Abstract
The budding of enveloped viruses from cellular membranes is believed to be dependent on the specific interaction between transmembrane spike proteins and cytoplasmic core components of the virus. We found that the cytoplasmic domain of the E2 transmembrane spike glycoprotein of Semliki Forest virus contains two essential determinants which are absolutely needed for budding. The first constitutes a single tyrosine residue in the context of a direct pentapeptide repeat. The tyrosine could only partially be substituted for other residues with aromatic or bulky hydrophobic side chains, although these immediately reverted to the original genotype. The second determinant involves palmitylated cysteine residues flanking the tyrosine repeat motif. The function of these is probably to anchor the tail against the inner surface of the membrane so that the tyrosine-containing motif is properly presented to the nucleocapsid. This is the first example where a membrane virus employs a tyrosine signal for the selective incorporation of spike proteins into budding structures.
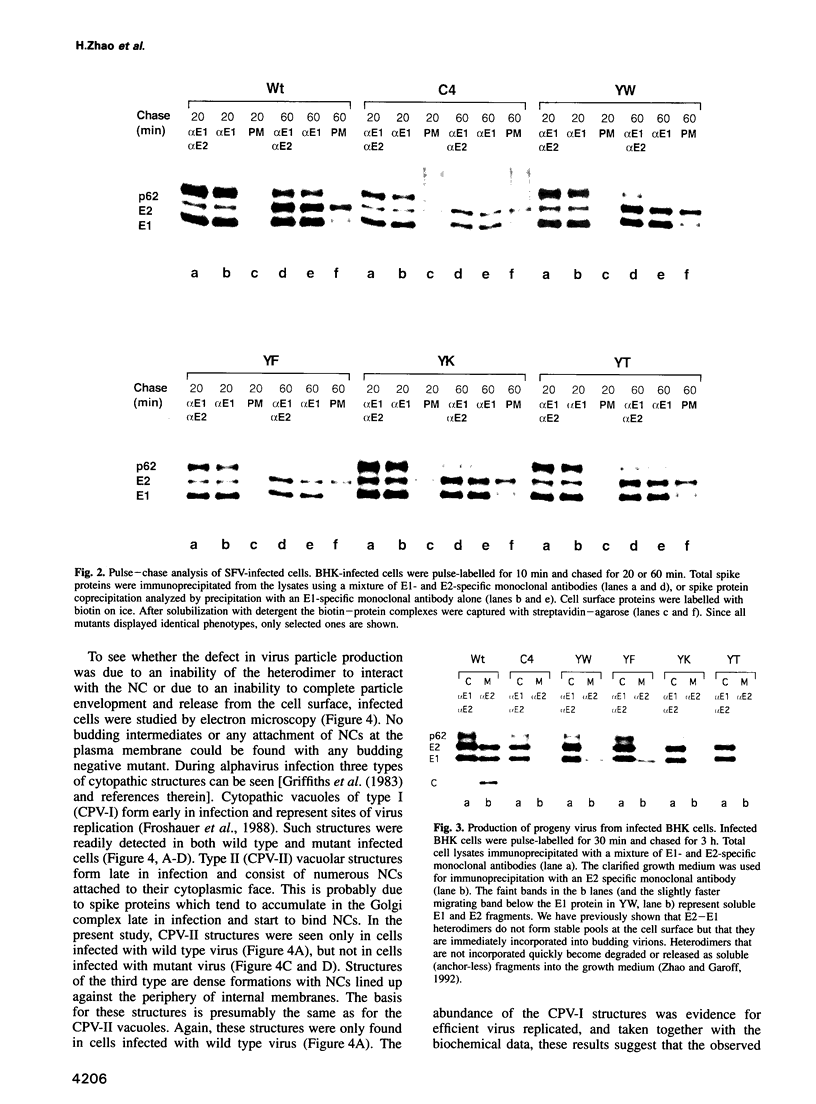
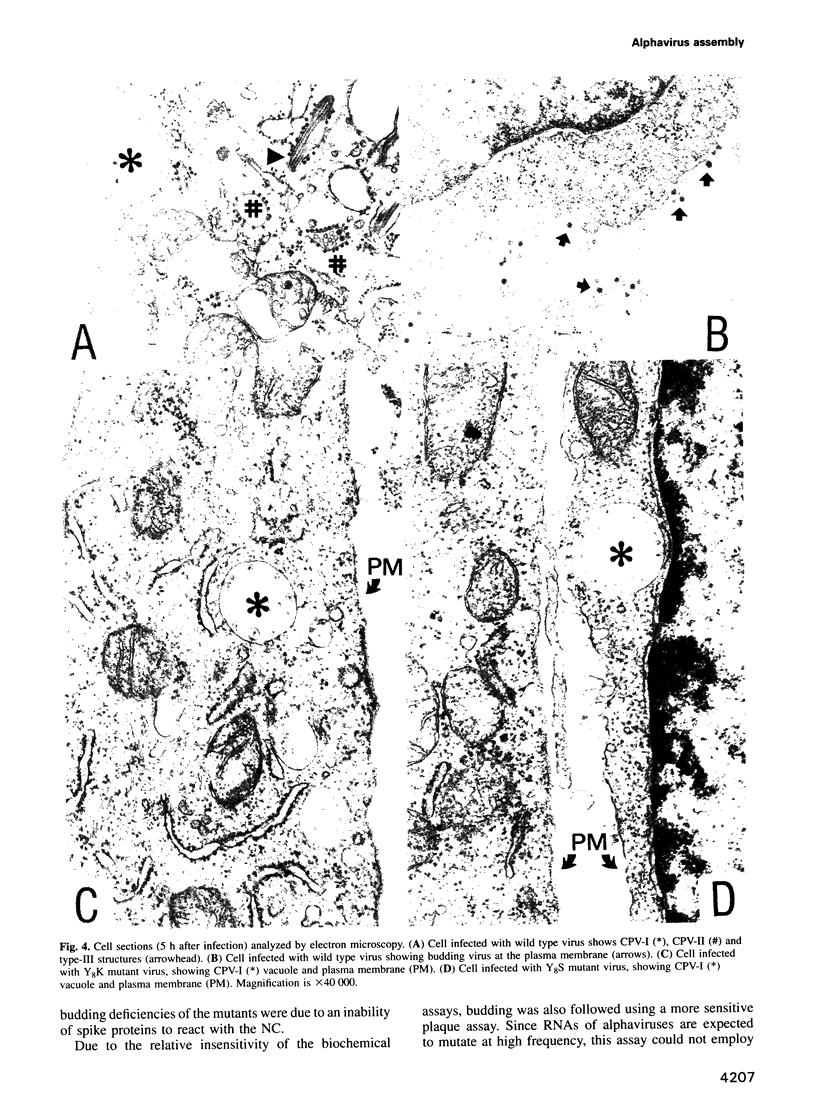
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barth B. U., Suomalainen M., Liljeström P., Garoff H. Alphavirus assembly and entry: role of the cytoplasmic tail of the E1 spike subunit. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7560–7564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7560-7564.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berglund P., Sjöberg M., Garoff H., Atkins G. J., Sheahan B. J., Liljeström P. Semliki Forest virus expression system: production of conditionally infectious recombinant particles. Biotechnology (N Y) 1993 Aug;11(8):916–920. doi: 10.1038/nbt0893-916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilsel P., Castrucci M. R., Kawaoka Y. Mutations in the cytoplasmic tail of influenza A virus neuraminidase affect incorporation into virions. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6762–6767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6762-6767.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boere W. A., Harmsen T., Vinjé J., Benaissa-Trouw B. J., Kraaijeveld C. A., Snippe H. Identification of distinct antigenic determinants on Semliki Forest virus by using monoclonal antibodies with different antiviral activities. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):575–582. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.575-582.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos K., Wraight C., Stanley K. K. TGN38 is maintained in the trans-Golgi network by a tyrosine-containing motif in the cytoplasmic domain. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2219–2228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05870.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer C. B., Roth M. G. A single amino acid change in the cytoplasmic domain alters the polarized delivery of influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):413–421. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruss V., Ganem D. The role of envelope proteins in hepatitis B virus assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1059–1063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J. E., Apodaca G., Mostov K. E. An autonomous signal for basolateral sorting in the cytoplasmic domain of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90139-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang G. J., Trent D. W. Nucleotide sequence of the genome region encoding the 26S mRNA of eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus and the deduced amino acid sequence of the viral structural proteins. J Gen Virol. 1987 Aug;68(Pt 8):2129–2142. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-8-2129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi H. K., Tong L., Minor W., Dumas P., Boege U., Rossmann M. G., Wengler G. Structure of Sindbis virus core protein reveals a chymotrypsin-like serine proteinase and the organization of the virion. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):37–43. doi: 10.1038/354037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier N. C., Knox K., Schlesinger M. J. Inhibition of influenza virus formation by a peptide that corresponds to sequences in the cytoplasmic domain of the hemagglutinin. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):769–772. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgarno L., Rice C. M., Strauss J. H. Ross River virus 26 s RNA: complete nucleotide sequence and deduced sequence of the encoded structural proteins. