Abstract
Integration host factor (IHF) is required in lambda site-specific recombination to deform the DNA substrates into conformations active for recombination. HU, a homolog of IHF, can also deform DNA but binds without any apparent sequence specificity. We demonstrate that HU can replace IHF by cooperating with the recombinase protein, integrase, to generate a stable and specific complex with electrophoretic mobility and biochemical activity very close to the complex formed by IHF and integrase. The eukaryotic HMG1 and HMG2 proteins differ entirely in structure from HU but they also bind DNA non-specifically and induce or stabilize deformed DNA. We show that the eukaryotic HMG1 and HMG2 proteins cooperate with integrase at least as well as does HU to make a defined structure. We also find that the eukaryotic core histone dimer H2A-H2B can replace IHF, suggesting that the histone dimer is functional outside the context of a nucleosome. HU and the HMG proteins not only contribute to the formation of stable complexes, but they can at least partially replace IHF for the integrative and excisive recombination reactions. These results, together with our analysis of nucleoprotein complexes made with damaged recombination sites, lead us to conclude that the cooperation between HU and integrase does not depend on protein-protein contacts. Rather, cooperation is manifested through building of higher order structures and depends on the capacity of the non-specific DNA binding proteins to bend DNA. While all these non-specific binding proteins appear to fulfil the same bending function, they do so with different efficiencies. This probably reflects subtle structural differences between the assembled complexes.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball C. A., Johnson R. C. Efficient excision of phage lambda from the Escherichia coli chromosome requires the Fis protein. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4027–4031. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4027-4031.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better M., Wickner S., Auerbach J., Echols H. Role of the Xis protein of bacteriophage lambda in a specific reactive complex at the attR prophage attachment site. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90506-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E., Beltrame M., Paonessa G. Specific recognition of cruciform DNA by nuclear protein HMG1. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2922595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefoy E., Rouvière-Yaniv J. HU, the major histone-like protein of E. coli, modulates the binding of IHF to oriC. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4489–4496. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05550.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boubrik F., Bonnefoy E., Rouvière-Yaniv J. HU and IHF: similarities and differences. In Escherichia coli, the lack of HU is not compensated for by IHF. Res Microbiol. 1991 Feb-Apr;142(2-3):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90036-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn S. L., Pil P. M., Essigmann J. M., Housman D. E., Lippard S. J. Isolation and characterization of human cDNA clones encoding a high mobility group box protein that recognizes structural distortions to DNA caused by binding of the anticancer agent cisplatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2307–2311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman W., Thompson J. F., Vargas L., Landy A. Control of directionality in lambda site specific recombination. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):906–911. doi: 10.1126/science.2932798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Sequence and spacing requirements of a retrovirus integration site. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90378-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditto M. D., Roberts D., Weisberg R. A. Growth phase variation of integration host factor level in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jun;176(12):3738–3748. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.12.3738-3748.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Rouviere-Yaniv J. Histonelike proteins of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):301–319. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.301-319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I. Integration host factor: a protein for all reasons. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. F., Nash H. A. Role of Escherichia coli IHF protein in lambda site-specific recombination. A mutational analysis of binding sites. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 20;191(2):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90255-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Cox J., Grosschedl R. The HMG domain of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 bends DNA and facilitates assembly of functional nucleoprotein structures. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90129-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nash H. A. Functional replacement of a protein-induced bend in a DNA recombination site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):251–254. doi: 10.1038/341251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nicholson S. C., Nash H. A. Deformation of DNA during site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda: replacement of IHF protein by HU protein or sequence-directed bends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11910–11914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granston A. E., Nash H. A. Characterization of a set of integration host factor mutants deficient for DNA binding. J Mol Biol. 1993 Nov 5;234(1):45–59. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
