Abstract
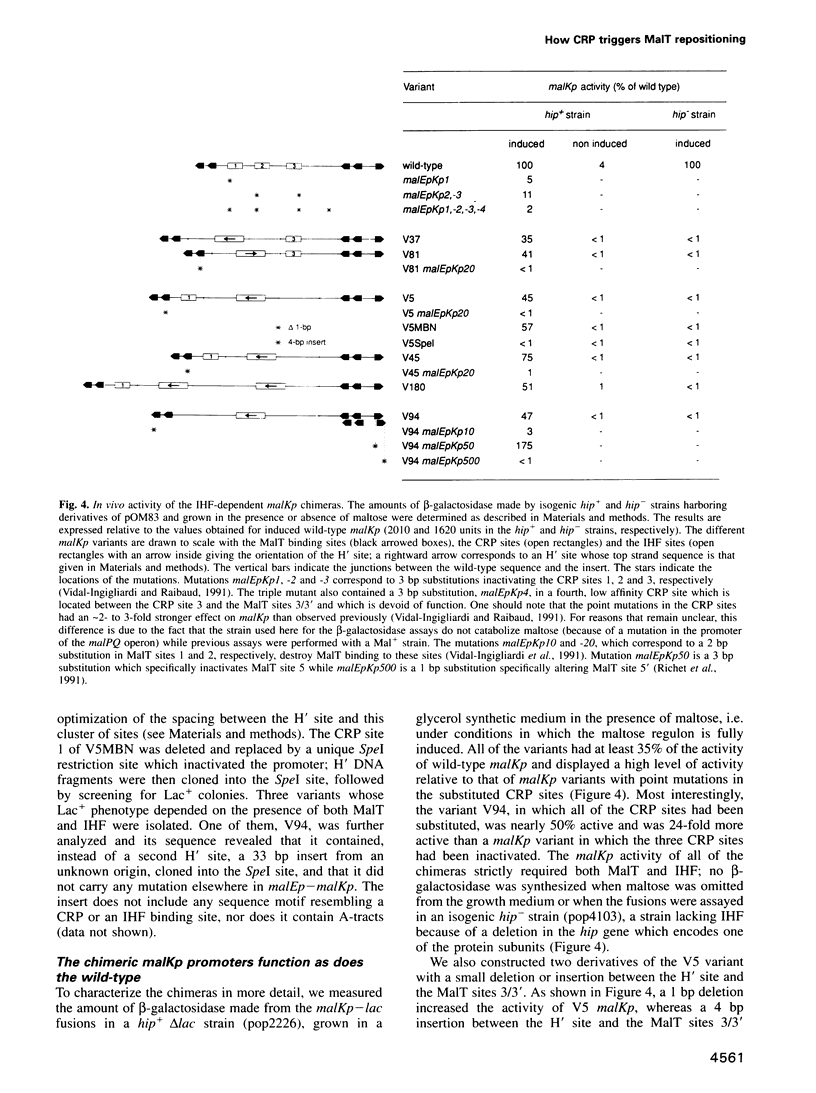
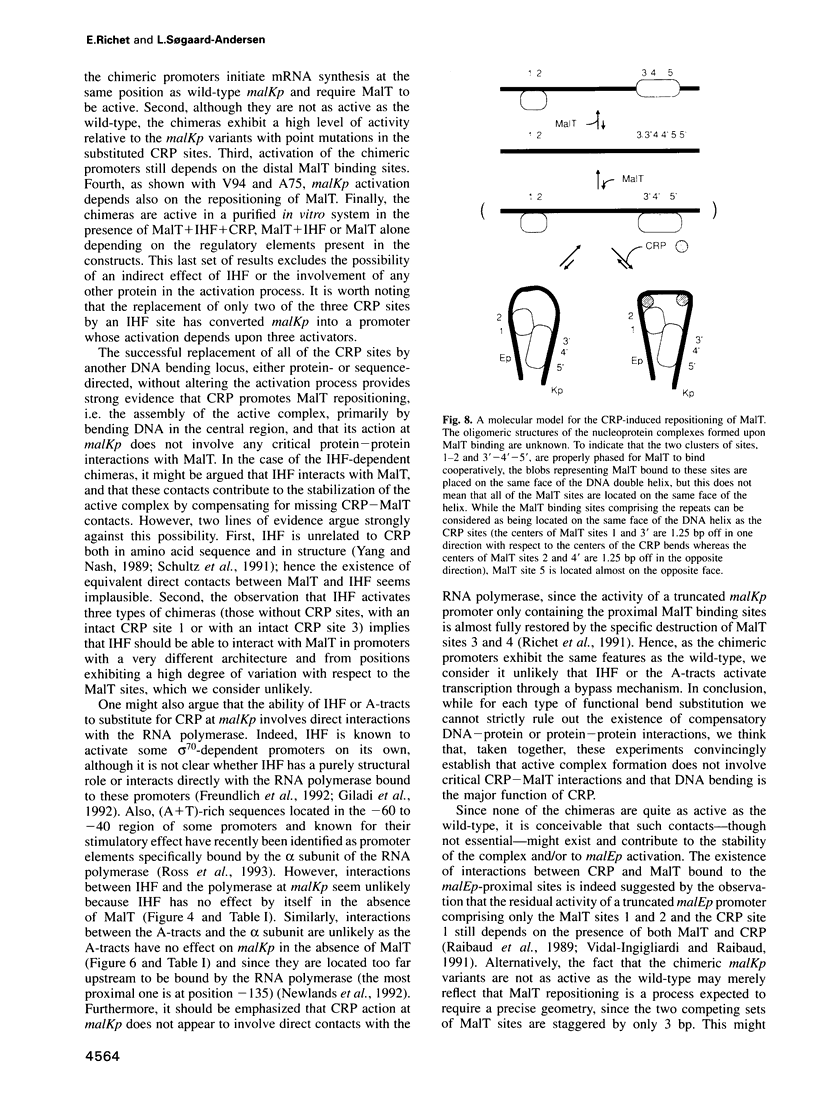
Activation of transcription initiation at the Escherichia coli malKp promoter requires the repositioning of MalT, the primary activator, from a set of non-productive sites to a set of productive sites, which is staggered by 3 bp. Occupation of the latter relies on the formation of a higher order structure involving distal MalT sites and the binding of CRP (cAMP receptor protein) to three sites located in the intervening region. We show here that one can successfully replace all of the CRP sites by the binding site of another DNA-bending protein, integration host factor, or by a sequence-directed bend without altering the process of malKp activation. This observation indicates that CRP action at malKp does not involve critical interactions with MalT and that CRP promotes MalT repositioning primarily through DNA bending. This structural role of CRP differs markedly from its role in the activation of the lac promoter.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell A., Gaston K., Williams R., Chapman K., Kolb A., Buc H., Minchin S., Williams J., Busby S. Mutations that alter the ability of the Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein to activate transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7243–7250. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Drak J. Global features of DNA structure by comparative gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1992;212:46–71. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)12005-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debarbouille M., Cossart P., Raibaud O. A DNA sequence containing the control sites for gene malT and for the malPQ operon. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(1):88–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00333795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H. Transcription activation at Class I CAP-dependent promoters. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):797–802. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenlauer A. C., Reznikoff W. S. Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein mutants defective in positive control of lac operon transcription. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5024–5029. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5024-5029.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsman K., Sondén B., Göransson M., Uhlin B. E. Antirepression function in Escherichia coli for the cAMP-cAMP receptor protein transcriptional activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9880–9884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich M., Ramani N., Mathew E., Sirko A., Tsui P. The role of integration host factor in gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2557–2563. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I. Integration host factor: a protein for all reasons. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. Synthetic DNA bending sequences increase the rate of in vitro transcription initiation at the Escherichia coli lac promoter. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):217–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90563-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giladi H., Igarashi K., Ishihama A., Oppenheim A. B. Stimulation of the phage lambda pL promoter by integration host factor requires the carboxy terminus of the alpha-subunit of RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):985–990. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90514-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nash H. A. Functional replacement of a protein-induced bend in a DNA recombination site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):251–254. doi: 10.1038/341251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover T. R., Santero E., Porter S., Kustu S. The integration host factor stimulates interaction of RNA polymerase with NIFA, the transcriptional activator for nitrogen fixation operons. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90284-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi A., Flamm E., Weisberg R. A. An Escherichia coli mutant unable to support site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90207-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Zwieb C., Wu C., Adhya S. Bending of DNA by gene-regulatory proteins: construction and use of a DNA bending vector. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Busby S., Buc H., Garges S., Adhya S. Transcriptional regulation by cAMP and its receptor protein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:749–795. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobell R. B., Schleif R. F. AraC-DNA looping: orientation and distance-dependent loop breaking by the cyclic AMP receptor protein. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90872-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Bending and supercoiling of DNA at the attachment site of bacteriophage lambda. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jun;15(6):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlands J. T., Josaitis C. A., Ross W., Gourse R. L. Both fis-dependent and factor-independent upstream activation of the rrnB P1 promoter are face of the helix dependent. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):719–726. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Chandler M., Galas D. J. Escherichia coli integration host factor bends the DNA at the ends of IS1 and in an insertion hotspot with multiple IHF binding sites. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2479–2487. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02529.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Martín J., Espinosa M. Protein-induced bending as a transcriptional switch. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):805–807. doi: 10.1126/science.8387228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Martín J., Rojo F., de Lorenzo V. Promoters responsive to DNA bending: a common theme in prokaryotic gene expression. Microbiol Rev. 1994 Jun;58(2):268–290. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.2.268-290.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Vidal-Ingigliardi D., Richet E. A complex nucleoprotein structure involved in activation of transcription of two divergent Escherichia coli promoters. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 5;205(3):471–485. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Raibaud O. MalT, the regulatory protein of the Escherichia coli maltose system, is an ATP-dependent transcriptional activator. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):981–987. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03461.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Raibaud O. Supercoiling is essential for the formation and stability of the initiation complex at the divergent malEp and malKp promoters. J Mol Biol. 1991 Apr 5;218(3):529–542. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90699-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Vidal-Ingigliardi D., Raibaud O. A new mechanism for coactivation of transcription initiation: repositioning of an activator triggered by the binding of a second activator. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1185–1195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90041-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson C. A., Nash H. A. Bending of the bacteriophage lambda attachment site by Escherichia coli integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3554–3557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Gosink K. K., Salomon J., Igarashi K., Zou C., Ishihama A., Severinov K., Gourse R. L. A third recognition element in bacterial promoters: DNA binding by the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1407–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.8248780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1001–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1653449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires C., Krainer A., Barry G., Shen W. F., Squires C. L. Nucleotide sequence at the end of the gene for the RNA polymerase beta' subunit (rpoC). Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6827–6840. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Søgaard-Andersen L., Mironov A. S., Pedersen H., Sukhodelets V. V., Valentin-Hansen P. Single amino acid substitutions in the cAMP receptor protein specifically abolish regulation by the CytR repressor in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4921–4925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin-Hansen P., Albrechtsen B., Løve Larsen J. E. DNA-protein recognition: demonstration of three genetically separated operator elements that are required for repression of the Escherichia coli deoCABD promoters by the DeoR repressor. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):2015–2021. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal-Ingigliardi D., Raibaud O. A convenient technique to compare the efficiency of promoters in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 26;13(16):5919–5926. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.16.5919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal-Ingigliardi D., Raibaud O. Three adjacent binding sites for cAMP receptor protein are involved in the activation of the divergent malEp-malKp promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):229–233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal-Ingigliardi D., Richet E., Raibaud O. Two MalT binding sites in direct repeat. A structural motif involved in the activation of all the promoters of the maltose regulons in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 20;218(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90715-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Nash H. A. The interaction of E. coli IHF protein with its specific binding sites. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):869–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90801-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y., Zhang X., Ebright R. H. Identification of the activating region of catabolite gene activator protein (CAP): isolation and characterization of mutants of CAP specifically defective in transcription activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6081–6085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. Comparative gel electrophoresis measurement of the DNA bend angle induced by the catabolite activator protein. Biopolymers. 1990 Jan;29(1):29–38. doi: 10.1002/bip.360290106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]