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):170–187. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90404-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dargemont C., Le Bivic A., Rothenberger S., Iacopetta B., Kühn L. C. The internalization signal and the phosphorylation site of transferrin receptor are distinct from the main basolateral sorting information. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1713–1721. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05816.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delchambre M., Gheysen D., Thines D., Thiriart C., Jacobs E., Verdin E., Horth M., Burny A., Bex F. The GAG precursor of simian immunodeficiency virus assembles into virus-like particles. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2653–2660. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08405.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekström M., Liljeström P., Garoff H. Membrane protein lateral interactions control Semliki Forest virus budding. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 1;13(5):1058–1064. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froshauer S., Kartenbeck J., Helenius A. Alphavirus RNA replicase is located on the cytoplasmic surface of endosomes and lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2075–2086. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. D. The T=4 envelope of Sindbis virus is organized by interactions with a complementary T=3 capsid. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):923–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90701-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaedigk-Nitschko K., Schlesinger M. J. Site-directed mutations in Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein's cytoplasmic domain and the 6K protein lead to similar defects in virus assembly and budding. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):206–214. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90133-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Frischauf A. M., Simons K., Lehrach H., Delius H. Nucleotide sequence of cdna coding for Semliki Forest virus membrane glycoproteins. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):236–241. doi: 10.1038/288236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Huylebroeck D., Robinson A., Tillman U., Liljeström P. The signal sequence of the p62 protein of Semliki Forest virus is involved in initiation but not in completing chain translocation. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):867–876. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheysen D., Jacobs E., de Foresta F., Thiriart C., Francotte M., Thines D., De Wilde M. Assembly and release of HIV-1 precursor Pr55gag virus-like particles from recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):103–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90873-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Quinn P., Warren G. Dissection of the Golgi complex. I. Monensin inhibits the transport of viral membrane proteins from medial to trans Golgi cisternae in baby hamster kidney cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):835–850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarnieri F. G., Arterburn L. M., Penno M. B., Cha Y., August J. T. The motif Tyr-X-X-hydrophobic residue mediates lysosomal membrane targeting of lysosome-associated membrane protein 1. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1941–1946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn C. S., Lustig S., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Western equine encephalitis virus is a recombinant virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5997–6001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Kartenbeck J. The effects of octylglucoside on the Semliki forest virus membrane. Evidence for a spike-protein--nucleocapsid interaction. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(2):613–618. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04609.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. S., Peters P. J., Yuan L. C., Bonifacino J. S. Localization of TGN38 to the trans-Golgi network: involvement of a cytoplasmic tyrosine-containing sequence. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1123–1135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker W., Harter C., Matter K., Mellman I. Basolateral sorting in MDCK cells requires a distinct cytoplasmic domain determinant. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):907–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90437-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova L., Schlesinger M. J. Site-directed mutations in the Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein identify palmitoylation sites and affect virus budding. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2546–2551. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2546-2551.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kail M., Hollinshead M., Ansorge W., Pepperkok R., Frank R., Griffiths G., Vaux D. The cytoplasmic domain of alphavirus E2 glycoprotein contains a short linear recognition signal required for viral budding. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2343–2351. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07773.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinney R. M., Johnson B. J., Brown V. L., Trent D. W. Nucleotide sequence of the 26 S mRNA of the virulent Trinidad donkey strain of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus and deduced sequence of the encoded structural proteins. Virology. 1986 Jul 30;152(2):400–413. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90142-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladinsky M. S., Howell K. E. The trans-Golgi network can be dissected structurally and functionally from the cisternae of the Golgi complex by brefeldin A. Eur J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;59(1):92–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson R. S., Strauss J. H., Strauss E. G. Complete sequence of the genomic RNA of O'nyong-nyong virus and its use in the construction of alphavirus phylogenetic trees. Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):110–123. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90191-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P., Garoff H. A new generation of animal cell expression vectors based on the Semliki Forest virus replicon. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Dec;9(12):1356–1361. doi: 10.1038/nbt1291-1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P., Garoff H. Internally located cleavable signal sequences direct the formation of Semliki Forest virus membrane proteins from a polyprotein precursor. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):147–154. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.147-154.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P., Lusa S., Huylebroeck D., Garoff H. In vitro mutagenesis of a full-length cDNA clone of Semliki Forest virus: the small 6,000-molecular-weight membrane protein modulates virus release. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4107–4113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4107-4113.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu N., Brown D. T. Transient translocation of the cytoplasmic (endo) domain of a type I membrane glycoprotein into cellular membranes. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(4):877–883. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.4.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez S., Yao J. S., Kuhn R. J., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Nucleocapsid-glycoprotein interactions required for assembly of alphaviruses. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1316–1323. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1316-1323.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusa S., Garoff H., Liljeström P. Fate of the 6K membrane protein of Semliki Forest virus during virus assembly. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):843–846. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90556-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter K., Hunziker W., Mellman I. Basolateral sorting of LDL receptor in MDCK cells: the cytoplasmic domain contains two tyrosine-dependent targeting determinants. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90551-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metsikkö K., Garoff H. Oligomers of the cytoplasmic domain of the p62/E2 membrane protein of Semliki Forest virus bind to the nucleocapsid in vitro. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4678–4683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4678-4683.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. J., Rose J. K. Cytoplasmic domain requirement for incorporation of a foreign envelope protein into vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):360–365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.360-365.