Abstract
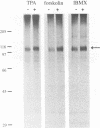
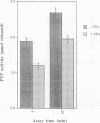
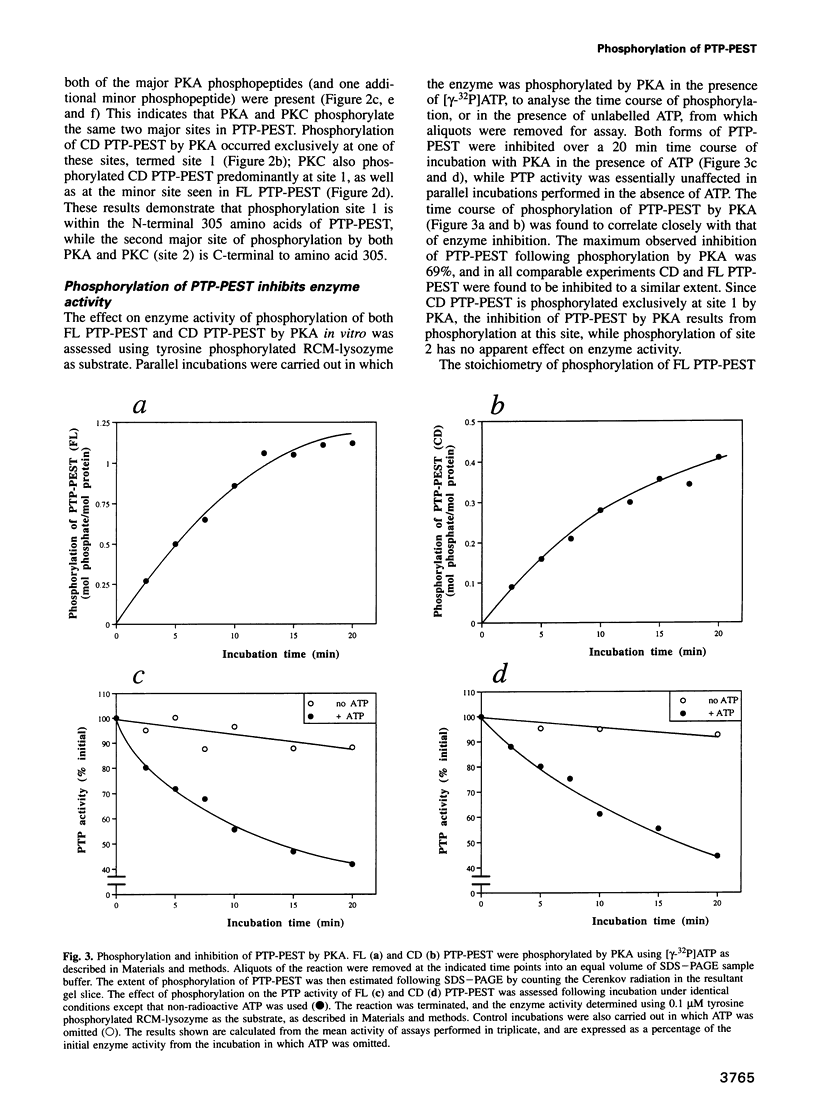
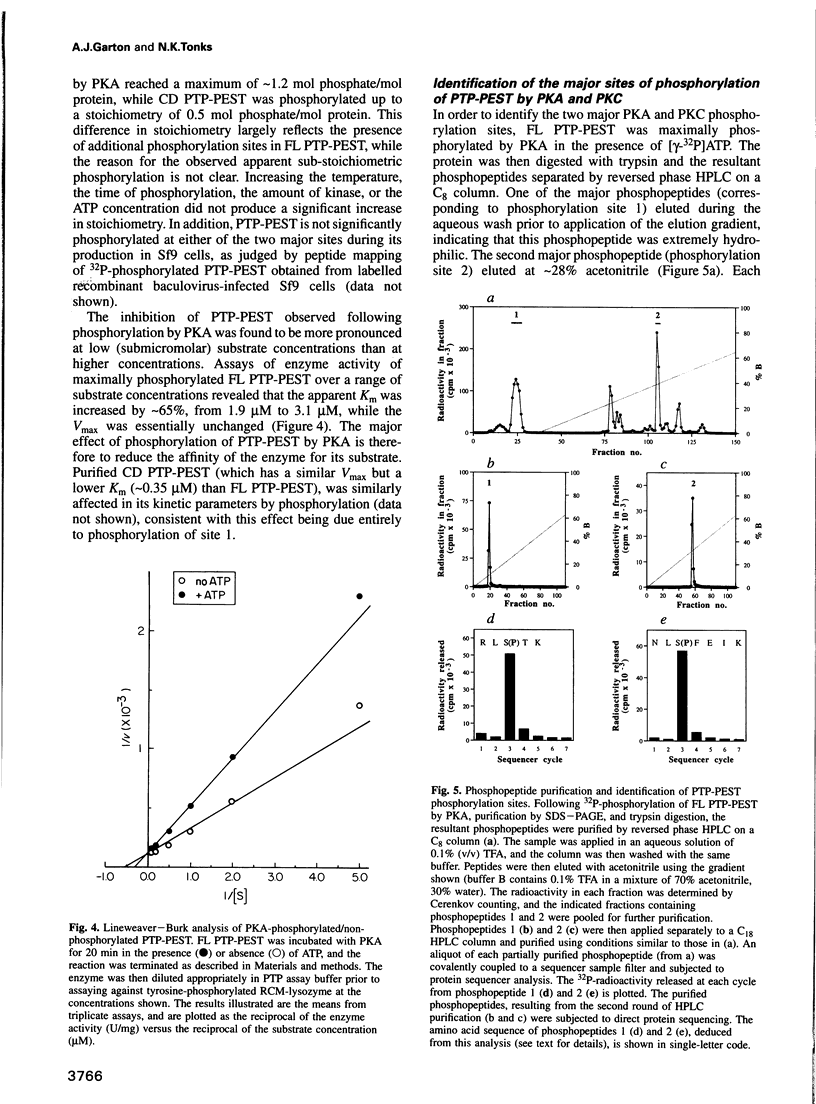
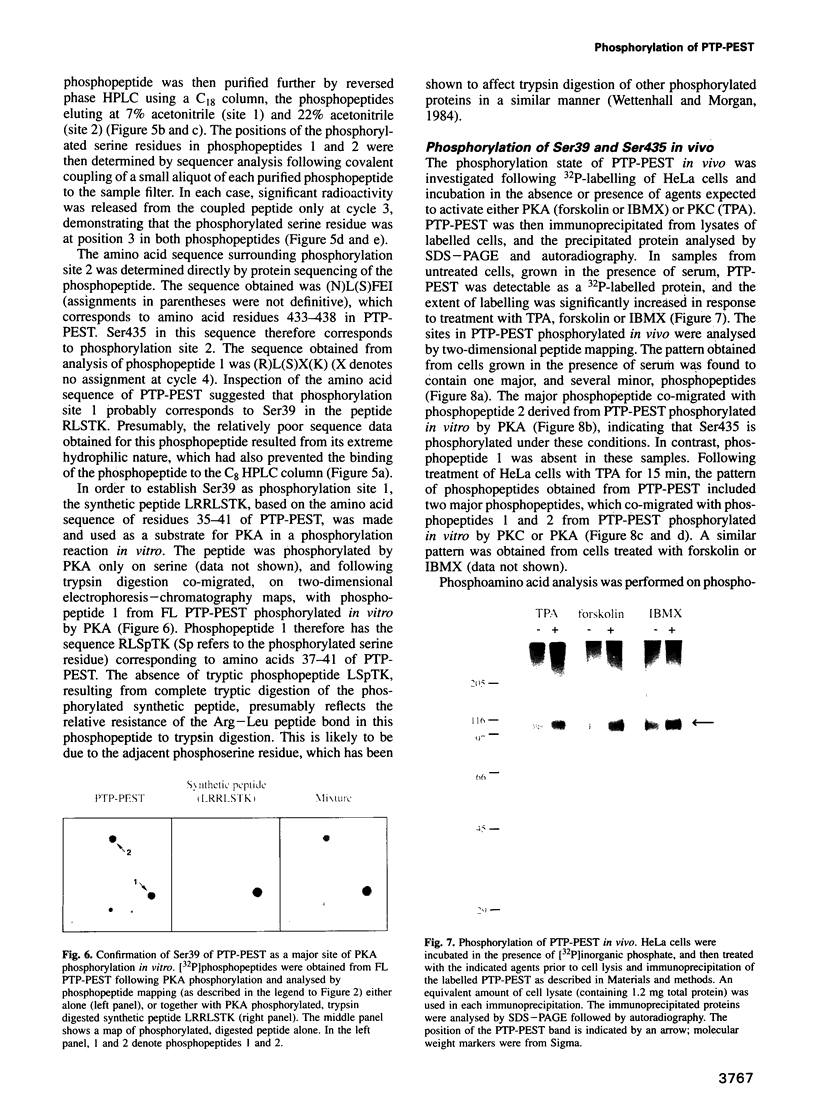
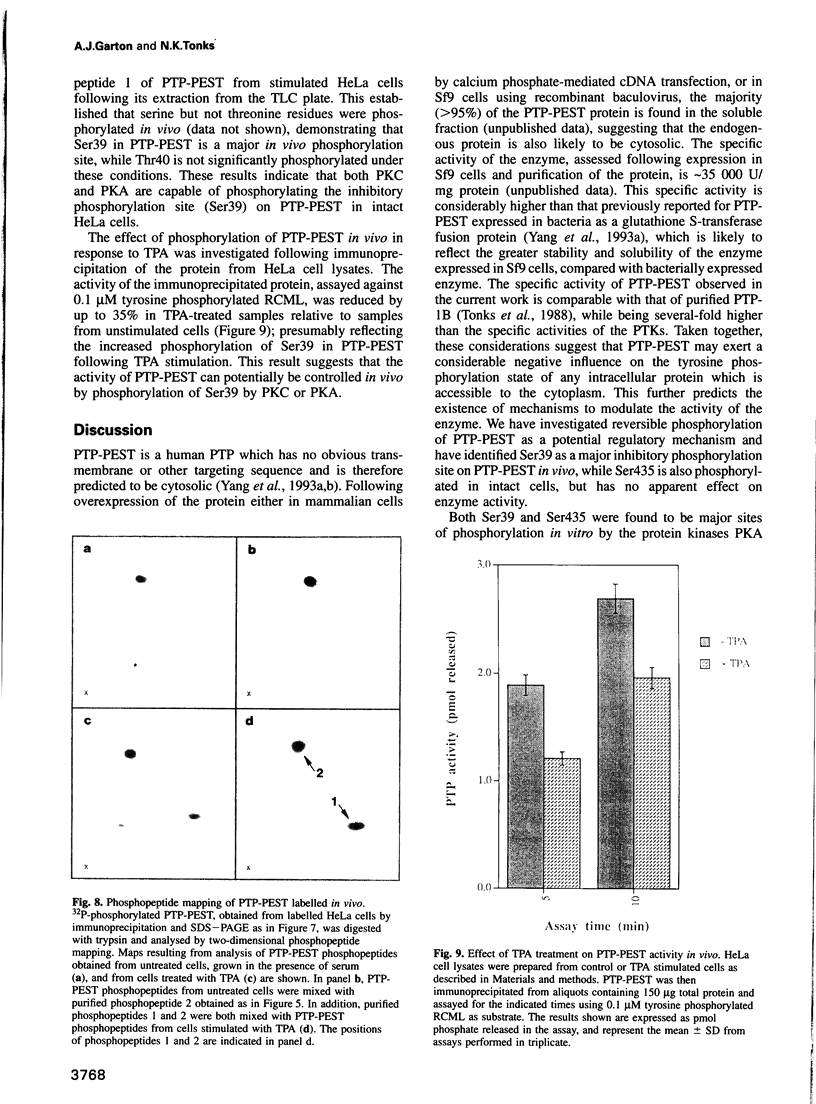
The protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP-PEST is an 88 kDa cytosolic enzyme which is ubiquitously expressed in mammalian tissues. We have expressed PTP-PEST using recombinant baculovirus, and purified the protein essentially to homogeneity in order to investigate phosphorylation as a potential mechanism of regulation of the enzyme. PTP-PEST is phosphorylated in vitro by both cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and protein kinase C (PKC) at two major sites, which we have identified as Ser39 and Ser435. PTP-PEST is also phosphorylated on both Ser39 and Ser435 following treatment of intact HeLa cells with TPA, forskolin or isobutyl methyl xanthine (IBMX). Phosphorylation of Ser39 in vitro decreases the activity of PTP-PEST by reducing its affinity for substrate. In addition, PTP-PEST immunoprecipitated from TPA-treated cells displayed significantly lower PTP activity than enzyme obtained from untreated cells. Our results suggest that both PKC and PKA are capable of phosphorylating, and therefore inhibiting, PTP-PEST in vivo, offering a mechanism whereby signal transduction pathways acting through either PKA or PKC may directly influence cellular processes involving reversible tyrosine phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Autero M., Saharinen J., Pessa-Morikawa T., Soula-Rothhut M., Oetken C., Gassmann M., Bergman M., Alitalo K., Burn P., Gahmberg C. G. Tyrosine phosphorylation of CD45 phosphotyrosine phosphatase by p50csk kinase creates a binding site for p56lck tyrosine kinase and activates the phosphatase. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1308–1321. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barford D., Flint A. J., Tonks N. K. Crystal structure of human protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. Science. 1994 Mar 11;263(5152):1397–1404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K. 1002 protein phosphatases? Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:463–493. