion S. R., Tadaki D. K., Niyogi S. K. Evaluation of the role of electrostatic residues in human epidermal growth factor by site-directed mutagenesis and chemical modification. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Sep;50(1):35–42. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240500108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi H. C., Hui C. F. Primary structure of the Drosophila laminin B2 chain and comparison with human, mouse, and Drosophila laminin B1 and B2 chains. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1543–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. M., Wilkinson A. J., Baron M., Pastore A., Tappin M. J., Campbell I. D., Gregory H., Sheard B. The solution structure of human epidermal growth factor. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):339–341. doi: 10.1038/327339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Cutting G. R., Pyeritz R. E., Maslen C. L., Sakai L. Y., Corson G. M., Puffenberger E. G., Hamosh A., Nanthakumar E. J., Curristin S. M. Marfan syndrome caused by a recurrent de novo missense mutation in the fibrillin gene. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):337–339. doi: 10.1038/352337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. EGF-like domains in extracellular matrix proteins: localized signals for growth and differentiation? FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81417-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. W., Mayer U., Nischt R., Aumailley M., Reinhardt D., Wiedemann H., Mann K., Timpl R., Krieg T., Engel J. Recombinant nidogen consists of three globular domains and mediates binding of laminin to collagen type IV. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3137–3146. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04875.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerl M., Mann K., Aumailley M., Timpl R. Localization of a major nidogen-binding site to domain III of laminin B2 chain. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Nov 15;202(1):167–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handford P. A., Mayhew M., Baron M., Winship P. R., Campbell I. D., Brownlee G. G. Key residues involved in calcium-binding motifs in EGF-like domains. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):164–167. doi: 10.1038/351164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoare D. G., Koshland D. E., Jr A method for the quantitative modification and estimation of carboxylic acid groups in proteins. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2447–2453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallunki P., Sainio K., Eddy R., Byers M., Kallunki T., Sariola H., Beck K., Hirvonen H., Shows T. B., Tryggvason K. A truncated laminin chain homologous to the B2 chain: structure, spatial expression, and chromosomal assignment. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):679–693. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley M. R., Kidd S., Deutsch W. A., Young M. W. Mutations altering the structure of epidermal growth factor-like coding sequences at the Drosophila Notch locus. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):539–548. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Godfrey M., Vitale E., Hori H., Mattei M. G., Sarfarazi M., Tsipouras P., Ramirez F., Hollister D. W. Linkage of Marfan syndrome and a phenotypically related disorder to two different fibrillin genes. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):330–334. doi: 10.1038/352330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K., Deutzmann R., Timpl R. Characterization of proteolytic fragments of the laminin-nidogen complex and their activity in ligand-binding assays. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Dec 1;178(1):71–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinkovich M. P., Verrando P., Keene D. R., Meneguzzi G., Lunstrum G. P., Ortonne J. P., Burgeson R. E. Basement membrane proteins kalinin and nicein are structurally and immunologically identical. Lab Invest. 1993 Sep;69(3):295–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer U., Aumailley M., Mann K., Timpl R., Engel J. Calcium-dependent binding of basement membrane protein BM-40 (osteonectin, SPARC) to basement membrane collagen type IV. Eur J Biochem. 1991 May 23;198(1):141–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer U., Nischt R., Pöschl E., Mann K., Fukuda K., Gerl M., Yamada Y., Timpl R. A single EGF-like motif of laminin is responsible for high affinity nidogen binding. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1879–1885. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelione G. T., Wüthrich K., Nice E. C., Burgess A. W., Scheraga H. A. Solution structure of murine epidermal growth factor: determination of the polypeptide backbone chain-fold by nuclear magnetic resonance and distance geometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5226–5230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moy F. J., Scheraga H. A., Liu J. F., Wu R., Montelione G. T. Conformational characterization of a single-site mutant of murine epidermal growth factor (EGF) by 1H NMR provides evidence that leucine-47 is involved in the interactions with the EGF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9836–9840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nischt R., Pottgiesser J., Krieg T., Mayer U., Aumailley M., Timpl R. Recombinant expression and properties of the human calcium-binding extracellular matrix protein BM-40. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Sep 1;200(2):529–536. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi M., Suganuma T., Hiromi K. The role of tyrosine residue of bacterial liquefying alpha-amylase in the enzymatic hydrolysis of linear substrates as studied by chemical modification with acetic anhydride. J Biochem. 1974 Jul;76(1):7–13. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikkarainen T., Kallunki T., Tryggvason K. Human laminin B2 chain. Comparison of the complete amino acid sequence with the B1 chain reveals variability in sequence homology between different structural domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6751–6758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
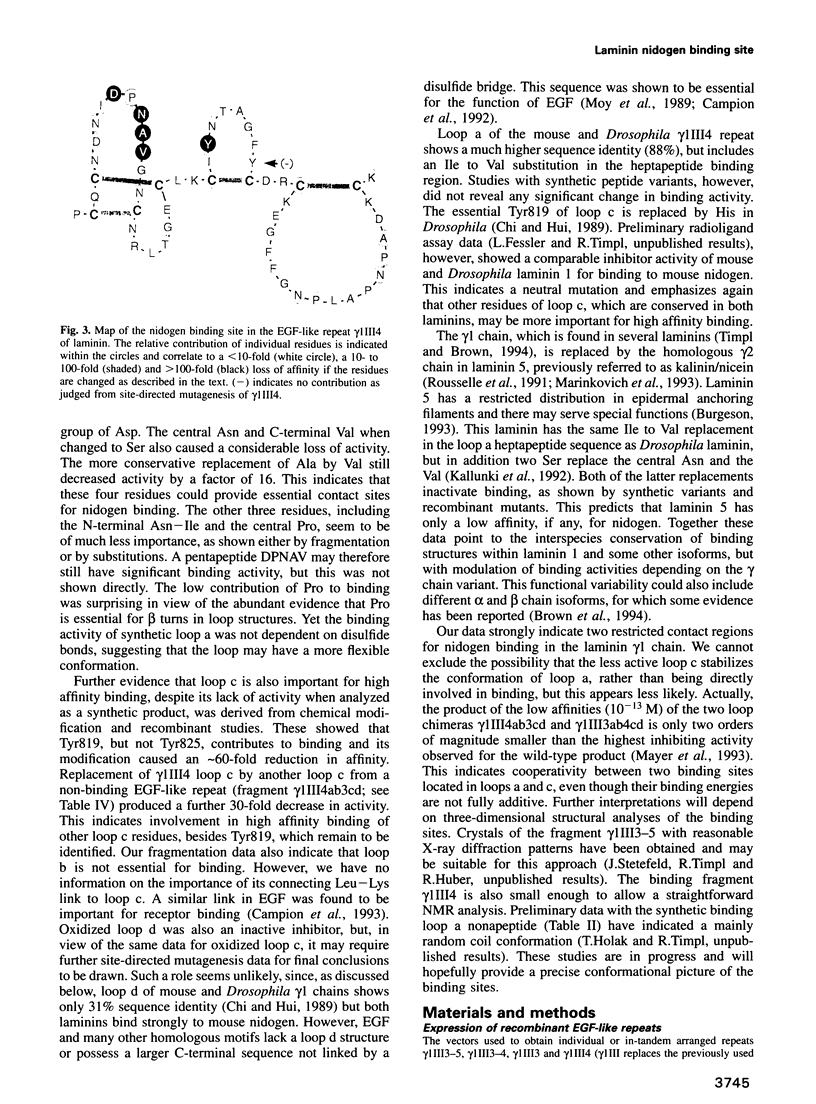
- Rees D. J., Jones I. M., Handford P. A., Walter S. J., Esnouf M. P., Smith K. J., Brownlee G. G. The role of beta-hydroxyaspartate and adjacent carboxylate residues in the first EGF domain of human factor IX. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2053–2061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousselle P., Lunstrum G. P., Keene D. R., Burgeson R. E. Kalinin: an epithelium-specific basement membrane adhesion molecule that is a component of anchoring filaments. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):567–576. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Yamada Y. The laminin B2 chain has a multidomain structure homologous to the B1 chain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17111–17117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander-Sunnerhagen M., Ullner M., Persson E., Teleman O., Stenflo J., Drakenberg T. How an epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain binds calcium. High resolution NMR structure of the calcium form of the NH2-terminal EGF-like domain in coagulation factor X. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19642–19649. doi: 10.2210/pdb1ccf/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]