Abstract
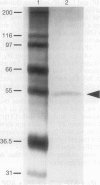
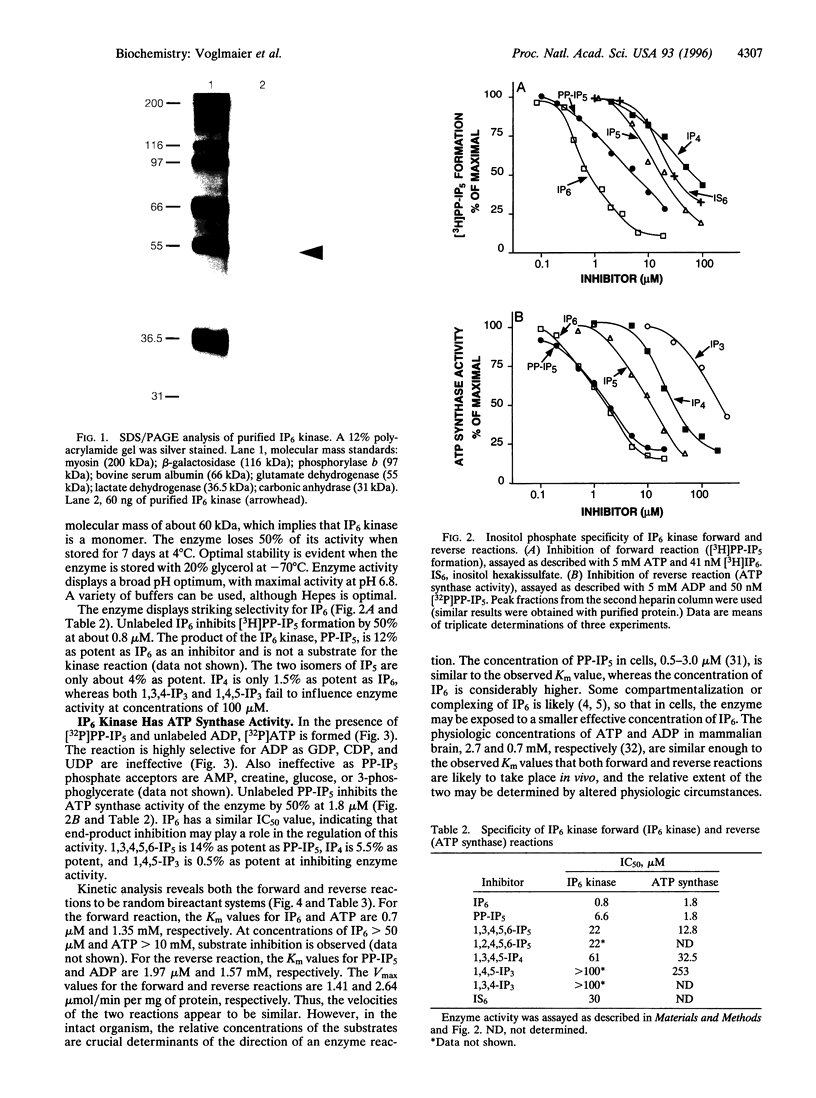
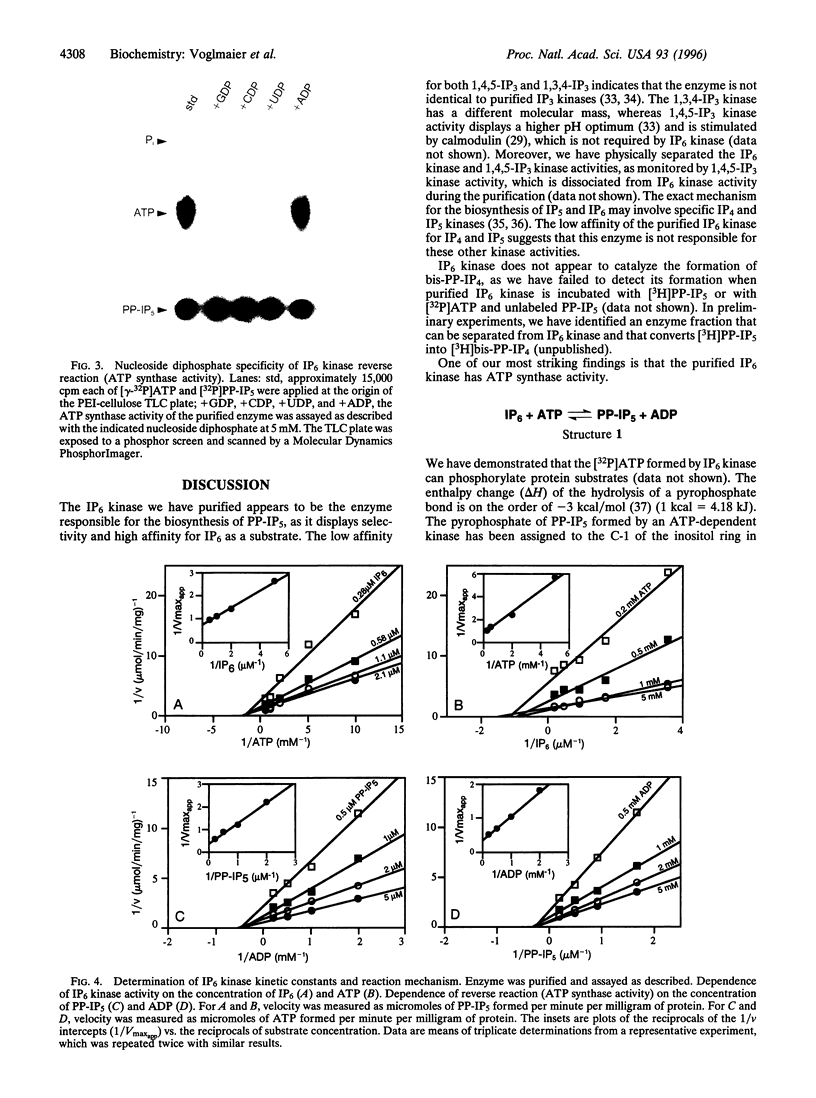
Diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate (PP-IP5) and bis(diphospho)inositol tetrakisphosphate (bis-PP-IP4) are recently identified inositol phosphates that possess pyrophosphate bonds. We have purified an inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) kinase from rat brain supernatants. The pure protein, a monomer of 54 kDa, displays high affinity (Km = 0.7 microM) and selectivity for inositol hexakisphosphate as substrate. It can be dissociated from bis(diphospho)inositol tetrakisphosphate synthetic activity. The purified enzyme transfers a phosphate from PP-IP5 to ADP to form ATP. This ATP synthase activity indicates the high phosphate group transfer potential of PP-IP5 and may represent a physiological role for PP-IP5.
Full text
PDF



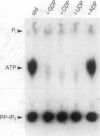
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdullah M., Hughes P. J., Craxton A., Gigg R., Desai T., Marecek J. F., Prestwich G. D., Shears S. B. Purification and characterization of inositol-1,3,4-trisphosphate 5/6-kinase from rat liver using an inositol hexakisphosphate affinity column. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22340–22345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali N., Craxton A., Shears S. B. Hepatic Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 3-phosphatase is compartmentalized inside endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6161–6167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali N., Duden R., Bembenek M. E., Shears S. B. The interaction of coatomer with inositol polyphosphates is conserved in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J. 1995 Aug 15;310(Pt 1):279–284. doi: 10.1042/bj3100279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck K. A., Keen J. H. Interaction of phosphoinositide cycle intermediates with the plasma membrane-associated clathrin assembly protein AP-2. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4442–4447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas S., Maity I. B., Chakrabarti S., Biswas B. B. Purification and characterization of myo-inositol hexaphosphate-adenosine diphosphate phosphotransferase from Phaseolus aureus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jan 30;185(2):557–566. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P. Inositol phosphates: a family of signal molecules? Trends Neurosci. 1988 Aug;11(8):336–338. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Xie J., Mayrleitner M., Shears S. B., Palmer D. J., Fleischer S. Golgi coatomer binds, and forms K(+)-selective channels gated by, inositol polyphosphates. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 8;269(27):17826–17832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda M., Aruga J., Niinobe M., Aimoto S., Mikoshiba K. Inositol-1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate binding to C2B domain of IP4BP/synaptotagmin II. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 18;269(46):29206–29211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glennon M. C., Shears S. B. Turnover of inositol pentakisphosphates, inositol hexakisphosphate and diphosphoinositol polyphosphates in primary cultured hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 15;293(Pt 2):583–590. doi: 10.1042/bj2930583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf E., Eaton J. W. Suppression of colonic cancer by dietary phytic acid. Nutr Cancer. 