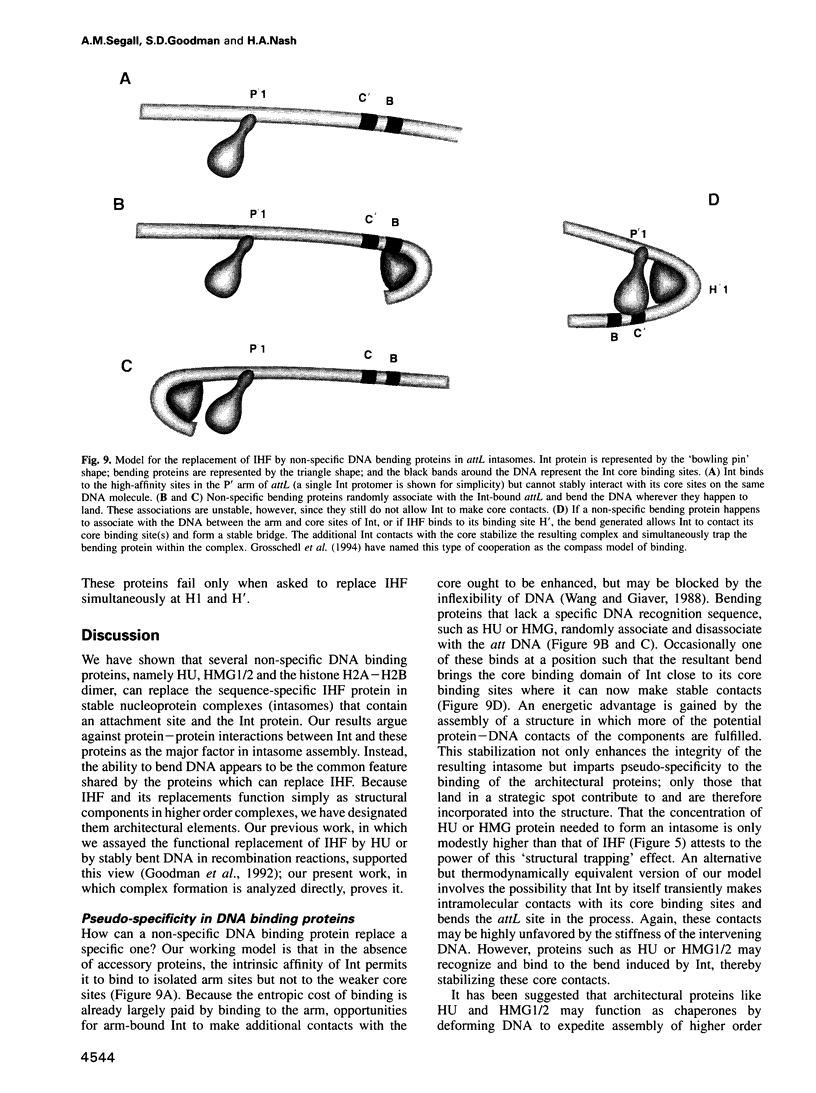
- Grosschedl R., Giese K., Pagel J. HMG domain proteins: architectural elements in the assembly of nucleoprotein structures. Trends Genet. 1994 Mar;10(3):94–100. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han Y. W., Gumport R. I., Gardner J. F. Mapping the functional domains of bacteriophage lambda integrase protein. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 21;235(3):908–925. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges-Garcia Y., Hagerman P. J., Pettijohn D. E. DNA ring closure mediated by protein HU. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14621–14623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang D. S., Kornberg A. Opening of the replication origin of Escherichia coli by DnaA protein with protein HU or IHF. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23083–23086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano Y., Imamoto F. Requirement of integration host factor (IHF) for growth of Escherichia coli deficient in HU protein. Gene. 1990 Apr 30;89(1):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90216-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerrigan L. A., Kadonaga J. T. Periodic binding of individual core histones to DNA: inadvertent purification of the core histone H2B as a putative enhancer-binding factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6673–6680. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Landy A. Lambda Int protein bridges between higher order complexes at two distant chromosomal loci attL and attR. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):198–203. doi: 10.1126/science.1533056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Moitoso de Vargas L., Nunes-Düby S. E., Landy A. Mapping of a higher order protein-DNA complex: two kinds of long-range interactions in lambda attL. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landsman D., Bustin M. A signature for the HMG-1 box DNA-binding proteins. Bioessays. 1993 Aug;15(8):539–546. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie B. D., Chaconas G. Immunoelectron microscopic analysis of the A, B, and HU protein content of bacteriophage Mu transpososomes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1623–1627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie B. D., Chaconas G. Site-specific HU binding in the Mu transpososome: conversion of a sequence-independent DNA-binding protein into a chemical nuclease. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2510–2519. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. DNA--protein interactions. HMG has DNA wrapped up. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):282–283. doi: 10.1038/357282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megraw T. L., Chae C. B. Functional complementarity between the HMG1-like yeast mitochondrial histone HM and the bacterial histone-like protein HU. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12758–12763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson I., Gottesman M., Oppenheim A. B. HU and integration host factor function as auxiliary proteins in cleavage of phage lambda cohesive ends by terminase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1670–1676. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1670-1676.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mensa-Wilmot K., Carroll K., McMacken R. Transcriptional activation of bacteriophage lambda DNA replication in vitro: regulatory role of histone-like protein HU of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2393–2402. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08369.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moitoso de Vargas L., Kim S., Landy A. DNA looping generated by DNA bending protein IHF and the two domains of lambda integrase. Science. 1989 Jun 23;244(4911):1457–1461. doi: 10.1126/science.2544029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morisato D., Kleckner N. Tn10 transposition and circle formation in vitro. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Bending and supercoiling of DNA at the attachment site of bacteriophage lambda. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jun;15(6):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Robertson C. A. Heteroduplex substrates for bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination: cleavage and strand transfer products. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3523–3533. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numrych T. E., Gumport R. I., Gardner J. F. A comparison of the effects of single-base and triple-base changes in the integrase arm-type binding sites on the site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3953–3959. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogura T., Niki H., Kano Y., Imamoto F., Hiraga S. Maintenance of plasmids in HU and IHF mutants of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jan;220(2):197–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00260482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paull T. T., Haykinson M. J., Johnson R. C. The nonspecific DNA-binding and -bending proteins HMG1 and HMG2 promote the assembly of complex nucleoprotein structures. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1521–1534. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pil P. M., Chow C. S., Lippard S. J. High-mobility-group 1 protein mediates DNA bending as determined by ring closures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9465–9469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pil P. M., Lippard S. J. Specific binding of chromosomal protein HMG1 to DNA damaged by the anticancer drug cisplatin. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):234–237. doi: 10.1126/science.1566071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontiggia A., Negri A., Beltrame M., Bianchi M. E. Protein HU binds specifically to kinked DNA. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Feb;7(3):343–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read C. M., Cary P. D., Crane-Robinson C., Driscoll P. C., Norman D. G. Solution structure of a DNA-binding domain from HMG1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 25;21(15):3427–3436. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.15.3427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Abcarian P., Nash H. A. Synapsis of attachment sites during lambda integrative recombination involves capture of a naked DNA by a protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90526-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Abcarian P., Nash H. A. The interaction of recombination proteins with supercoiled DNA: defining the role of supercoiling in lambda integrative recombination. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1011–1021. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90700-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A. Bacteriophage lambda int protein recognizes two classes of sequence in the phage att site: characterization of arm-type sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7724–7728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A. Patterns of lambda Int recognition in the regions of strand exchange. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90355-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid M. B. More than just "histone-like" proteins. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):451–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90438-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall A. M., Nash H. A. Synaptic intermediates in bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination: integrase can align pairs of attachment sites. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4567–4576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06145.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarstad K., Baker T. A., Kornberg A. Strand separation required for initiation of replication at the chromosomal origin of E.coli is facilitated by a distant RNA--DNA hybrid. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2341–2348. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surette M. G., Chaconas G. A protein factor which reduces the negative supercoiling requirement in the Mu DNA strand transfer reaction is Escherichia coli integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):3028–3034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos D., Maniatis T. The high mobility group protein HMG I(Y) is required for NF-kappa B-dependent virus induction of the human IFN-beta gene. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90554-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Moitoso de Vargas L., Koch C., Kahmann R., Landy A. Cellular factors couple recombination with growth phase: characterization of a new component in the lambda site-specific recombination pathway. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90516-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Ner S. S., Churchill M. E. DNA chaperones: a solution to a persistence problem? Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):167–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tupper A. E., Owen-Hughes T. A., Ussery D. W., Santos D. S., Ferguson D. J., Sidebotham J. M., Hinton J. C., Higgins C. F. The chromatin-associated protein H-NS alters DNA topology in vitro. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):258–268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada M., Kano Y., Ogawa T., Okazaki T., Imamoto F. Construction and characterization of the deletion mutant of hupA and hupB genes in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 5;204(3):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90357-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Giaever G. N. Action at a distance along a DNA. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):300–304. doi: 10.1126/science.3281259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q., Calvo J. M. Lrp, a major regulatory protein in Escherichia coli, bends DNA and can organize the assembly of a higher-order nucleoprotein structure. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2495–2501. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05904.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir H. M., Kraulis P. J., Hill C. S., Raine A. R., Laue E. D., Thomas J. O. Structure of the HMG box motif in the B-domain of HMG1. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1311–1319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Nash H. A. The interaction of E. coli IHF protein with its specific binding sites. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):869–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90801-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Clevers H. Sequence-specific interaction of the HMG box proteins TCF-1 and SRY occurs within the minor groove of a Watson-Crick double helix. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3039–3044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]