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embi N., Parker P. J., Cohen P. A reinvestigation of the phosphorylation of rabbit skeletal-muscle glycogen synthase by cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase. Identification of the third site of phosphorylation as serine-7. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):405–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T. Signalling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:453–481. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng G. S., Hui C. C., Pawson T. SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase as a target of protein-tyrosine kinases. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1607–1611. doi: 10.1126/science.8096088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint A. J., Gebbink M. F., Franza B. R., Jr, Hill D. E., Tonks N. K. Multi-site phosphorylation of the protein tyrosine phosphatase, PTP1B: identification of cell cycle regulated and phorbol ester stimulated sites of phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1937–1946. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05843.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangioni J. V., Beahm P. H., Shifrin V., Jost C. A., Neel B. G. The nontransmembrane tyrosine phosphatase PTP-1B localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum via its 35 amino acid C-terminal sequence. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):545–560. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90190-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hippen K. L., Jakes S., Richards J., Jena B. P., Beck B. L., Tabatabai L. B., Ingebritsen T. S. Acidic residues are involved in substrate recognition by two soluble protein tyrosine phosphatases, PTP-5 and rrbPTP-1. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 23;32(46):12405–12412. doi: 10.1021/bi00097a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleider R. J., Freeman R. M., Jr, Neel B. G. Tyrosyl phosphorylation and growth factor receptor association of the human corkscrew homologue, SH-PTP2. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13434–13438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. J., Bowne D. B., Flores E., Thomas M. L. Characterization of hematopoietic intracellular protein tyrosine phosphatases: description of a phosphatase containing an SH2 domain and another enriched in proline-, glutamic acid-, serine-, and threonine-rich sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2396–2405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Nurse P., Russell P. Regulation of mitosis by cyclic accumulation of p80cdc25 mitotic inducer in fission yeast. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):549–552. doi: 10.1038/344549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash R., Tokiwa G., Anand S., Erickson K., Futcher A. B. The WHI1+ gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae tethers cell division to cell size and is a cyclin homolog. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4335–4346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Trowbridge I. S. Negative regulation of CD45 protein tyrosine phosphatase activity by ionomycin in T cells. Science. 1991 Sep 20;253(5026):1423–1425. doi: 10.1126/science.1654595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase phosphorylation site sequences and consensus specificity motifs: tabulations. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:62–81. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00127-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo G. L., Vandenberg M. T., Yu I. J., Bae Y. S., Franza B. R., Jr, Marshak D. R. Casein kinase II phosphorylates p34cdc2 kinase in G1 phase of the HeLa cell division cycle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20317–20325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahin M., Hockfield S. Protein tyrosine phosphatases expressed in the developing rat brain. J Neurosci. 1993 Nov;13(11):4968–4978. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-11-04968.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausfeld U., Fernandez A., Capony J. P., Girard F., Lautredou N., Derancourt J., Labbe J. C., Lamb N. J. Activation of p34cdc2 protein kinase by microinjection of human cdc25C into mammalian cells. Requirement for prior phosphorylation of cdc25C by p34cdc2 on sites phosphorylated at mitosis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):5989–6000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takekawa M., Itoh F., Hinoda Y., Arimura Y., Toyota M., Sekiya M., Adachi M., Imai K., Yachi A. Cloning and characterization of a human cDNA encoding a novel putative cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):1223–1230. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92335-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H. Purification of the major protein-tyrosine-phosphatases of human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6722–6730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M., Tokiwa G., Nash R., Futcher B. The Cln3-Cdc28 kinase complex of S. cerevisiae is regulated by proteolysis and phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1773–1784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine M. A., Widmer M. B., Ledbetter J. A., Pinault F., Voice R., Clark E. A., Gallis B., Brautigan D. L. Interleukin 2 stimulates serine phosphorylation of CD45 in CTLL-2.4 cells. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):913–919. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettenhall R. E., Morgan F. J. Phosphorylation of hepatic ribosomal protein S6 on 80 and 40 S ribosomes. Primary structure of S6 in the region of the major phosphorylation sites for cAMP-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2084–2091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Q., Co D., Sommercorn J., Tonks N. K. Cloning and expression of PTP-PEST. A novel, human, nontransmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17650–17650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Q., Co D., Sommercorn J., Tonks N. K. Cloning and expression of PTP-PEST. A novel, human, nontransmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6622–6628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Q., Tonks N. K. Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding a human protein-tyrosine phosphatase with homology to the cytoskeletal-associated proteins band 4.1, ezrin, and talin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):5949–5953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung Y. G., Berg K. L., Pixley F. J., Angeletti R. H., Stanley E. R. Protein tyrosine phosphatase-1C is rapidly phosphorylated in tyrosine in macrophages in response to colony stimulating factor-1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23447–23450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi T., Cleveland J. L., Ihle J. N. Identification of novel protein tyrosine phosphatases of hematopoietic cells by polymerase chain reaction amplification. Blood. 1991 Nov 1;78(9):2222–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]