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prill V., Lehmann L., von Figura K., Peters C. The cytoplasmic tail of lysosomal acid phosphatase contains overlapping but distinct signals for basolateral sorting and rapid internalization in polarized MDCK cells. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2181–2193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05866.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaves B., Horn M., Banting G. TGN38/41 recycles between the cell surface and the TGN: brefeldin A affects its rate of return to the TGN. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):93–105. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. S., Hui H. X., Hunter E. Preassembled capsids of type D retroviruses contain a signal sufficient for targeting specifically to the plasma membrane. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3844–3852. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3844-3852.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Strauss J. H. Nucleotide sequence of the 26S mRNA of Sindbis virus and deduced sequence of the encoded virus structural proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2062–2066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen M., Garoff H. Alphavirus spike-nucleocapsid interaction and network antibodies. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5106–5109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5106-5109.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen M., Liljeström P., Garoff H. Spike protein-nucleocapsid interactions drive the budding of alphaviruses. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4737–4747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4737-4747.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong L., Wengler G., Rossmann M. G. Refined structure of Sindbis virus core protein and comparison with other chymotrypsin-like serine proteinase structures. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):228–247. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S., Collawn J. F., Hopkins C. R. Signal-dependent membrane protein trafficking in the endocytic pathway. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:129–161. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. J., Helenius A., Mellman I. Spike--nucleocapsid interaction in Semliki Forest virus reconstructed using network antibodies. Nature. 1988 Nov 3;336(6194):36–42. doi: 10.1038/336036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlberg J. M., Boere W. A., Garoff H. The heterodimeric association between the membrane proteins of Semliki Forest virus changes its sensitivity to low pH during virus maturation. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):4991–4997. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.4991-4997.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitt M. A., Chong L., Rose J. K. Glycoprotein cytoplasmic domain sequences required for rescue of a vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein mutant. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3569–3578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3569-3578.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokode M., Pathak R. K., Hammer R. E., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G. Cytoplasmic sequence required for basolateral targeting of LDL receptor in livers of transgenic mice. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):39–46. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao H., Garoff H. Role of cell surface spikes in alphavirus budding. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7089–7095. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7089-7095.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziemiecki A., Garofff H. Subunit composition of the membrane glycoprotein complex of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jul 5;122(3):259–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90189-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Curtis I., Simons K. Dissection of Semliki Forest virus glycoprotein delivery from the trans-Golgi network to the cell surface in permeabilized BHK cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8052–8056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bonsdorff C. H., Harrison S. C. Hexagonal glycoprotein arrays from Sindbis virus membranes. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):578–583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.578-583.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]