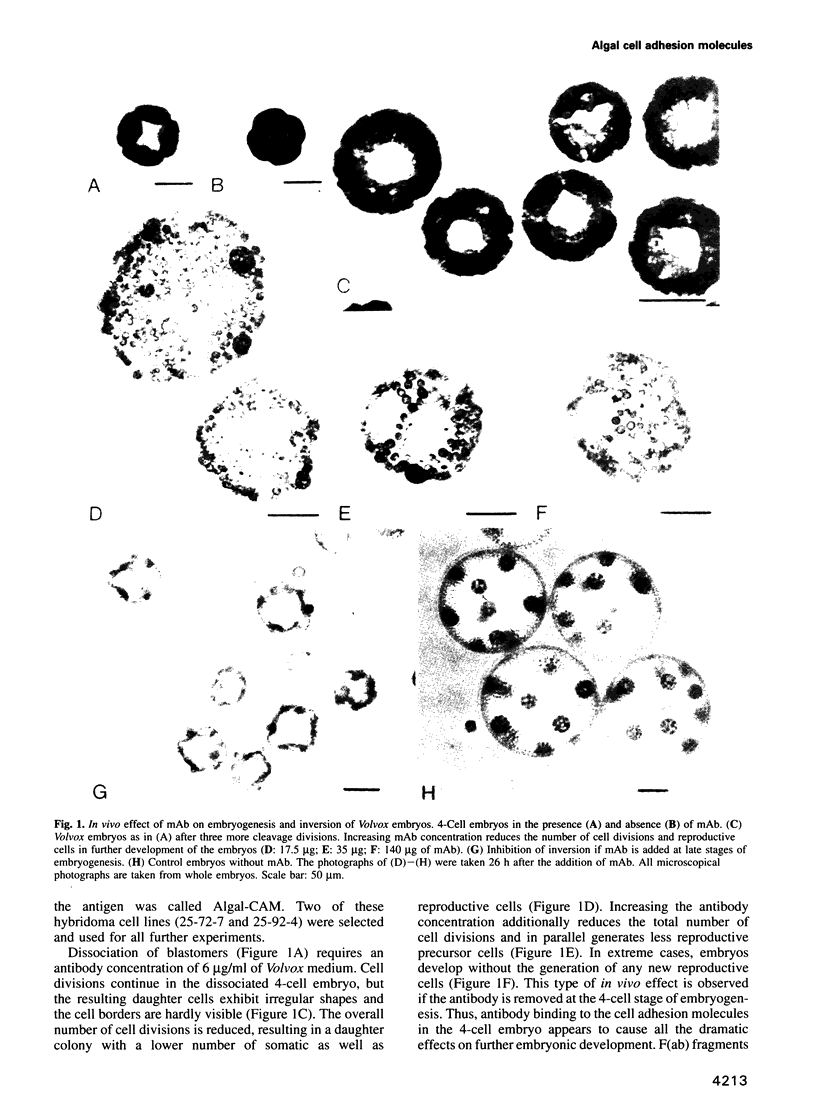
Abstract
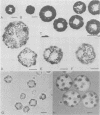
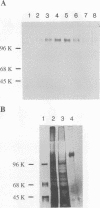
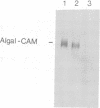
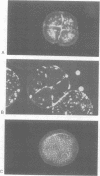
Proof that plants possess homologs of animal adhesion proteins is lacking. In this paper we describe the generation of monoclonal antibodies that interfere with cell-cell contacts in the 4-cell embryo of the multicellular alga Volvox carteri, resulting in a hole between the cells. The number of following cell divisions is reduced and the cell division pattern is altered drastically. Antibodies given at a later stage of embryogenesis specifically inhibit inversion of the embryo, a morphogenetic movement that turns the embryo inside out. Immunofluorescence microscopy localizes the antigen (Algal-CAM) at cell contact sites of the developing embryo. Algal-CAM is a protein with a three-domain structure: an N-terminal extensin-like domain characteristic for plant cell walls and two repeats with homology to fasciclin I, a cell adhesion molecule involved in the neuronal development of Drosophila. Alternatively spliced variants of Algal-CAM mRNA were detected that are produced under developmental control. Thus, Algal-CAM is the first plant homolog of animal adhesion proteins.
