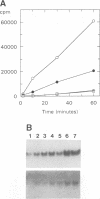
Abstract
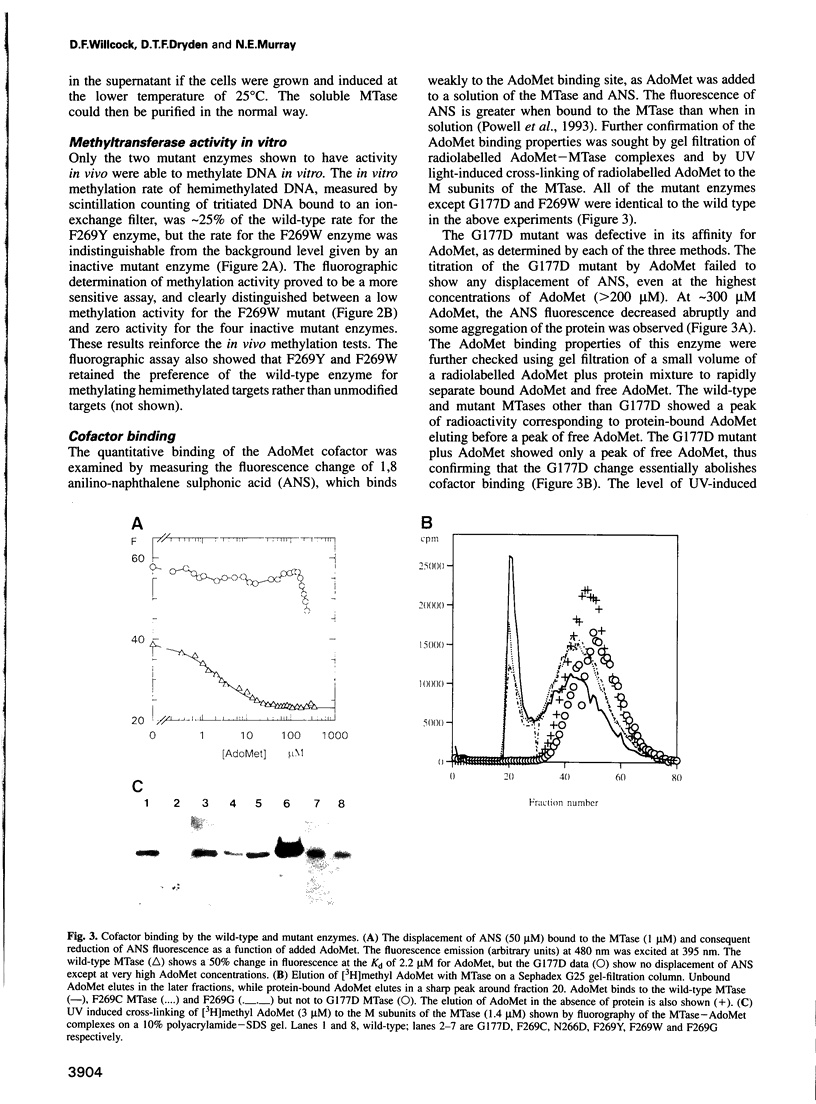
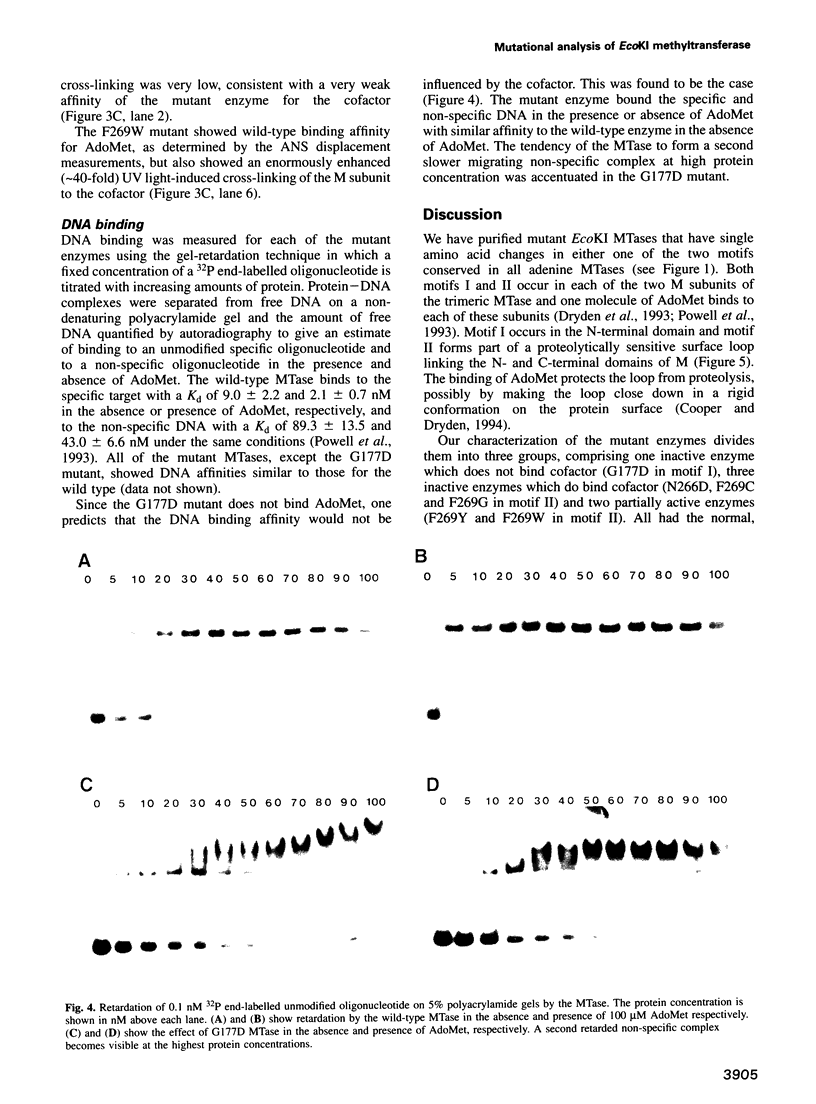
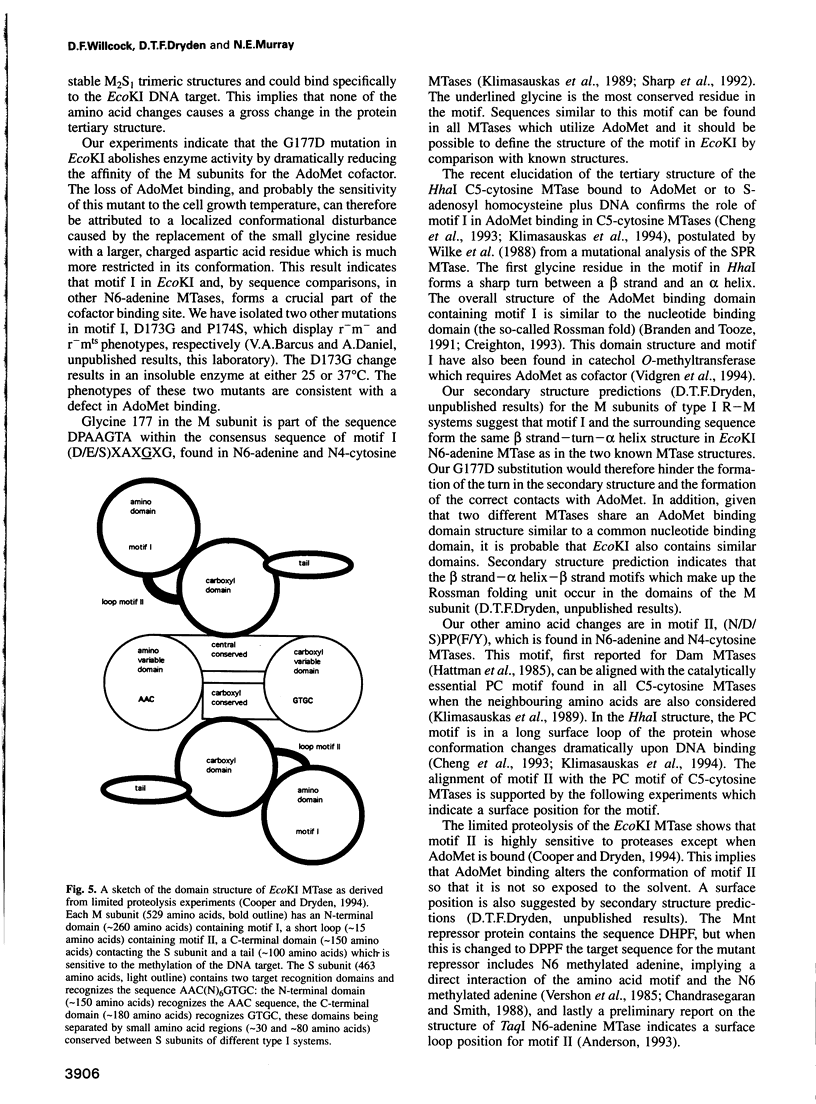
All methyltransferases that use S-adenosyl methionine as the methyl group donor contain a sequence similar to (D/E/S)XFXGXG which has been postulated to form part of the cofactor binding site. In N6-adenine DNA methyltransferases there is a second motif, (D/N)PP(Y/F), which has been proposed to play a role similar to the catalytically essential PC motif conserved in all C5-cytosine DNA methyltransferases. We have made a series of amino acid changes in these two motifs in the EcoKI N6-adenine DNA methyltransferase. The mutant enzymes have been purified to homogeneity and characterized by physical biochemical methods. The first G is the most conserved residue in motif I. Changing this G to D completely abolished S-adenosyl methionine binding, but left enzyme structure and DNA target recognition unaltered, thus documenting the S-adenosyl methionine binding function of motif I in N6-adenine methyltransferases. Substitution of the N with D, or F with either G or C, in motif II abolished enzyme activity, but left S-adenosyl methionine and DNA binding unaltered. Changes of F to Y or W resulted in partial enzyme activity, implying that an aromatic residue is important for methylation. The substitution of W for F greatly enhanced UV-induced cross-linking between the enzyme and S-adenosyl methionine, suggesting that the aromatic residue is close in space to the methyl-group donor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of New Lysogenic Types during Growth of a Doubly Lysogenic Strain Derived from Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):440–452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barras F., Marinus M. G. The great GATC: DNA methylation in E. coli. Trends Genet. 1989 May;5(5):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickle T. A., Krüger D. H. Biology of DNA restriction. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Jun;57(2):434–450. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.2.434-450.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., MacMillan A. M., Chang W., Ezaz-Nikpay K., Lane W. S., Verdine G. L. Direct identification of the active-site nucleophile in a DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 19;30(46):11018–11025. doi: 10.1021/bi00110a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng X., Kumar S., Posfai J., Pflugrath J. W., Roberts R. J. Crystal structure of the HhaI DNA methyltransferase complexed with S-adenosyl-L-methionine. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90421-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper L. P., Dryden D. T. The domains of a type I DNA methyltransferase. Interactions and role in recognition of DNA methylation. J Mol Biol. 1994 Mar 4;236(4):1011–1021. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(94)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degtyarev Skh, Prikhod'ko E. A., Prikhod'ko G. G., Krasnykh V. N. Vspl methylase belongs to m6A-gamma class of adenine methylases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):2015–2015. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryden D. T., Cooper L. P., Murray N. E. Purification and characterization of the methyltransferase from the type 1 restriction and modification system of Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13228–13236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürste J. P., Pansegrau W., Frank R., Blöcker H., Scholz P., Bagdasarian M., Lanka E. Molecular cloning of the plasmid RP4 primase region in a multi-host-range tacP expression vector. Gene. 1986;48(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90358-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough J. A., Murray N. E. Sequence diversity among related genes for recognition of specific targets in DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 5;166(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyot J. B., Grassi J., Hahn U., Guschlbauer W. The role of the preserved sequences of Dam methylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3183–3190. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattman S., Wilkinson J., Swinton D., Schlagman S., Macdonald P. M., Mosig G. Common evolutionary origin of the phage T4 dam and host Escherichia coli dam DNA-adenine methyltransferase genes. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):932–937. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.932-937.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitman J. On the origins, structures and functions of restriction-modification enzymes. Genet Eng (N Y) 1993;15:57–108. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1666-2_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan N. C., Lautenberger J. A., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd The nucleotide sequence recognized by the Escherichia coli K12 restriction and modification enzymes. J Mol Biol. 1979 May 15;130(2):191–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90426-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher J. E., Daniel A. S., Murray N. E. Mutations that confer de novo activity upon a maintenance methyltransferase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 20;221(2):431–440. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimasauskas S., Kumar S., Roberts R. J., Cheng X. HhaI methyltransferase flips its target base out of the DNA helix. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90342-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimasauskas S., Timinskas A., Menkevicius S., Butkienè D., Butkus V., Janulaitis A. Sequence motifs characteristic of DNA[cytosine-N4]methyltransferases: similarity to adenine and cytosine-C5 DNA-methylases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9823–9832. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kossykh V. G., Schlagman S. L., Hattman S. Conserved sequence motif DPPY in region IV of the phage T4 Dam DNA-[N-adenine]-methyltransferase is important for S-adenosyl-L-methionine binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 25;21(15):3563–3566. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.15.3563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer B., Kramer W., Fritz H. J. Different base/base mismatches are corrected with different efficiencies by the methyl-directed DNA mismatch-repair system of E. coli. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Cheng X., Klimasauskas S., Mi S., Posfai J., Roberts R. J., Wilson G. G. The DNA (cytosine-5) methyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jan 11;22(1):1–10. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., Daniel A. S., Braymer H. D., Murray N. E. Organization and sequence of the hsd genes of Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):159–170. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90303-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley C. A., Murray N. E. T4 polynucleotide kinase; cloning of the gene (pseT) and amplification of its product. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2695–2703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03989.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyer-Weidner M., Trautner T. A. Methylation of DNA in prokaryotes. EXS. 1993;64:39–108. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-9118-9_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell L. M., Dryden D. T., Willcock D. F., Pain R. H., Murray N. E. DNA recognition by the EcoK methyltransferase. The influence of DNA methylation and the cofactor S-adenosyl-L-methionine. J Mol Biol. 1993 Nov 5;234(1):60–71. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pósfai J., Bhagwat A. S., Pósfai G., Roberts R. J. Predictive motifs derived from cytosine methyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2421–2435. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sain B., Murray N. E. The hsd (host specificity) genes of E. coli K 12. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(1):35–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00267350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Kelleher J. E., Daniel A. S., Cowan G. M., Murray N. E. Roles of selection and recombination in the evolution of type I restriction-modification systems in enterobacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9836–9840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki H., Kita K., Takanami M. The FokI restriction-modification system. II. Presence of two domains in FokI methylase responsible for modification of different DNA strands. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5757–5761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suri B., Bickle T. A. EcoA: the first member of a new family of type I restriction modification systems. Gene organization and enzymatic activities. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90258-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidgren J., Svensson L. A., Liljas A. Crystal structure of catechol O-methyltransferase. Nature. 1994 Mar 24;368(6469):354–358. doi: 10.1038/368354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilke K., Rauhut E., Noyer-Weidner M., Lauster R., Pawlek B., Behrens B., Trautner T. A. Sequential order of target-recognizing domains in multispecific DNA-methyltransferases. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2601–2609. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. G., Murray N. E. Restriction and modification systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:585–627. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.003101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]