Abstract
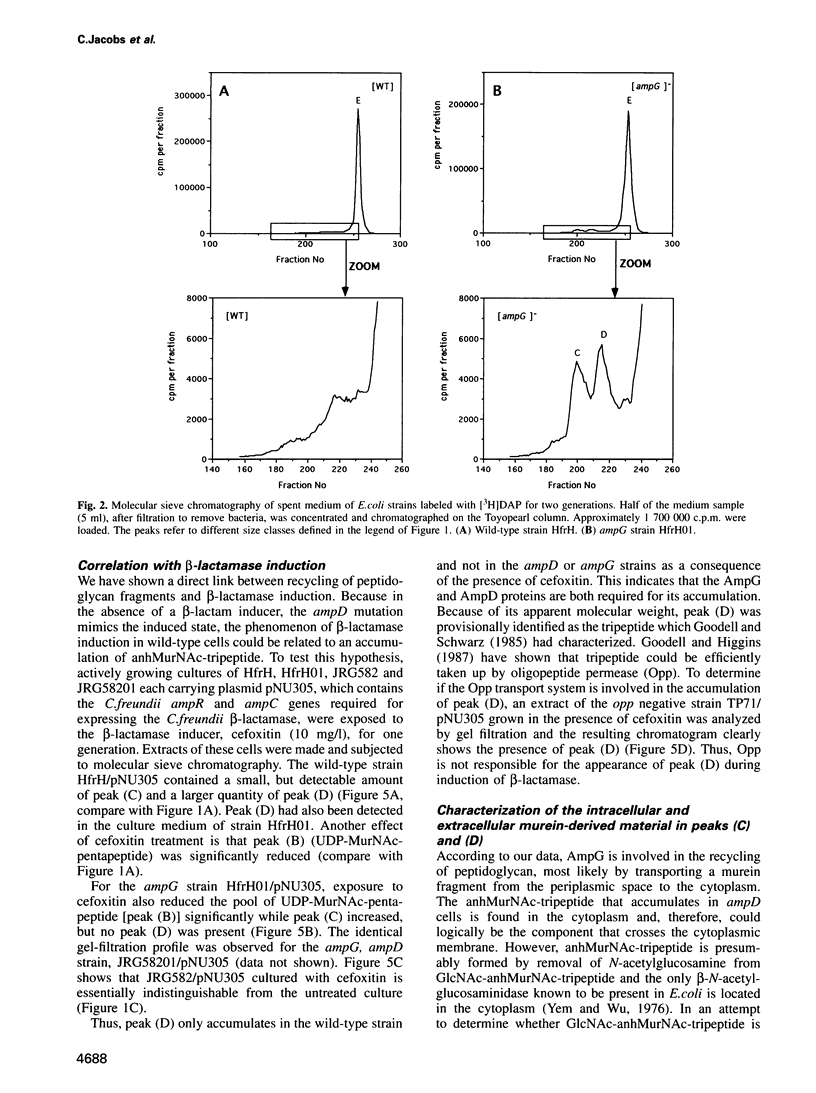
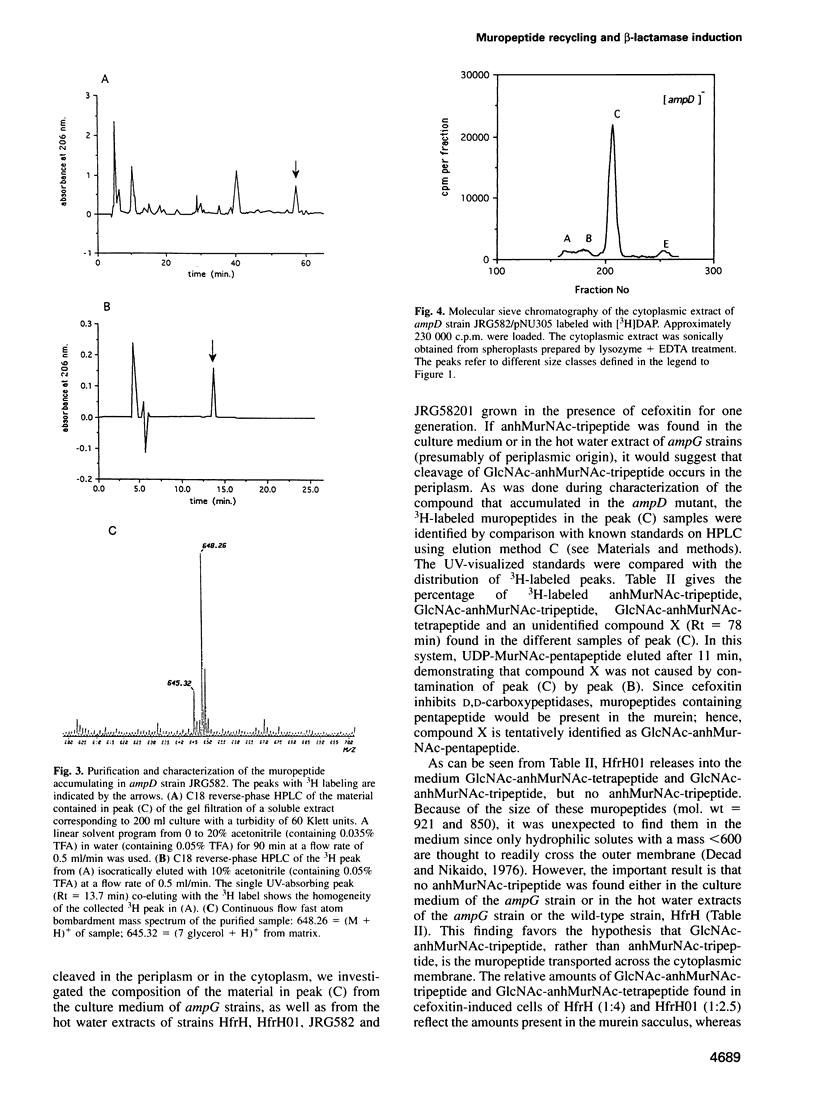
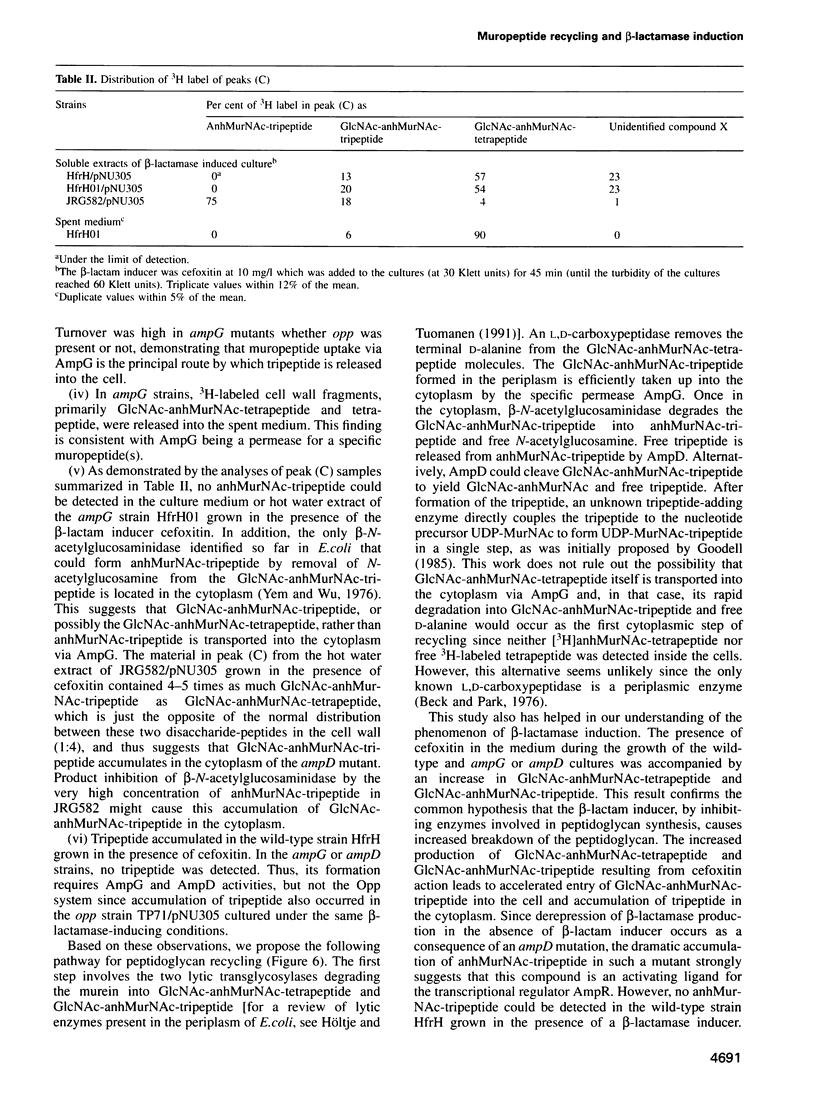
A mechanism for bacteria to monitor the status of their vital cell wall peptidoglycan is suggested by the convergence of two phenomena: peptidoglycan recycling and beta-lactamase induction. ampG and ampD, genes essential for beta-lactamase regulation, are here shown to be required for recycling as well. Cells lacking either AmpG or AmpD lose up to 40% of their peptidoglycan per generation, whereas Escherichia coli normally suffers minimal losses and instead recycles 40 or 50% of the tripeptide, L-alanyl-D-glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelic acid, from its peptidoglycan each generation. The ampG mutant releases peptidoglycan-derived material into the medium. In contrast, the ampD mutant accumulates a novel cell wall muropeptide, 1,6-anhydro N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelic acid (anhMurNAc-tripeptide), in its cytoplasm. This work suggests that AmpG is the permease for a large muropeptide and AmpD is a novel cytosolic N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase that cleaves anhMurNAc-tripeptide to release tripeptide, which is then recycled. These results also suggest that the phenomenon of beta-lactamase induction is regulated by the level of muropeptide(s) in the cytoplasm, since an ampD mutation that results in beta-lactamase expression even in the absence of a beta-lactamase inducer coincides with accumulation of anhMurNAc-tripeptide. The transcriptional regulator AmpR is presumably converted into an activator for beta-lactamase production by sensing the higher level of muropeptide(s). This may be an example of a general mechanism for signaling the progress of external events such as cell wall maturation, cell division or cell wall damage.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck B. D., Park J. T. Activity of three murein hydrolases during the cell division cycle of Escherichia coli K-12 as measured in toluene-treated cells. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1250–1260. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1250-1260.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decad G. M., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. XII. Molecular-sieving function of cell wall. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):325–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.325-336.