1993;19(1):11–19. doi: 10.1080/01635589309514232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf E., Empson K. L., Eaton J. W. Phytic acid. A natural antioxidant. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11647–11650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg L., Brune M., Rossander L. Iron absorption in man: ascorbic acid and dose-dependent inhibition by phytate. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989 Jan;49(1):140–144. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/49.1.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Poyner D. R., Jackson T. R., Letcher A. J., Lander D. A., Irvine R. F. Inhibition of iron-catalysed hydroxyl radical formation by inositol polyphosphates: a possible physiological function for myo-inositol hexakisphosphate. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 15;294(Pt 3):929–934. doi: 10.1042/bj2940929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M., Pollock W. K., Smith P. M., Wreggett K. A. Inositol phosphates: proliferation, metabolism and function. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):281–298. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson R. A., Hansen C. A., Williamson J. R. Purification of D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7465–7471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Lang E. J., Morita M., Fukuda M., Niinobe M., Mikoshiba K. The inositol high-polyphosphate series blocks synaptic transmission by preventing vesicular fusion: a squid giant synapse study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12990–12993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON R. K., RAISON J. K. A COMPLETE INTRACELLULAR UNIT FOR INCORPORATION OF AMINO-ACID INTO STORAGE PROTEIN UTILIZING ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE GENERATED FROM PHYTATE. Nature. 1963 Nov 2;200:429–433. doi: 10.1038/200429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menniti F. S., Miller R. N., Putney J. W., Jr, Shears S. B. Turnover of inositol polyphosphate pyrophosphates in pancreatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3850–3856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menniti F. S., Oliver K. G., Putney J. W., Jr, Shears S. B. Inositol phosphates and cell signaling: new views of InsP5 and InsP6. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Feb;18(2):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90053-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niinobe M., Yamaguchi Y., Fukuda M., Mikoshiba K. Synaptotagmin is an inositol polyphosphate binding protein: isolation and characterization as an Ins 1,3,4,5-P4 binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Dec 15;205(2):1036–1042. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris F. A., Ungewickell E., Majerus P. W. Inositol hexakisphosphate binds to clathrin assembly protein 3 (AP-3/AP180) and inhibits clathrin cage assembly in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 6;270(1):214–217. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.1.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palczewski K., Pulvermüller A., Buczylko J., Gutmann C., Hofmann K. P. Binding of inositol phosphates to arrestin. FEBS Lett. 1991 Dec 16;295(1-3):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81416-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R. Rab GTPases: master regulators of membrane trafficking. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;6(4):522–526. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillippy B. Q., Ullah A. H., Ehrlich K. C. Purification and some properties of inositol 1,3,4,5,6-Pentakisphosphate 2-kinase from immature soybean seeds. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 11;269(45):28393–28399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittet D., Schlegel W., Lew D. P., Monod A., Mayr G. W. Mass changes in inositol tetrakis- and pentakisphosphate isomers induced by chemotactic peptide stimulation in HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18489–18493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poyner D. R., Cooke F., Hanley M. R., Reynolds D. J., Hawkins P. T. Characterization of metal ion-induced [3H]inositol hexakisphosphate binding to rat cerebellar membranes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1032–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raison J. K., Evans W. J. The enthalpy change in the hydrolysis of the phosphate esters of myo-inositol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 23;170(2):448–451. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Mechanisms of intracellular protein transport. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):55–63. doi: 10.1038/372055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G. Catalytic properties of inositol trisphosphate kinase: activation by Ca2+ and calmodulin. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):388–393. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.5.2824270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa N., Sharif M., Hanley M. R. Metabolism and biological activities of inositol pentakisphosphate and inositol hexakisphosphate. Biochem Pharmacol. 1995 Jul 17;50(2):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(95)00059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo G., Gmachl M. J., Stenbeck G., Söllner T. H., Rothman J. E. A possible docking and fusion particle for synaptic transmission. Nature. 1995 Dec 14;378(6558):733–736. doi: 10.1038/378733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. L., Carter L. L. ATP is required for receptor-mediated endocytosis in intact cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2307–2318. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. L., Smythe E. Stage-specific assays for coated pit formation and coated vesicle budding in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(5):869–880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.5.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. L. The mechanism of receptor-mediated endocytosis: more questions than answers. Bioessays. 1992 Sep;14(9):589–596. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaman M. N., Ball C. L., Robinson M. S. Targeting and mistargeting of plasma membrane adaptors in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(5):1093–1105. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.5.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B., Ali N., Craxton A., Bembenek M. E. Synthesis and metabolism of bis-diphosphoinositol tetrakisphosphate in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10489–10497. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe E., Carter L. L., Schmid S. L. Cytosol- and clathrin-dependent stimulation of endocytosis in vitro by purified adaptors. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1163–1171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe E., Pypaert M., Lucocq J., Warren G. Formation of coated vesicles from coated pits in broken A431 cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):843–853. