Abstract
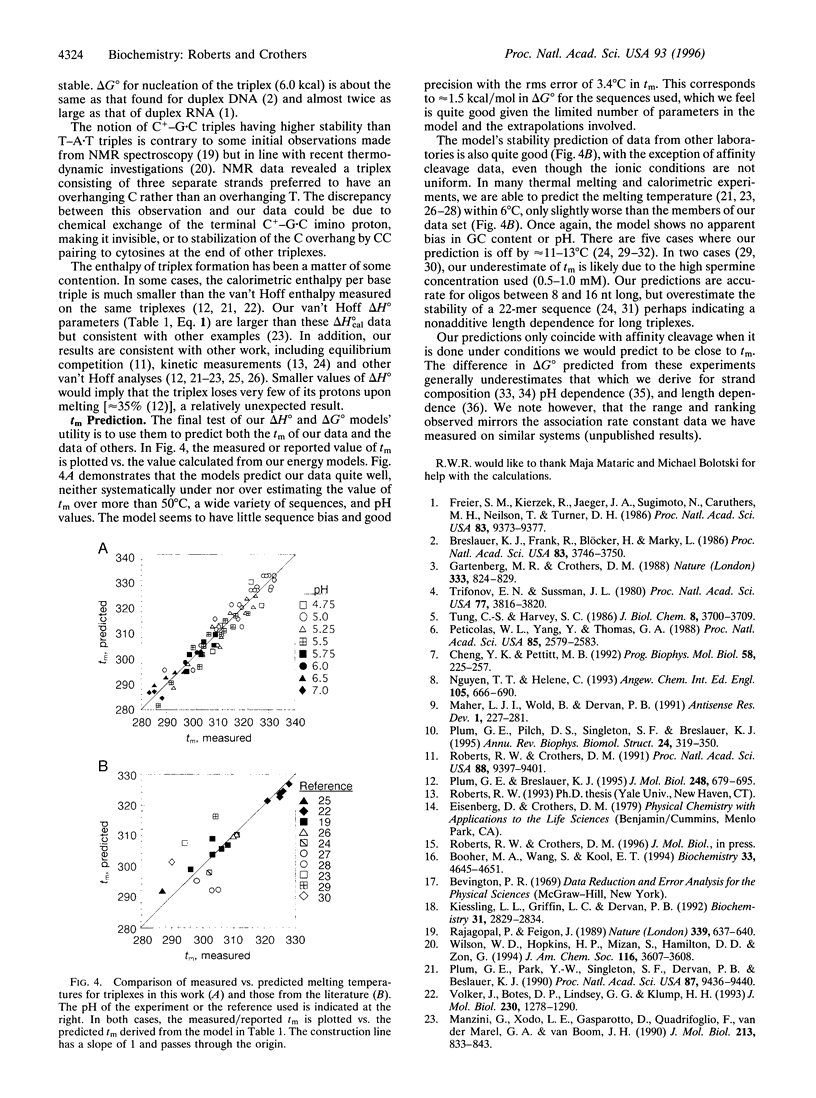
We present rules that allow one to predict the stability of DNA pyrimidine.purine.pyrimidine (Y.R.Y) triple helices on the basis of the sequence. The rules were derived from van't Hoff analysis of 23 oligonucleotide triplexes tested at a variety of pH values. To predict the enthalpy of triplex formation (delta H degrees), a simple nearest-neighbor model was found to be sufficient. However, to accurately predict the free energy of the triplex (delta G degrees), a combination model consisting of five parameters was needed. These parameters were (i) the delta G degrees for helix initiation, (ii) the delta G degrees for adding a T-A.T triple, (iii) the delta G degrees for adding a C(+)-G.C triple, (iv) the penalty for adjacent C bases, and (v) the pH dependence of the C(+)-G.C triple's stability. The fitted parameters are highly consistent with thermodynamic data from the basis set, generally predicting both delta H degrees and delta G degrees to within the experimental error. Examination of the parameters points out several interesting features. The combination model predicts that C(+) -G.C. triples are much more stabilizing than T-A.T triples below pH 7.0 and that the stability of the former increases approximately equal to 1 kcal/mol per pH unit as the pH is decreased. Surprisingly though, the most stable sequence is predicted to be a CT repeat, as adjacent C bases partially cancel the stability of one another. The parameters successfully predict tm values from other laboratories, with some interesting exceptions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booher M. A., Wang S., Kool E. T. Base pairing and steric interactions between pyrimidine strand bridging loops and the purine strand in DNA pyrimidine.purine.pyrimidine triplexes. Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 19;33(15):4645–4651. doi: 10.1021/bi00181a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslauer K. J., Frank R., Blöcker H., Marky L. A. Predicting DNA duplex stability from the base sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3746–3750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. K., Pettitt B. M. Stabilities of double- and triple-strand helical nucleic acids. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1992;58(3):225–257. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(92)90007-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escudé C., François J. C., Sun J. S., Ott G., Sprinzl M., Garestier T., Hélène C. Stability of triple helices containing RNA and DNA strands: experimental and molecular modeling studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 11;21(24):5547–5553. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.24.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. DNA sequence determinants of CAP-induced bending and protein binding affinity. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):824–829. doi: 10.1038/333824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han H., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical RNA and RNA.DNA by triple helix formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin R., Chapman W. H., Jr, Srinivasan A. R., Olson W. K., Breslow R., Breslauer K. J. Comparative spectroscopic, calorimetric, and computational studies of nucleic acid complexes with 2',5"-versus 3',5"-phosphodiester linkages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10568–10572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling L. L., Griffin L. C., Dervan P. B. Flanking sequence effects within the pyrimidine triple-helix motif characterized by affinity cleaving. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 17;31(10):2829–2834. doi: 10.1021/bi00125a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Wold B., Dervan P. B. Oligonucleotide-directed DNA triple-helix formation: an approach to artificial repressors? Antisense Res Dev. 1991 Fall;1(3):277–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzini G., Xodo L. E., Gasparotto D., Quadrifoglio F., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H. Triple helix formation by oligopurine-oligopyrimidine DNA fragments. Electrophoretic and thermodynamic behavior. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):833–843. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergny J. L., Collier D., Rougée M., Montenay-Garestier T., Hélène C. Intercalation of ethidium bromide into a triple-stranded oligonucleotide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1521–1526. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergny J. L., Duval-Valentin G., Nguyen C. H., Perrouault L., Faucon B., Rougée M., Montenay-Garestier T., Bisagni E., Hélène C. Triple helix-specific ligands. Science. 