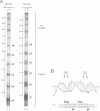
Abstract
The choice of retroviral integration sites is strongly influenced by chromatin: integration in vitro occurs more efficiently into nucleosomal DNA than into naked DNA, and a characteristic pattern of preferred insertion sites with a 10 bp periodicity is observed at the outer face of the nucleosomal DNA. At least three features of nucleosomal DNA could be responsible for the creation of these favored sites: the presence of histones, attachment of the DNA to a protein surface, and DNA bending. To test each of these possibilities, we studied integration in vitro with human immunodeficiency virus and murine leukemia virus integrases into four model targets that mimic features of nucleosomal DNA: (i) catabolite activator protein-DNA complexes; (ii) lac repressor-operator complexes; (iii) lac repressor-induced loops; and (iv) intrinsically bent A-tract DNA. We found that bending of the target DNA can create favored integration sites at the outer face of the helix, irrespective of whether the bent DNA is attached to a protein surface. Our findings offer an explanation for the preferred usage of nucleosomes as integration targets. In addition, they suggest that bending of the target DNA might be an intrinsic feature of the integration reaction.
Full text
PDF

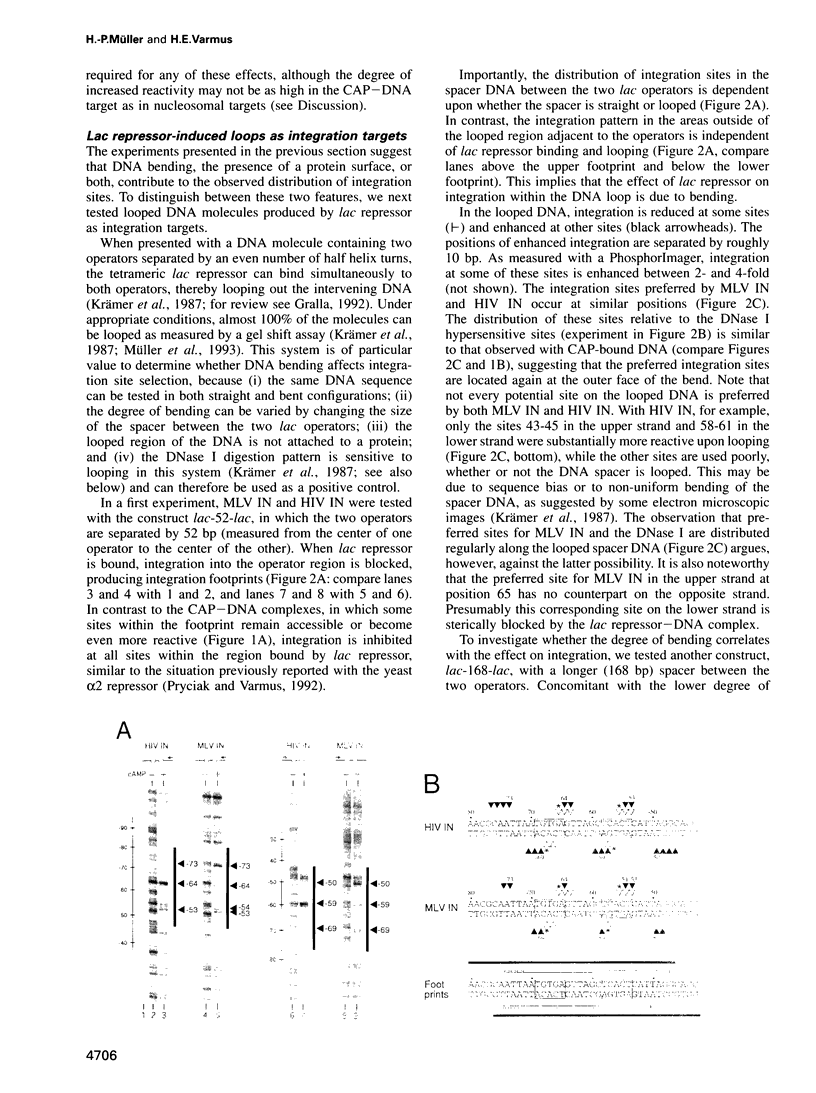

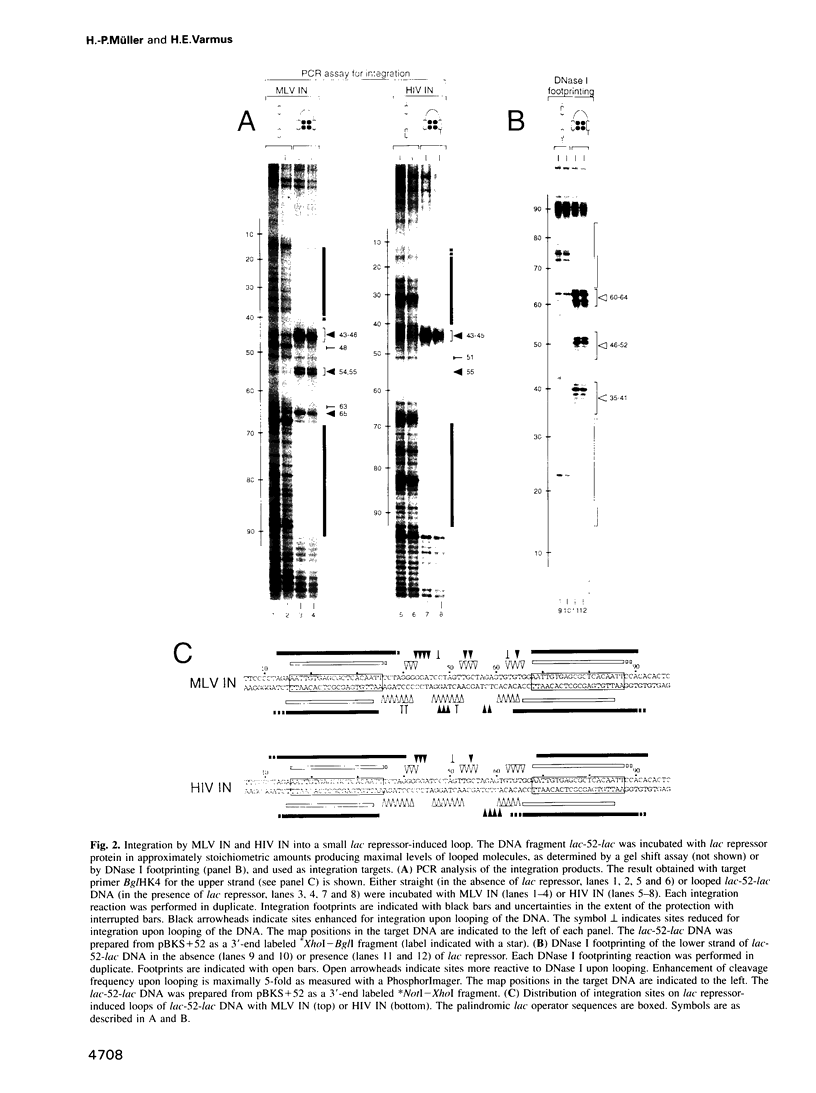

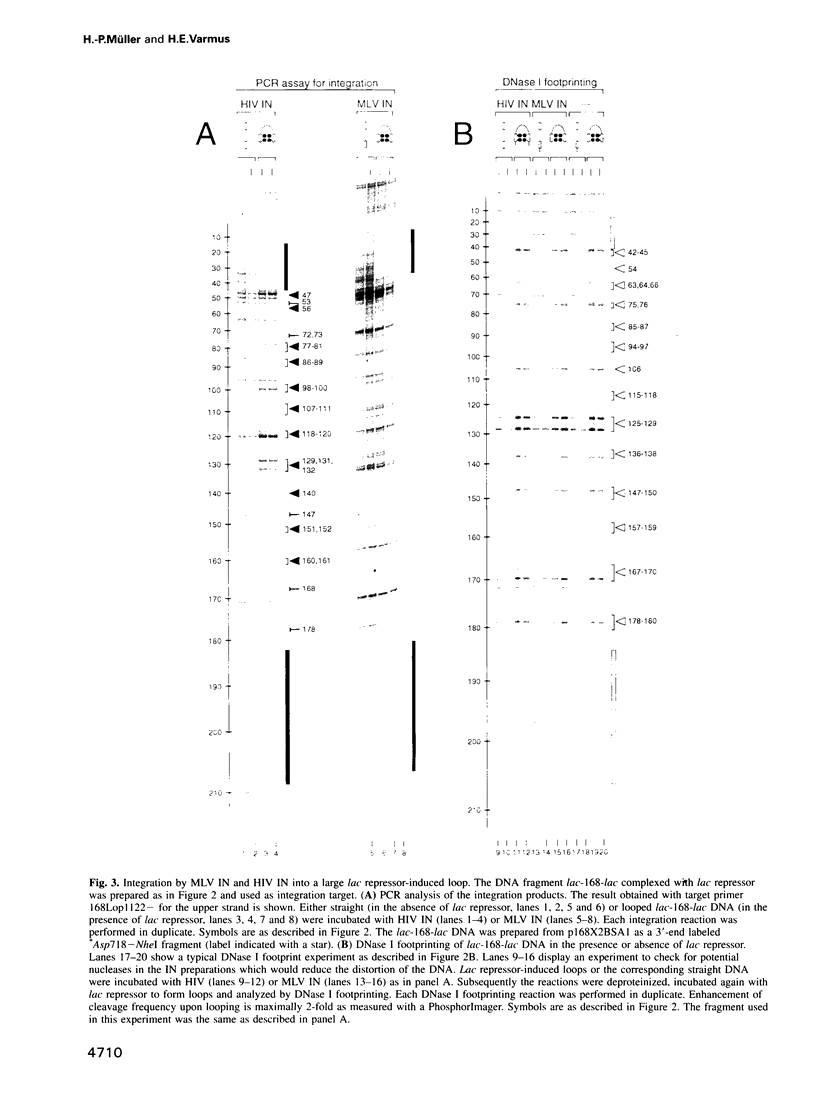



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams C. C., Workman J. L. Nucleosome displacement in transcription. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowerman B., Brown P. O., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. A nucleoprotein complex mediates the integration of retroviral DNA. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):469–478. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Retroviral integration: structure of the initial covalent product and its precursor, and a role for the viral IN protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Fujiwara T., Craigie R. Retroviral DNA integration directed by HIV integration protein in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1555–1558. doi: 10.1126/science.2171144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. Dodging the genes. Curr Biol. 1993 Aug 1;3(8):533–535. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalker D. L., Sandmeyer S. B. Ty3 integrates within the region of RNA polymerase III transcription initiation. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):117–128. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Fujiwara T., Bushman F. The IN protein of Moloney murine leukemia virus processes the viral DNA ends and accomplishes their integration in vitro. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):829–837. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90126-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R. Hotspots and warm spots: integration specificity of retroelements. Trends Genet. 