Full text
PDF


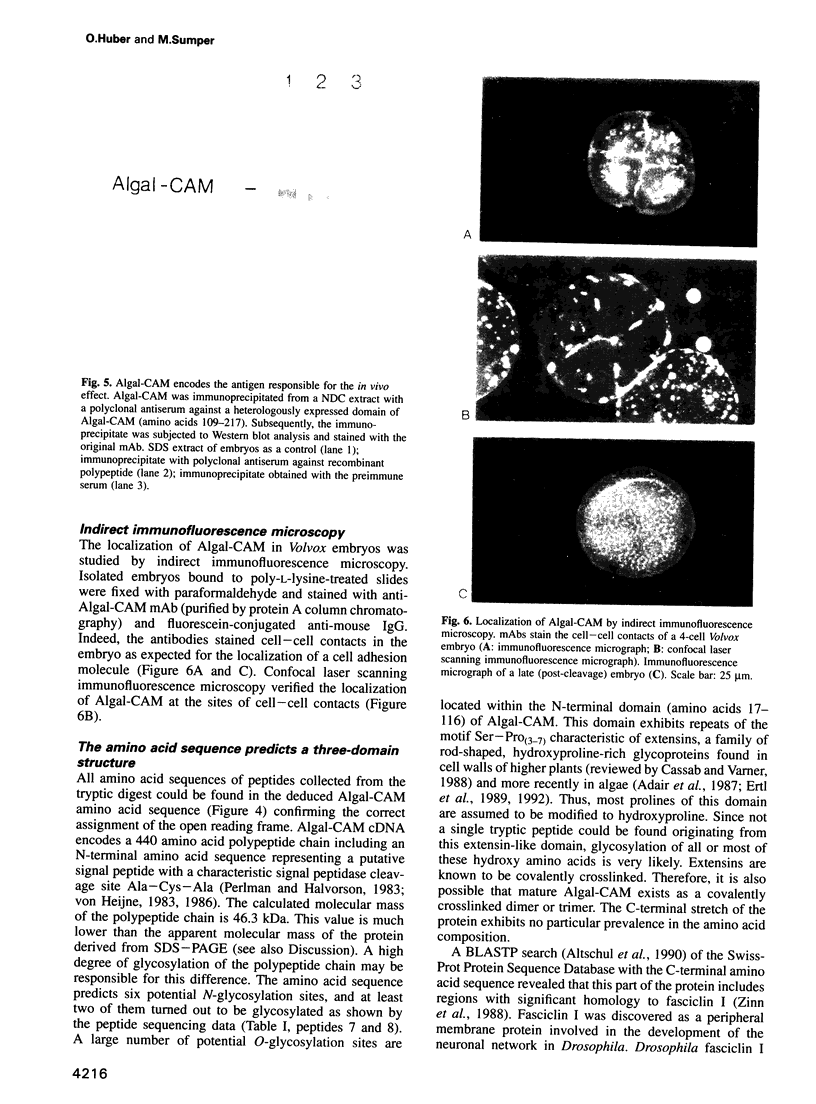






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adair W. S., Steinmetz S. A., Mattson D. M., Goodenough U. W., Heuser J. E. Nucleated assembly of Chlamydomonas and Volvox cell walls. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2373–2382. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. G., Cornish E. C., Clarke A. E. Specific expression of an extensin-like gene in the style of Nicotiana alata. Plant Cell. 1992 Sep;4(9):1053–1062. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.9.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Crossin K. L. Cell adhesion molecules: implications for a molecular histology. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:155–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Morphoregulatory molecules. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3533–3543. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P., Vestweber D., Kemler R. Cell-matrix interactions and cell adhesion during development. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:27–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkins T., Hortsch M., Bieber A. J., Snow P. M., Goodman C. S. Drosophila fasciclin I is a novel homophilic adhesion molecule that along with fasciclin III can mediate cell sorting. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1825–1832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkins T., Zinn K., McAllister L., Hoffmann F. M., Goodman C. S. Genetic analysis of a Drosophila neural cell adhesion molecule: interaction of fasciclin I and Abelson tyrosine kinase mutations. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):565–575. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90660-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englund P. T. The structure and biosynthesis of glycosyl phosphatidylinositol protein anchors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:121–138. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertl H., Hallmann A., Wenzl S., Sumper M. A novel extensin that may organize extracellular matrix biogenesis in Volvox carteri. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2055–2062. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05263.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertl H., Mengele R., Wenzl S., Engel J., Sumper M. The extracellular matrix of Volvox carteri: molecular structure of the cellular compartment. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3493–3501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry S. C. Isodityrosine, a new cross-linking amino acid from plant cell-wall glycoprotein. Biochem J. 1982 May 15;204(2):449–455. doi: 10.1042/bj2040449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B., Ayalon O. Cadherins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:307–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. H., Pezzotti M., Seurinck J., Mariani C. Developmental expression of tobacco pistil-specific genes encoding novel extensin-like proteins. Plant Cell. 1992 Sep;4(9):1041–1051. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.9.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. J., Kirk D. L. Cleavage patterns, cell lineages, and development of a cytoplasmic bridge system in Volvox embryos. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):743–755. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. J., Viamontes G. I., Kirk D. L. Mechanism of formation, ultrastructure, and function of the cytoplasmic bridge system during morphogenesis in Volvox. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):756–769. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallmann A., Sumper M. An inducible arylsulfatase of Volvox carteri with properties suitable for a reporter-gene system. Purification, characterization and molecular cloning. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Apr 1;221(1):143–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortsch M., Goodman C. S. Drosophila fasciclin I, a neural cell adhesion molecule, has a phosphatidylinositol lipid membrane anchor that is developmentally regulated. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15104–15109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk D. L., Birchem R., King N. The extracellular matrix of Volvox: a comparative study and proposed system of nomenclature. J Cell Sci. 1986 Feb;80:207–231. doi: 10.1242/jcs.80.1.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk D. L., Harper J. F. Genetic, biochemical, and molecular approaches to Volvox development and evolution. Int Rev Cytol. 