1992 Jun 19;256(5064):1681–1684. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5064.1681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergny J. L., Sun J. S., Rougée M., Montenay-Garestier T., Barcelo F., Chomilier J., Hélène C. Sequence specificity in triple-helix formation: experimental and theoretical studies of the effect of mismatches on triplex stability. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9791–9798. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peticolas W. L., Wang Y., Thomas G. A. Some rules for predicting the base-sequence dependence of DNA conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2579–2583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plum G. E., Breslauer K. J. Thermodynamics of an intramolecular DNA triple helix: a calorimetric and spectroscopic study of the pH and salt dependence of thermally induced structural transitions. J Mol Biol. 1995 May 5;248(3):679–695. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plum G. E., Park Y. W., Singleton S. F., Dervan P. B., Breslauer K. J. Thermodynamic characterization of the stability and the melting behavior of a DNA triplex: a spectroscopic and calorimetric study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9436–9440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plum G. E., Pilch D. S., Singleton S. F., Breslauer K. J. Nucleic acid hybridization: triplex stability and energetics. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1995;24:319–350. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.24.060195.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal P., Feigon J. Triple-strand formation in the homopurine:homopyrimidine DNA oligonucleotides d(G-A)4 and d(T-C)4. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):637–640. doi: 10.1038/339637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. W., Crothers D. M. Specificity and stringency in DNA triplex formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9397–9401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. W., Crothers D. M. Stability and properties of double and triple helices: dramatic effects of RNA or DNA backbone composition. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1463–1466. doi: 10.1126/science.1279808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougée M., Faucon B., Mergny J. L., Barcelo F., Giovannangeli C., Garestier T., Hélène C. Kinetics and thermodynamics of triple-helix formation: effects of ionic strength and mismatches. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 29;31(38):9269–9278. doi: 10.1021/bi00153a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton S. F., Dervan P. B. Influence of pH on the equilibrium association constants for oligodeoxyribonucleotide-directed triple helix formation at single DNA sites. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 17;31(45):10995–11003. doi: 10.1021/bi00160a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. S., François J. C., Montenay-Garestier T., Saison-Behmoaras T., Roig V., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific intercalating agents: intercalation at specific sequences on duplex DNA via major groove recognition by oligonucleotide-intercalator conjugates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9198–9202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. S., Giovannangeli C., François J. C., Kurfurst R., Montenay-Garestier T., Asseline U., Saison-Behmoaras T., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Triple-helix formation by alpha oligodeoxynucleotides and alpha oligodeoxynucleotide-intercalator conjugates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6023–6027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov E. N., Sussman J. L. The pitch of chromatin DNA is reflected in its nucleotide sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3816–3820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung C. S., Harvey S. C. Base sequence, local helix structure, and macroscopic curvature of A-DNA and B-DNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3700–3709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Völker J., Botes D. P., Lindsey G. G., Klump H. H. Energetics of a stable intramolecular DNA triple helix formation. J Mol Biol. 1993 Apr 20;230(4):1278–1290. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xodo L. E., Manzini G., Quadrifoglio F. Spectroscopic and calorimetric investigation on the DNA triplex formed by d(CTCTTCTTTCTTTTCTTTCTTCTC) and d(GAGAAGAAAGA) at acidic pH. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3557–3564. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]