1992 Jun;8(6):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90223-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Haran T. E., Nadeau J. G. Intrinsically bent DNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7093–7096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H. Nucleoprotein structures initiating DNA replication, transcription, and site-specific recombination. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14697–14700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman A., Mizuuchi K., Craigie R. HIV-1 DNA integration: mechanism of viral DNA cleavage and DNA strand transfer. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1211–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90297-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M. L., Vora A. C., Zeh W. G., Grandgenett D. P. Concerted integration of viral DNA termini by purified avian myeloblastosis virus integrase. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6257–6263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6257-6263.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Mizuuchi K. Retroviral DNA integration: structure of an integration intermediate. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. C., Pettersen E. F., Klein T. E., Ferrin T. E., Langridge R. Conic: a fast renderer for space-filling molecules with shadows. J Mol Graph. 1991 Dec;9(4):230-6, 242. doi: 10.1016/0263-7855(91)80016-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. D., Crothers D. M. Protein-induced bending and DNA cyclization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6343–6347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. D., Yun E., Crothers D. M. Detection of localized DNA flexibility. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):163–166. doi: 10.1038/368163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Merkel G., Kulkosky J., Leis J., Skalka A. M. The avian retroviral IN protein is both necessary and sufficient for integrative recombination in vitro. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90290-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Lee Y. M., Coffin J. M. Nonrandom integration of retroviral DNA in vitro: effect of CpG methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5532–5536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer H., Niemöller M., Amouyal M., Revet B., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. lac repressor forms loops with linear DNA carrying two suitably spaced lac operators. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1481–1491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahm A., Suck D. DNase I-induced DNA conformation. 2 A structure of a DNase I-octamer complex. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 5;222(3):645–667. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90502-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClarin J. A., Frederick C. A., Wang B. C., Greene P., Boyer H. W., Grable J., Rosenberg J. M. Structure of the DNA-Eco RI endonuclease recognition complex at 3 A resolution. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1526–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.3024321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milot E., Belmaaza A., Rassart E., Chartrand P. Association of a host DNA structure with retroviral integration sites in chromosomal DNA. Virology. 1994 Jun;201(2):408–412. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K. Polynucleotidyl transfer reactions in transpositional DNA recombination. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21273–21276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooslehner K., Karls U., Harbers K. Retroviral integration sites in transgenic Mov mice frequently map in the vicinity of transcribed DNA regions. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3056–3058. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3056-3058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. P., Pryciak P. M., Varmus H. E. Retroviral integration machinery as a probe for DNA structure and associated proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:533–541. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss D., Bushman F. D., Wolffe A. P. Human immunodeficiency virus integrase directs integration to sites of severe DNA distortion within the nucleosome core. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):5913–5917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryciak P. M., Müller H. P., Varmus H. E. Simian virus 40 minichromosomes as targets for retroviral integration in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9237–9241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryciak P. M., Varmus H. E. Nucleosomes, DNA-binding proteins, and DNA sequence modulate retroviral integration target site selection. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):769–780. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90289-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramstein J., Lavery R. Energetic coupling between DNA bending and base pair opening. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7231–7235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe T., Reynolds T. C., Yu G., Brown P. O. Integration of murine leukemia virus DNA depends on mitosis. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2099–2108. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05858.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohdewohld H., Weiher H., Reik W., Jaenisch R., Breindl M. Retrovirus integration and chromatin structure: Moloney murine leukemia proviral integration sites map near DNase I-hypersensitive sites. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):336–343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.336-343.