1986;99:217–293. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61428-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk M. M., Kirk D. L. Translational regulation of protein synthesis, in response to light, at a critical stage of Volvox development. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):419–428. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister L., Rehm E. J., Goodman G. S., Zinn K. Alternative splicing of micro-exons creates multiple forms of the insect cell adhesion molecule fasciclin I. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):895–905. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-00895.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochiai H., Schwarz H., Merkl R., Wagle G., Gerisch G. Stage-specific antigens reacting with monoclonal antibodies against contact site A, a cell-surface glycoprotein of Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell Differ. 1982 Jan;11(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(82)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiedlmeier B., Schmitt R., Müller W., Kirk M. M., Gruber H., Mages W., Kirk D. L. Nuclear transformation of Volvox carteri. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5080–5084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter A. M., Bell J. N., Cramer C. L., Bailey J. A., Varner J. E., Lamb C. J. Accumulation of hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein mRNAs in response to fungal elicitor and infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6551–6555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skonier J., Neubauer M., Madisen L., Bennett K., Plowman G. D., Purchio A. F. cDNA cloning and sequence analysis of beta ig-h3, a novel gene induced in a human adenocarcinoma cell line after treatment with transforming growth factor-beta. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;11(7):511–522. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R. C. Control of differentiation in Volvox. Symp Soc Dev Biol. 1970;29:59–100. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-395534-0.50009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R. C., Jaenicke L. Purification and characterization of the hormone initiating sexual morphogenesis in Volvox carteri f. nagariensis Iyengar. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1050–1054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumper M. Control of differentiation in volvox carteri: a model explaining pattern formation during embryogenesis. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80505-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi M. Cadherins: a molecular family important in selective cell-cell adhesion. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:237–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi M. The cadherins: cell-cell adhesion molecules controlling animal morphogenesis. Development. 1988 Apr;102(4):639–655. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.4.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita S., Kikuno R., Tezuka K., Amann E. Osteoblast-specific factor 2: cloning of a putative bone adhesion protein with homology with the insect protein fasciclin I. Biochem J. 1993 Aug 15;294(Pt 1):271–278. doi: 10.1042/bj2940271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viamontes G. I., Fochtmann L. J., Kirk D. L. Morphogenesis in Volvox: analysis of critical variables. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viamontes G. I., Kirk D. L. Cell shape changes and the mechanism of inversion in Volvox. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):719–730. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzl S., Sumper M. A novel glycosphingolipid that may participate in embryo inversion in Volvox carteri. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):633–639. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90889-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. P., Goodenough U. W. Molecular characterization of a zygote wall protein: an extensin-like molecule in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell. 1989 Sep;1(9):901–911. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.9.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., McAllister L., Goodman C. S. Sequence analysis and neuronal expression of fasciclin I in grasshopper and Drosophila. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90574-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]