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Higgins C. F. Uptake of cell wall peptides by Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3861–3865. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3861-3865.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W. Recycling of murein by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):305–310. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.305-310.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Schwarz U. Release of cell wall peptides into culture medium by exponentially growing Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):391–397. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.391-397.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Stephens P. E. Molecular cloning of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex genes of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Dec;121(2):277–292. doi: 10.1099/00221287-121-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré N., Nicolas M. H., Cole S. T. Regulation of enterobacterial cephalosporinase production: the role of a membrane-bound sensory transducer. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1121–1130. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tuomanen E. I. The murein hydrolases of Escherichia coli: properties, functions and impact on the course of infections in vivo. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Mar;137(3):441–454. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korfmann G., Sanders C. C. ampG is essential for high-level expression of AmpC beta-lactamase in Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1946–1951. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Lindquist S., Normark S. Inactivation of the ampD gene causes semiconstitutive overproduction of the inducible Citrobacter freundii beta-lactamase. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1923–1928. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1923-1928.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Normark S. Common mechanism of ampC beta-lactamase induction in enterobacteria: regulation of the cloned Enterobacter cloacae P99 beta-lactamase gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):758–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.758-763.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Westman L., Normark S. Regulatory components in Citrobacter freundii ampC beta-lactamase induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4620–4624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Galleni M., Lindberg F., Normark S. Signalling proteins in enterobacterial AmpC beta-lactamase regulation. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1091–1102. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00259.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Weston-Hafer K., Schmidt H., Pul C., Korfmann G., Erickson J., Sanders C., Martin H. H., Normark S. AmpG, a signal transducer in chromosomal beta-lactamase induction. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(4):703–715. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01731.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. Rapid mapping of conditional and auxotrophic mutations in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):798–812. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.798-812.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. T. Turnover and recycling of the murein sacculus in oligopeptide permease-negative strains of Escherichia coli: indirect evidence for an alternative permease system and for a monolayered sacculus. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(1):7–11. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.1.7-11.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego M., Higgins C. F., Pearce S. R., Gallagher M. P., Hoch J. A. The oligopeptide transport system of Bacillus subtilis plays a role in the initiation of sporulation. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):173–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Lindquist S., Sande S., Galleni M., Light K., Gage D., Normark S. Coordinate regulation of beta-lactamase induction and peptidoglycan composition by the amp operon. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):201–204. doi: 10.1126/science.1987637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wientjes F. B., Nanninga N. Rate and topography of peptidoglycan synthesis during cell division in Escherichia coli: concept of a leading edge. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3412–3419. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3412-3419.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yem D. W., Wu H. C. Purification and properties of beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):324–331. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.324-331.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



