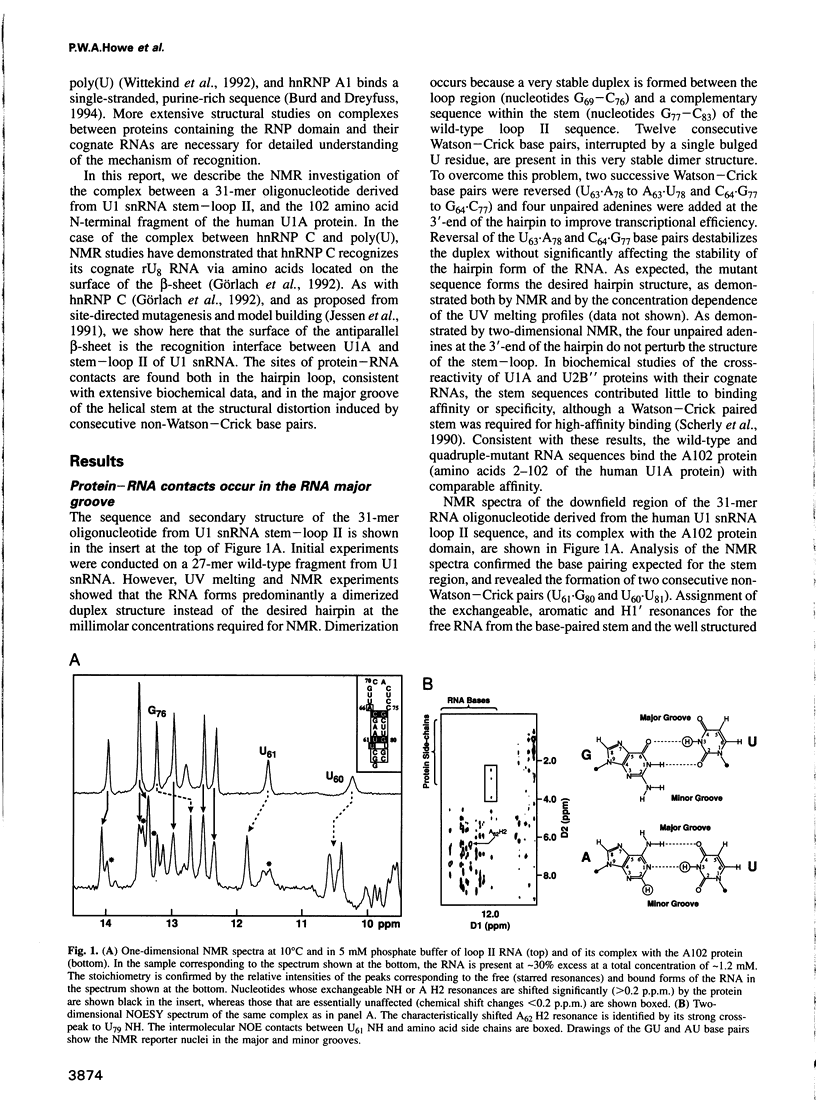
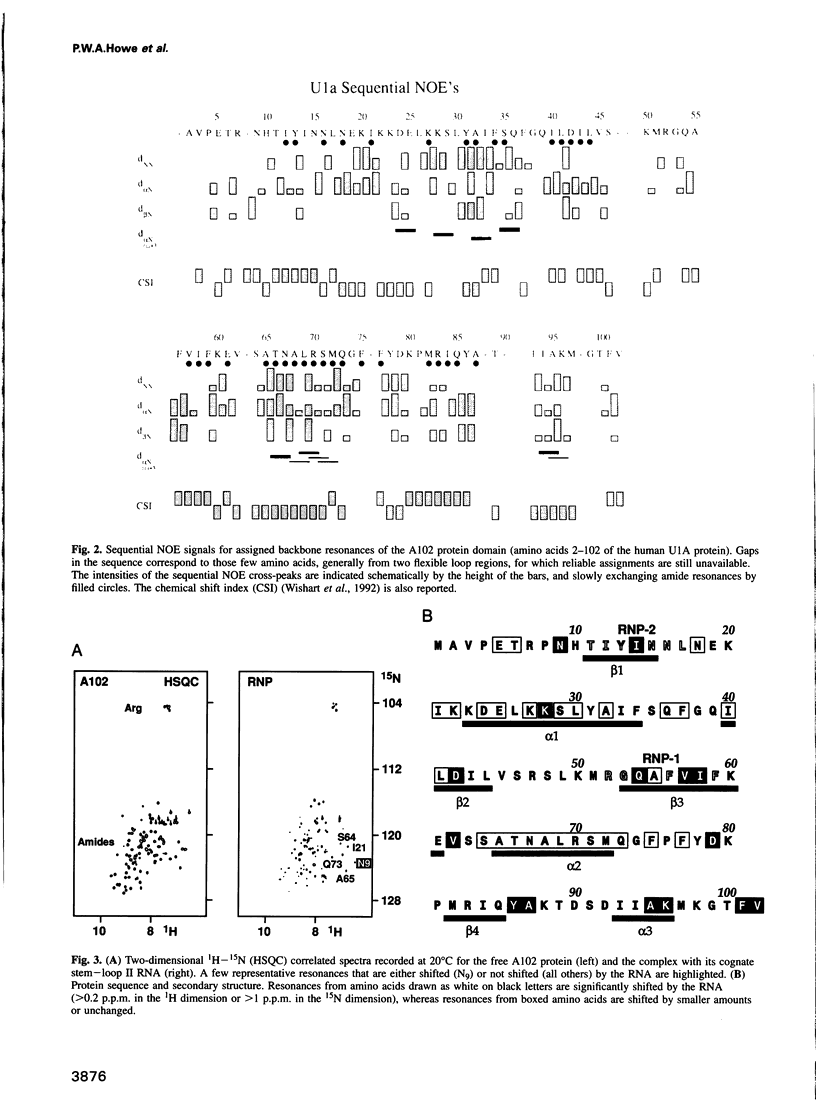
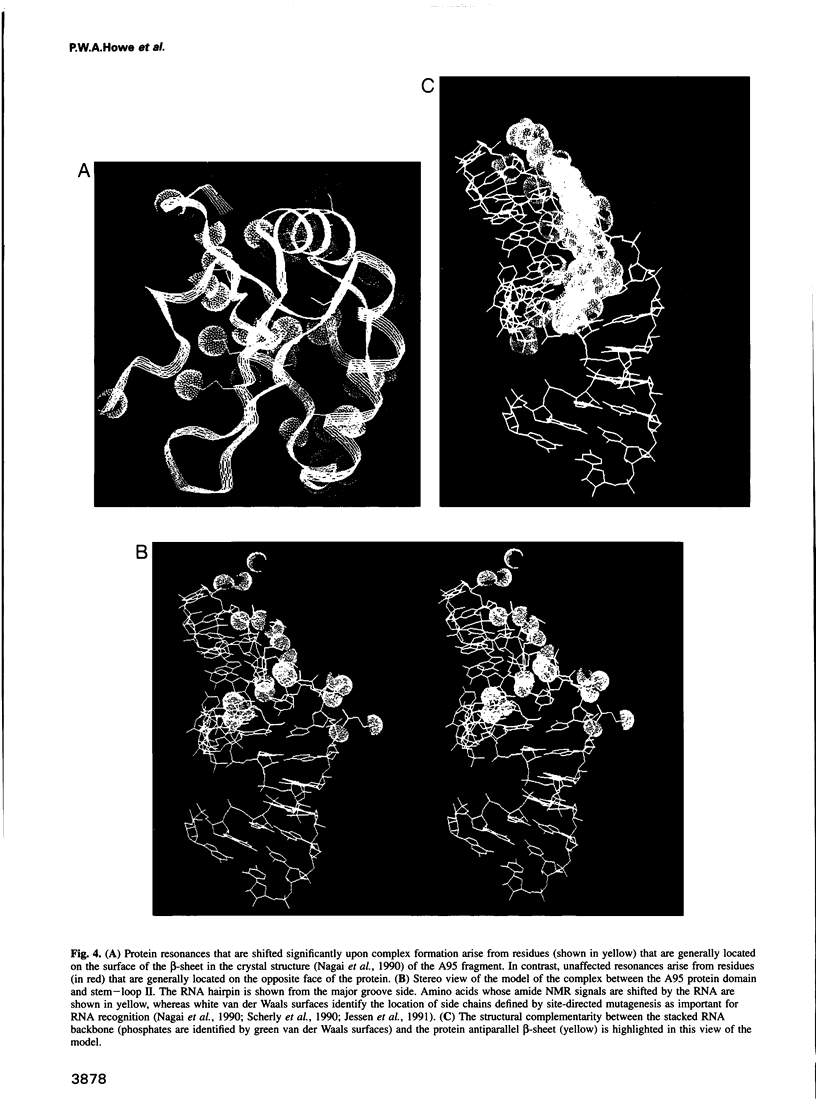
Abstract
The RNP domain is a very common motif found in hundreds of proteins, including many protein components of the RNA processing machinery. The 70-90 amino acid domain contains two highly conserved stretches of 6-8 amino acids (RNP-1 and RNP-2) in the central strands of a four-stranded antiparallel beta-sheet, packed against two alpha-helices by a conserved hydrophobic core. Using multidimensional heteronuclear NMR, we have mapped intermolecular contacts between the human U1A protein 102 amino acid N-terminal RNP domain and a 31-mer oligonucleotide derived from stem-loop II of U1 snRNA. Chemical shift changes induced on the protein by the RNA define the surface of the beta-sheet as the recognition interface. The reverse face of the protein, with the two alpha-helices, remains exposed to the solvent in the presence of the RNA, and is potentially available for protein-protein contacts in spliceosome assembly or splice site selection. Protein-RNA contacts occur at the single-stranded apical loop of the hairpin, but also in the major groove of the helical stem at neighbouring U.G and U.U non-Watson-Crick base pairs. Examination of a proposed model for the complex in the light of the present results reveals several features of RNA recognition by RNP proteins. The quality of the spectra for this complex of 22 kDa demonstrates the feasibility of NMR investigation of RNA-protein complexes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biamonti G., Riva S. New insights into the auxiliary domains of eukaryotic RNA binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1994 Feb 28;340(1-2):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80162-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biou V., Yaremchuk A., Tukalo M., Cusack S. The 2.9 A crystal structure of T. thermophilus seryl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Ser). Science. 1994 Mar 11;263(5152):1404–1410. doi: 10.1126/science.8128220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boelens W. C., Jansen E. J., van Venrooij W. J., Stripecke R., Mattaj I. W., Gunderson S. I. The human U1 snRNP-specific U1A protein inhibits polyadenylation of its own pre-mRNA. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):881–892. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90577-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd C. G., Dreyfuss G. RNA binding specificity of hnRNP A1: significance of hnRNP A1 high-affinity binding sites in pre-mRNA splicing. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 1;13(5):1197–1204. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06369.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. W., Jr, Kraut J. A proposed model for interaction of polypeptides with RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):283–287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavarelli J., Rees B., Ruff M., Thierry J. C., Moras D. Yeast tRNA(Asp) recognition by its cognate class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):181–184. doi: 10.1038/362181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colvin R. A., White S. W., Garcia-Blanco M. A., Hoffman D. W. Structural features of an RNA containing the CUGGGA loop of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 trans-activation response element. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 2;32(4):1105–1112. doi: 10.1021/bi00055a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flickinger T. W., Salz H. K. The Drosophila sex determination gene snf encodes a nuclear protein with sequence and functional similarity to the mammalian U1A snRNP protein. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 15;8(8):914–925. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.8.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn A. M., Bax A., Wingfield P. T., Clore G. M. A powerful method of sequential proton resonance assignment in proteins using relayed 15N-1H multiple quantum coherence spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 16;243(1):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson S. I., Beyer K., Martin G., Keller W., Boelens W. C., Mattaj L. W. The human U1A snRNP protein regulates polyadenylation via a direct interaction with poly(A) polymerase. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):531–541. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlach M., Wittekind M., Beckman R. A., Mueller L., Dreyfuss G. Interaction of the RNA-binding domain of the hnRNP C proteins with RNA. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3289–3295. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K. B., Stump W. T. Interaction of N-terminal domain of U1A protein with an RNA stem/loop. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4283–4290. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamy F., Asseline U., Grasby J., Iwai S., Pritchard C., Slim G., Butler P. J., Karn J., Gait M. J. Hydrogen-bonding contacts in the major groove are required for human immunodeficiency virus type-1 tat protein recognition of TAR RNA. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):111–123. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman D. W., Colvin R. A., Garcia-Blanco M. A., White S. W. Structural features of the trans-activation response RNA element of equine infectious anemia virus. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 2;32(4):1096–1104. doi: 10.1021/bi00055a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman D. W., Query C. C., Golden B. L., White S. W., Keene J. D. RNA-binding domain of the A protein component of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein analyzed by NMR spectroscopy is structurally similar to ribosomal proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. A., Tinoco I., Jr An NMR study of the HIV-1 TAR element hairpin. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 23;32(46):12522–12530. doi: 10.1021/bi00097a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessen T. H., Oubridge C., Teo C. H., Pritchard C., Nagai K. Identification of molecular contacts between the U1 A small nuclear ribonucleoprotein and U1 RNA. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3447–3456. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04909.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kambach C., Mattaj I. W. Intracellular distribution of the U1A protein depends on active transport and nuclear binding to U1 snRNA. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(1):11–21. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Nikolov D. B., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of a TATA element. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):520–527. doi: 10.1038/365520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Geiger J. H., Hahn S., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of a yeast TBP/TATA-box complex. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):512–520. doi: 10.1038/365512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohtz J. D., Jamison S. F., Will C. L., Zuo P., Lührmann R., Garcia-Blanco M. A., Manley J. L. Protein-protein interactions and 5'-splice-site recognition in mammalian mRNA precursors. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):119–124. doi: 10.1038/368119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A., Westhof E., Bach M., Lührmann R., Ebel J. P., Carbon P. Solution structure of human U1 snRNA. Derivation of a possible three-dimensional model. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3803–3811. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz C. S., Alwine J. C. Direct interaction of the U1 snRNP-A protein with the upstream efficiency element of the SV40 late polyadenylation signal. Genes Dev. 1994 Mar 1;8(5):576–586. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.5.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. RNA recognition: a family matter? Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):837–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90265-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Oubridge C., Jessen T. H., Li J., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of the RNA-binding domain of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):515–520. doi: 10.1038/348515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Wüthrich K. Heteronuclear filters in two-dimensional [1H,1H]-NMR spectroscopy: combined use with isotope labelling for studies of macromolecular conformation and intermolecular interactions. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Feb;23(1):39–96. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Chen L., Frankel A. D., Williamson J. R. Role of RNA structure in arginine recognition of TAR RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3680–3684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Tan R., Calnan B. J., Frankel A. D., Williamson J. R. Conformation of the TAR RNA-arginine complex by NMR spectroscopy. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):76–80. doi: 10.1126/science.1621097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Tinoco I., Jr Absorbance melting curves of RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:304–325. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y. Q., Otting G., Billeter M., Müller M., Gehring W., Wüthrich K. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of a DNA complex with the uniformly 13C-labeled Antennapedia homeodomain and structure determination of the DNA-bound homeodomain. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 20;234(4):1070–1083. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosbash M., Séraphin B. Who's on first? The U1 snRNP-5' splice site interaction and splicing. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 May;16(5):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rould M. A., Perona J. J., Söll D., Steitz T. A. Structure of E. coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Gln) and ATP at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1135–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.2479982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., Dathan N. A., van Venrooij W. J., Mattaj I. W. Major determinants of the specificity of interaction between small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1A and U2B'' and their cognate RNAs. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):502–506. doi: 10.1038/345502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Kambach C., Boelens W., van Venrooij W. J., Mattaj I. W. Conserved amino acid residues within and outside of the N-terminal ribonucleoprotein motif of U1A small nuclear ribonucleoprotein involved in U1 RNA binding. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jun 20;219(4):577–584. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90651-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spolar R. S., Record M. T., Jr Coupling of local folding to site-specific binding of proteins to DNA. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):777–784. doi: 10.1126/science.8303294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. Structural studies of protein-nucleic acid interaction: the sources of sequence-specific binding. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Aug;23(3):205–280. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terns M. P., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. A pre-export U1 snRNP in Xenopus laevis oocyte nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 25;21(19):4569–4573. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.19.4569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani G., Tinoco I., Jr RNA structure and NMR spectroscopy. Q Rev Biophys. 1991 Nov;24(4):479–532. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500003875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks K. M., Crothers D. M. RNA recognition by Tat-derived peptides: interaction in the major groove? Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):577–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimberly B., Varani G., Tinoco I., Jr The conformation of loop E of eukaryotic 5S ribosomal RNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 2;32(4):1078–1087. doi: 10.1021/bi00055a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishart D. S., Sykes B. D., Richards F. M. The chemical shift index: a fast and simple method for the assignment of protein secondary structure through NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1647–1651. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittekind M., Görlach M., Friedrichs M., Dreyfuss G., Mueller L. 1H, 13C, and 15N NMR assignments and global folding pattern of the RNA-binding domain of the human hnRNP C proteins. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 14;31(27):6254–6265. doi: 10.1021/bi00142a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gelder C. W., Gunderson S. I., Jansen E. J., Boelens W. C., Polycarpou-Schwarz M., Mattaj I. W., van Venrooij W. J. A complex secondary structure in U1A pre-mRNA that binds two molecules of U1A protein is required for regulation of polyadenylation. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5191–5200. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]