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Hawkins P. T., Stanley A. F., Moore T., Poyner D. R., Morris P. J., Hanley M. R., Kay R. R., Irvine R. F. myo-inositol pentakisphosphates. Structure, biological occurrence and phosphorylation to myo-inositol hexakisphosphate. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 15;275(Pt 2):485–499. doi: 10.1042/bj2750485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L., Radenberg T., Thiel U., Vogel G., Khoo K. H., Dell A., Jackson T. R., Hawkins P. T., Mayr G. W. The detection, purification, structural characterization, and metabolism of diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate(s) and bisdiphosphoinositol tetrakisphosphate(s). J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4009–4015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. A., Anderson K. L., French P. J., Kirk C. J., Michell R. H. The intracellular distribution of inositol polyphosphates in HL60 promyeloid cells. Biochem J. 1994 Oct 15;303(Pt 2):517–525. doi: 10.1042/bj3030517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szwergold B. S., Graham R. A., Brown T. R. Observation of inositol pentakis- and hexakis-phosphates in mammalian tissues by 31P NMR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 31;149(3):874–881. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90489-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Bennett M. K., Whiteheart S. W., Scheller R. H., Rothman J. E. A protein assembly-disassembly pathway in vitro that may correspond to sequential steps of synaptic vesicle docking, activation, and fusion. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timerman A. P., Mayrleitner M. M., Lukas T. J., Chadwick C. C., Saito A., Watterson D. M., Schindler H., Fleischer S. Inositol polyphosphate receptor and clathrin assembly protein AP-2 are related proteins that form potassium-selective ion channels in planar lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8976–8980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veech R. L., Lawson J. W., Cornell N. W., Krebs H. A. Cytosolic phosphorylation potential. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6538–6547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voglmaier S. M., Keen J. H., Murphy J. E., Ferris C. D., Prestwich G. D., Snyder S. H., Theibert A. B. Inositol hexakisphosphate receptor identified as the clathrin assembly protein AP-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Aug 31;187(1):158–163. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81473-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Rothberg K. G., Anderson R. G. Mis-assembly of clathrin lattices on endosomes reveals a regulatory switch for coated pit formation. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(5):1107–1117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.5.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye W., Ali N., Bembenek M. E., Shears S. B., Lafer E. M. Inhibition of clathrin assembly by high affinity binding of specific inositol polyphosphates to the synapse-specific clathrin assembly protein AP-3. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 27;270(4):1564–1568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Ouggouti S., Bournier O., Boivin P., Bertrand O., Dhermy D. Purification of erythrocyte protein 4.1 by selective interaction with inositol hexaphosphate. Protein Expr Purif. 1992 Dec;3(6):488–496. doi: 10.1016/1046-5928(92)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]