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeyer S. B., Hansen L. J., Chalker D. L. Integration specificity of retrotransposons and retroviruses. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:491–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. DNA looping. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:199–223. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz A. Cyclic AMP receptor proteins interacts with lactose operator DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):277–292. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1001–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1653449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C. C., Stoye J. P., Coffin J. M. Highly preferred targets for retrovirus integration. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):531–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90569-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spassky A., Busby S., Buc H. On the action of the cyclic AMP-cyclic AMP receptor protein complex at the Escherichia coli lactose and galactose promoter regions. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):43–50. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01759.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Lahm A., Oefner C. Structure refined to 2A of a nicked DNA octanucleotide complex with DNase I. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):464–468. doi: 10.1038/332464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. Why bend DNA? Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90729-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Plasterk R. H. The human immunodeficiency virus integrase protein. Trends Genet. 1993 Dec;9(12):433–438. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90107-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Yeheskiely E., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Plasterk R. H. Site-specific hydrolysis and alcoholysis of human immunodeficiency virus DNA termini mediated by the viral integrase protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6691–6698. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitcomb J. M., Hughes S. H. Retroviral reverse transcription and integration: progress and problems. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:275–306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler F. K., Banner D. W., Oefner C., Tsernoglou D., Brown R. S., Heathman S. P., Bryan R. K., Martin P. D., Petratos K., Wilson K. S. The crystal structure of EcoRV endonuclease and of its complexes with cognate and non-cognate DNA fragments. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1781–1795. doi: 10.2210/pdb4rve/pdb. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberger C., Vershon A. K., Liu B., Johnson A. D., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a MAT alpha 2 homeodomain-operator complex suggests a general model for homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]